Embed presentation
Downloaded 1,231 times


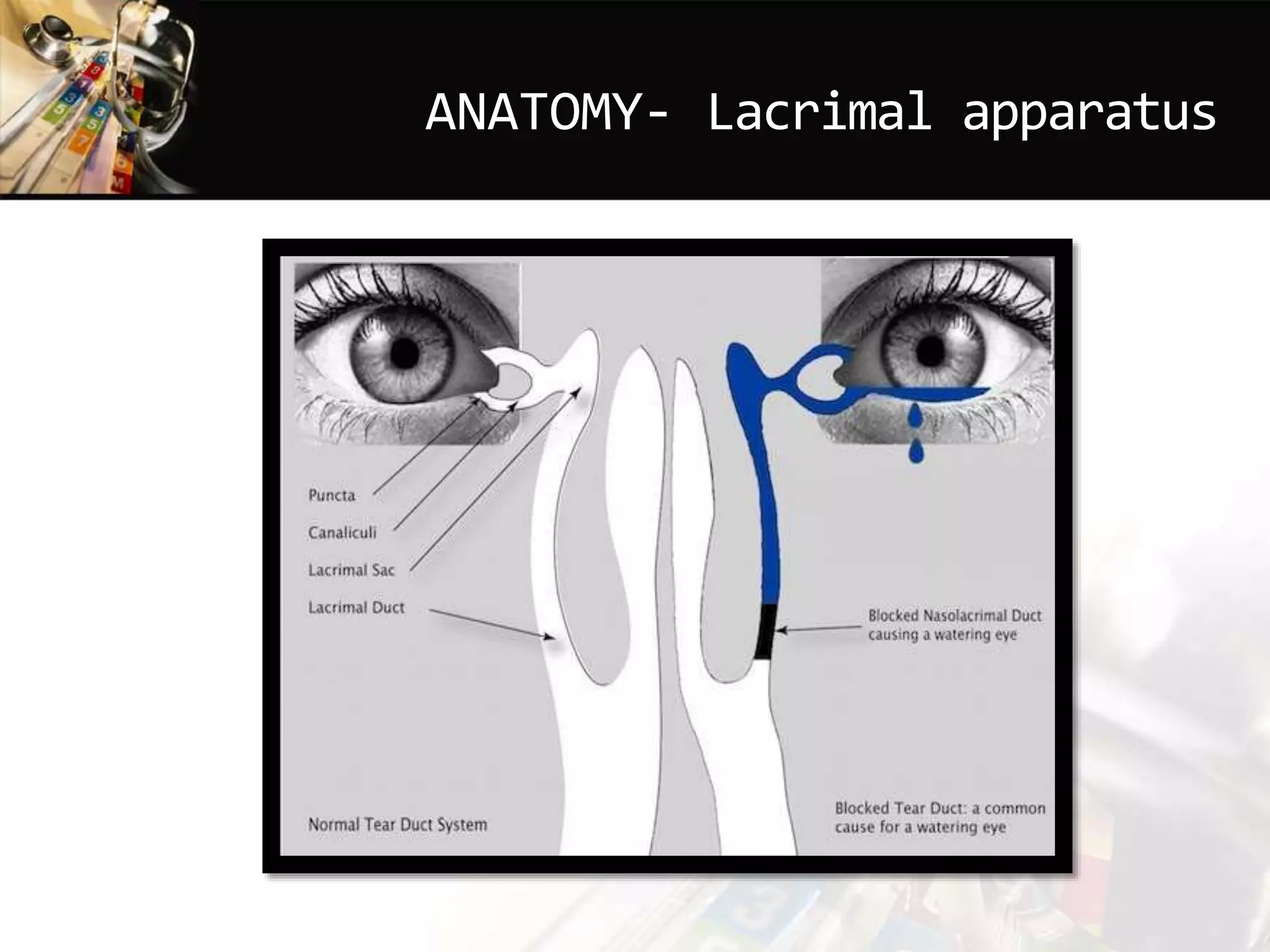
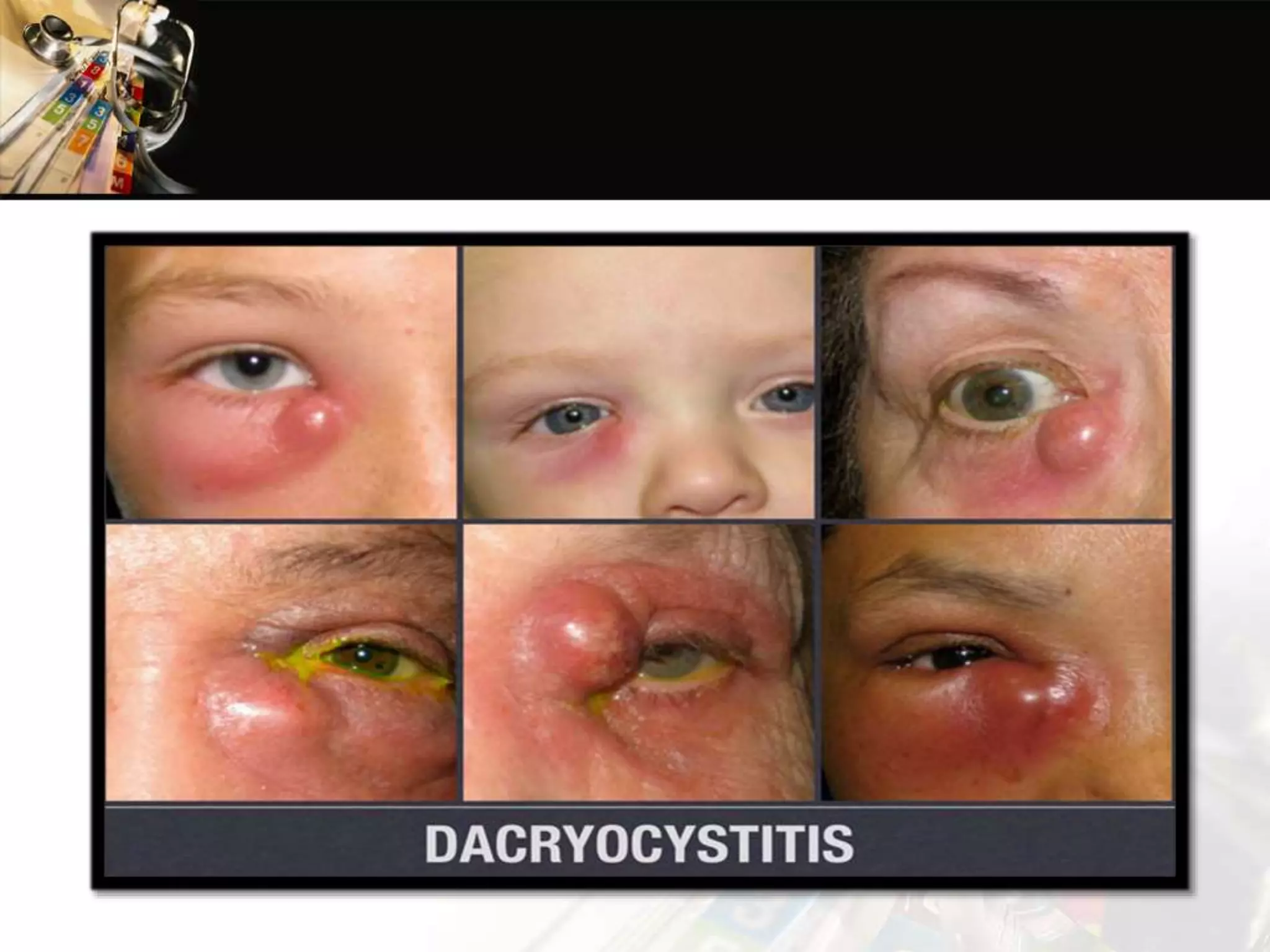
