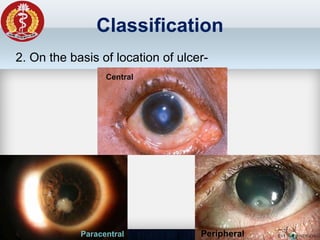
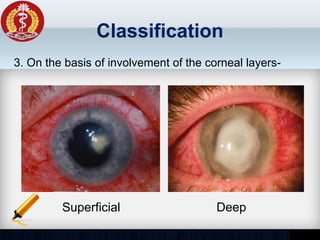
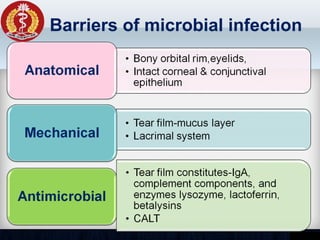
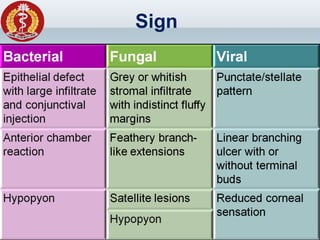
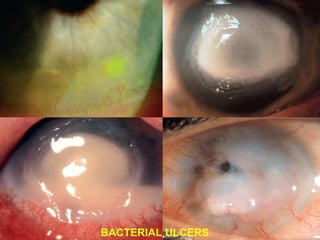
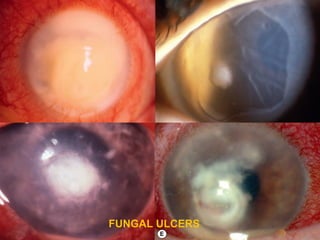
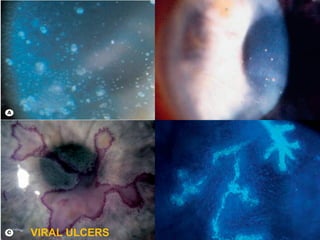
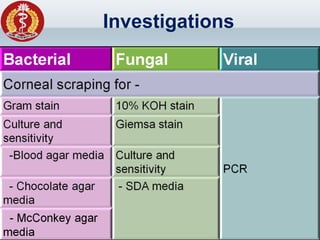
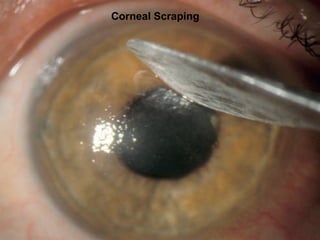
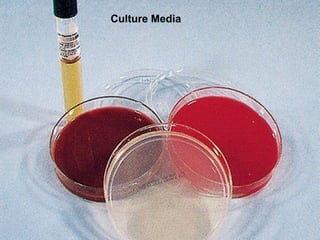
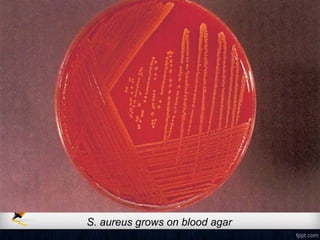
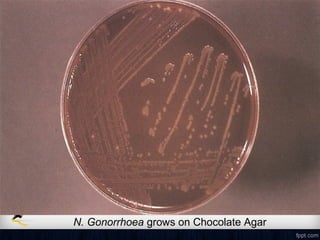
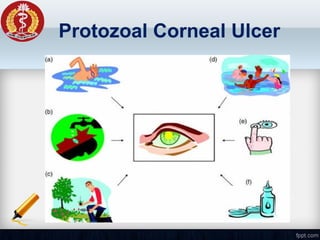
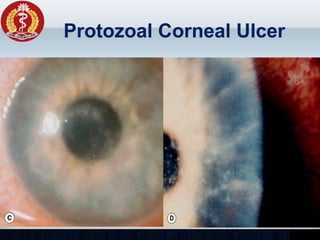
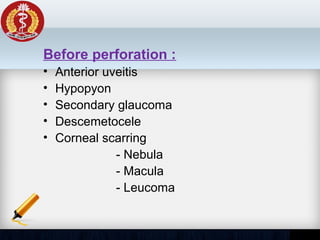
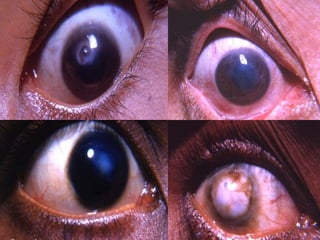
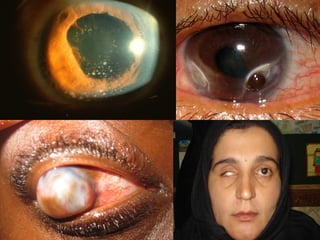
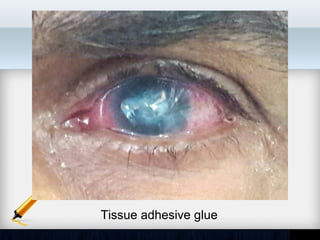
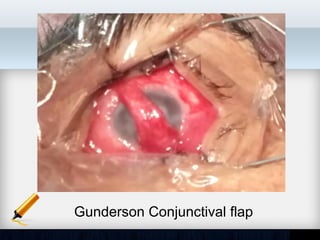
Corneal ulcer refers to corneal tissue excavation associated with an epithelial defect, usually with infiltration and necrosis. Corneal ulcers can be classified based on etiology, location, or involvement of corneal layers. Common causes include infection, trauma, dry eye, or contact lens overuse. Signs include pain, redness, tearing, photophobia, and a gray infiltrate. Diagnosis involves corneal scraping and culture. Treatment depends on cause but generally includes topical antibiotics, antifungals, antivirals, or amoebicides with cycloplegics. Complications include hypopyon, perforation, scarring, or endophthalmitis. Timely diagnosis and proper management can save vision.