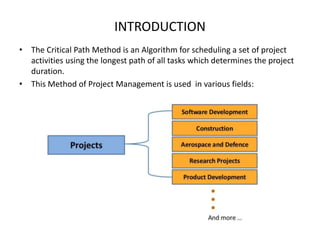
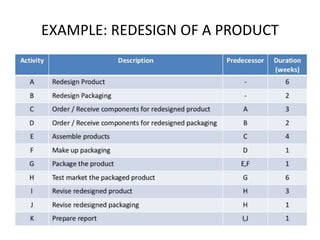
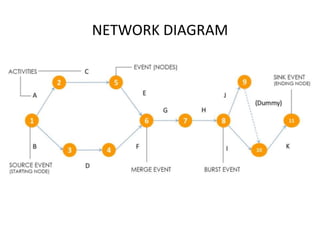
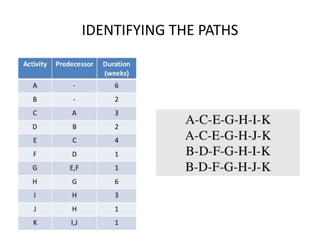
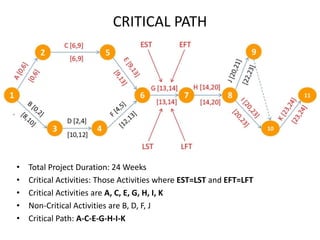
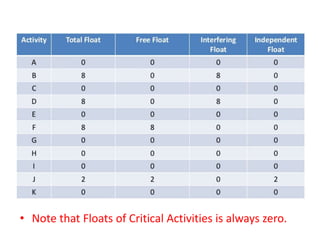
The Critical Path Method (CPM) is a project management algorithm that determines project duration by identifying the longest path through scheduled activities, classifying them into critical and non-critical tasks. Activities are categorized into predecessors, successors, concurrent, and dummy activities, while events are identified as source, merge, burst, and sink events. The document also discusses float and slack time, defining their impact on task scheduling and project deadlines.