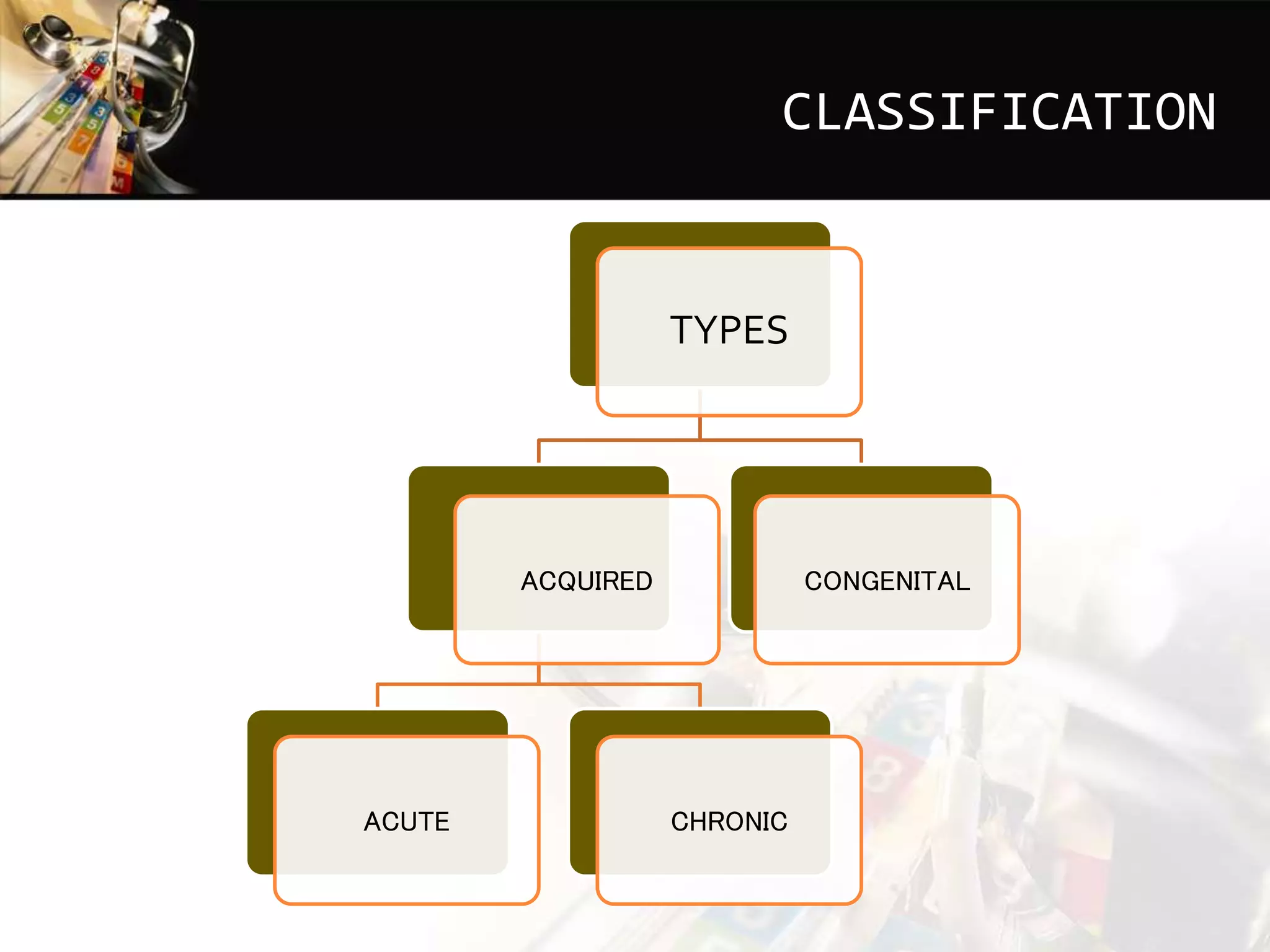


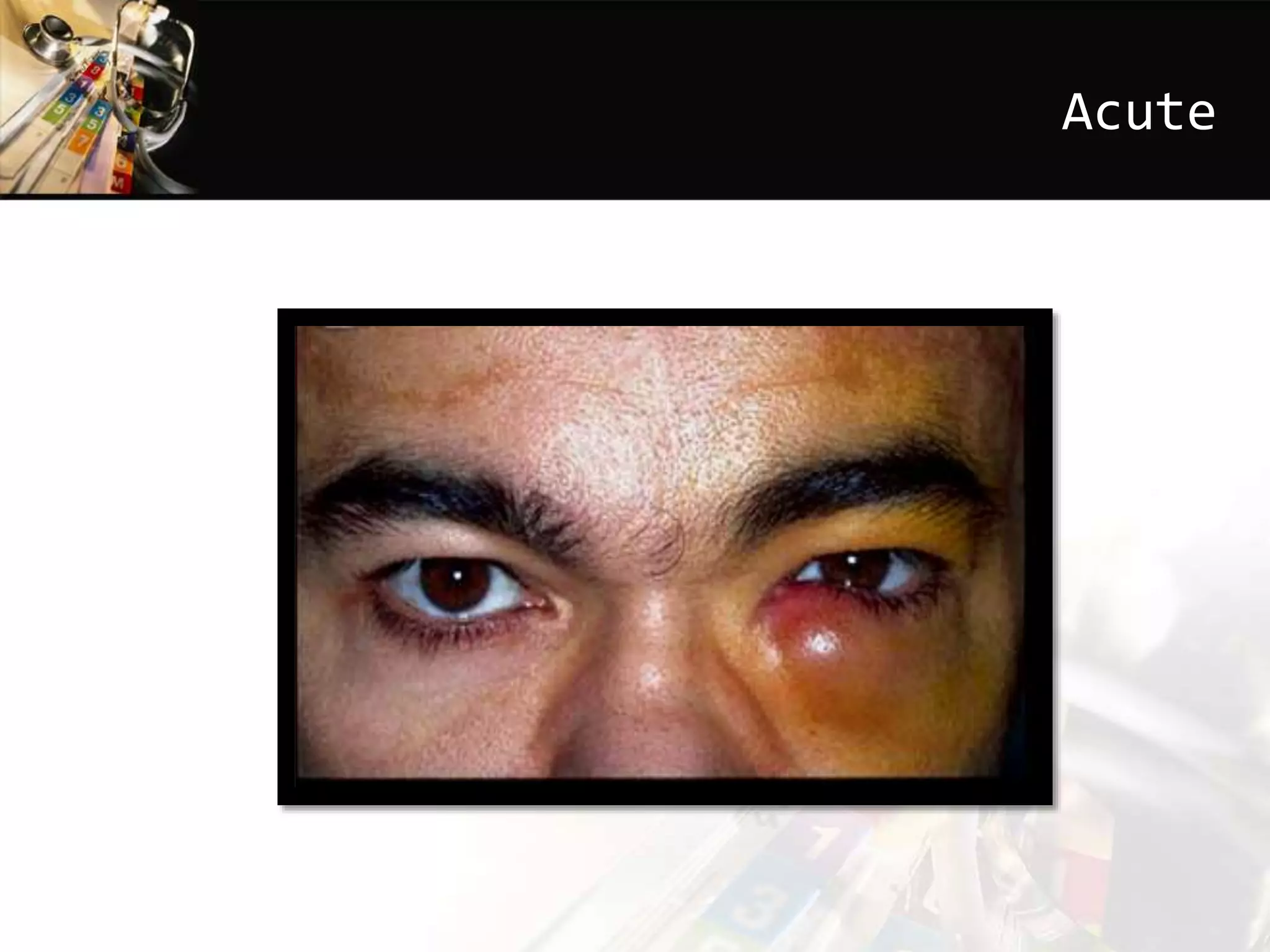

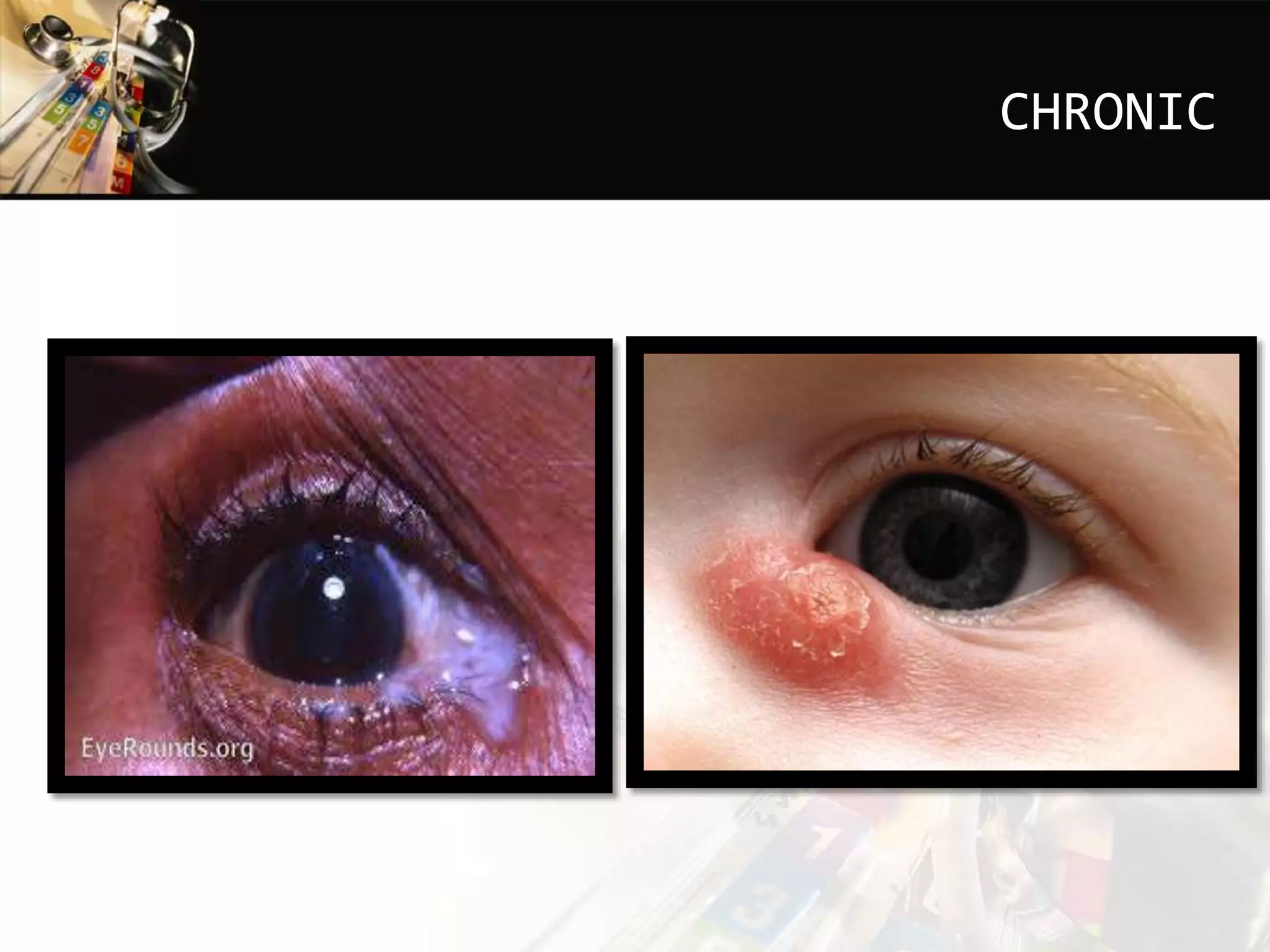
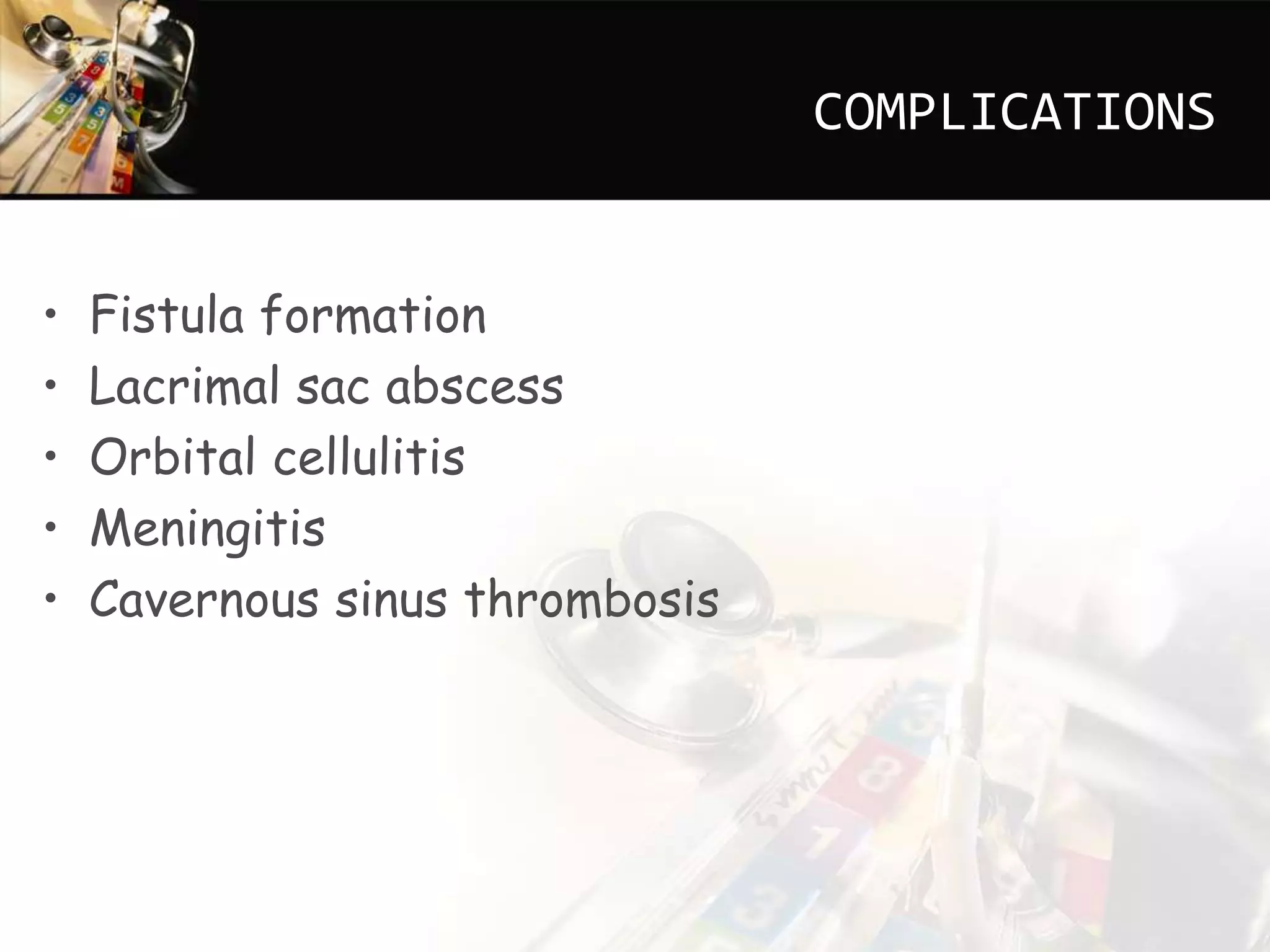


This document discusses dacryocystitis, which is an inflammation of the lacrimal sac. It is often caused by an obstruction of the naso-lacrimal duct followed by a bacterial infection. It can be either acute or chronic, and is classified based on whether it is acquired or congenital. Acute dacryocystitis causes pain, redness, and swelling and risks include older age and poor hygiene. Chronic dacryocystitis causes watering, mucopurulent discharge, and regurgitation of pus or mucus with pressure. Treatments include antibiotics, warm compresses, and surgery.












