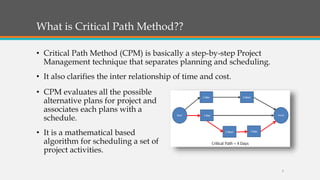
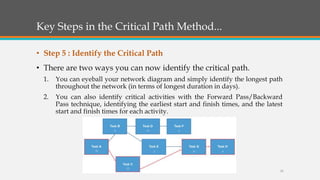
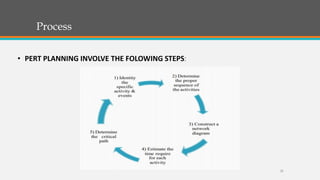
The document explains the Critical Path Method (CPM) and Program Evaluation Review Technique (PERT) used in project management to determine the sequence of project activities and their durations. CPM helps identify key tasks, reduce timelines, and compare planned versus actual progress, while PERT represents tasks and their sequence in a network diagram. The document outlines the steps to implement CPM, including specifying activities, establishing dependencies, drawing network diagrams, estimating completion times, identifying the critical path, and updating progress.