This document provides an overview of uveitis, including:
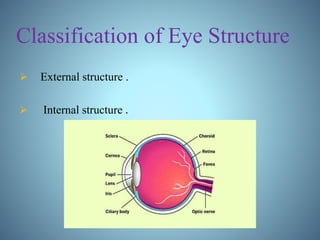
- Definitions of uveitis and the structures of the eye involved
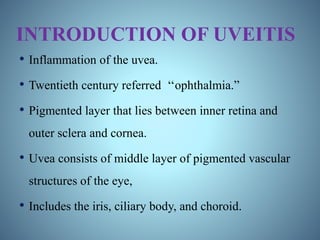
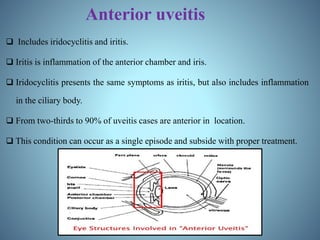
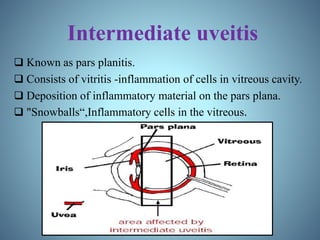
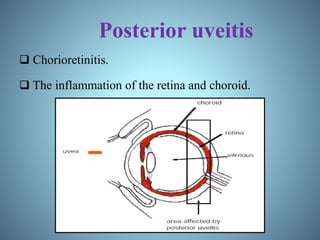
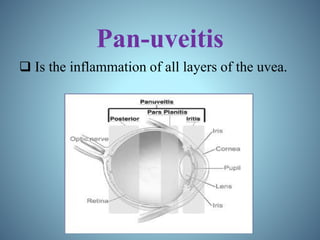
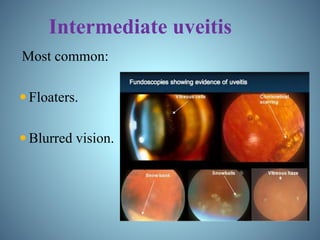
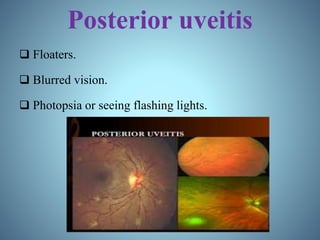
- Classification of uveitis into anterior, intermediate, posterior, and pan-uveitic types
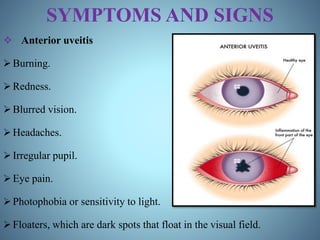
- Signs and symptoms, causes like infections and autoimmune diseases, and pathophysiology involving immune and genetic factors
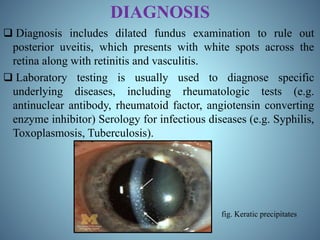
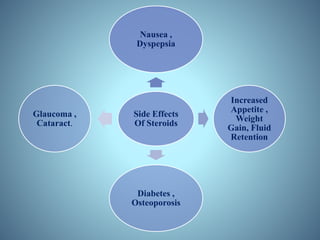
- Diagnosis through examination and testing, as well as treatment using steroids, immunosuppressants, mydriatics, and natural products like turmeric
- Prognosis being generally good with treatment but potential for vision loss, and epidemiology with uveitis affecting approximately 1 in 5,000 people.