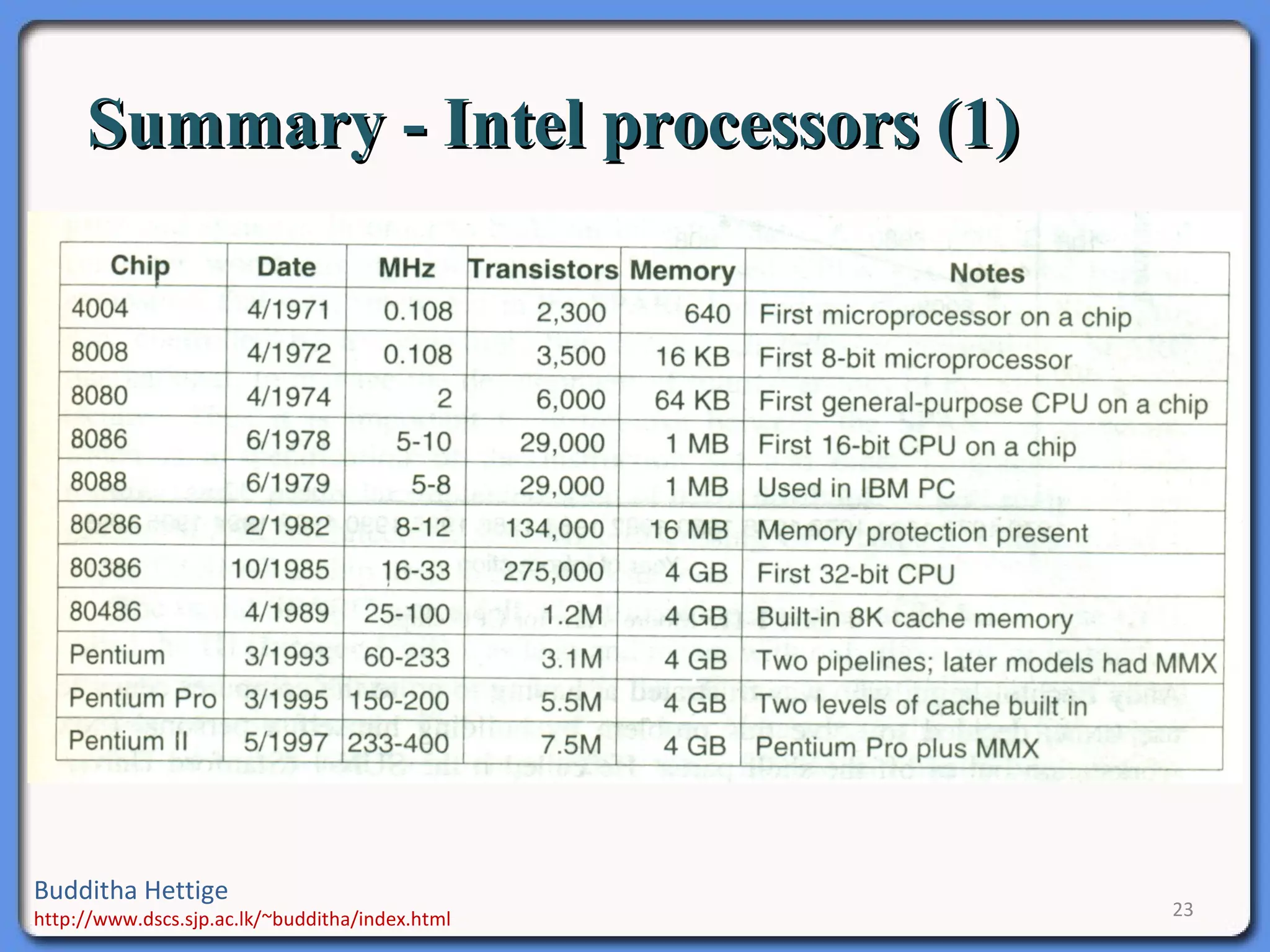
The document discusses the history and evolution of Intel microprocessors from 1971 to present. It describes each generation of Intel processors including the 4004, 8008, 8080, 8086, 80286, 80386, 80486, Pentium, Core, and i-series. For each processor, it provides details like clock speed, number of transistors, instruction sets, cache sizes, and new technologies introduced. The document aims to chronicle the major developments and improvements in Intel microprocessors over time that have made computers more powerful and advanced.