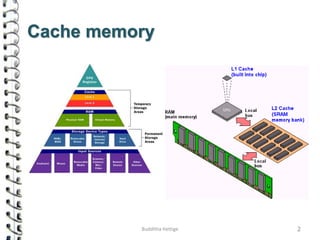
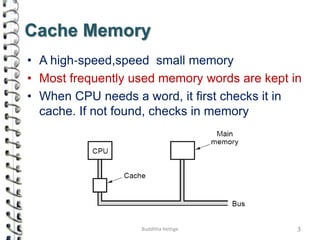
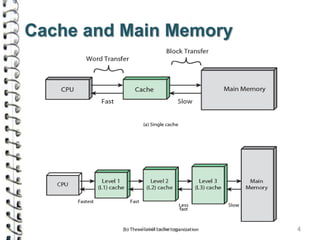
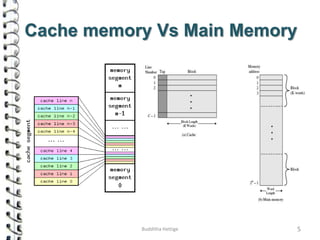
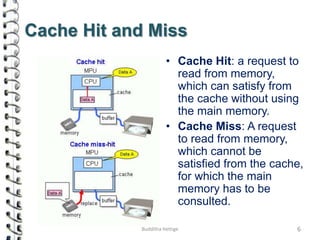
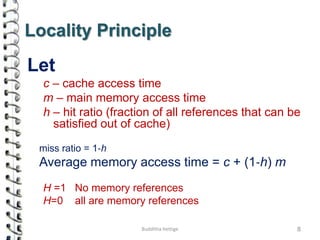
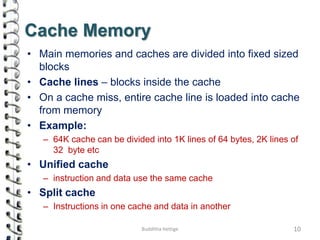
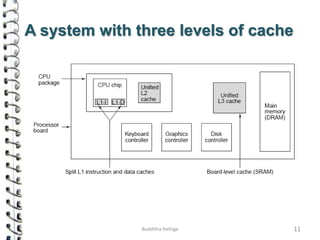
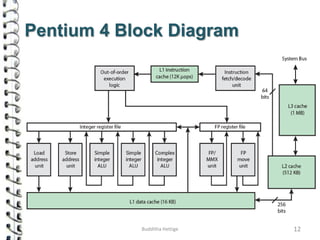
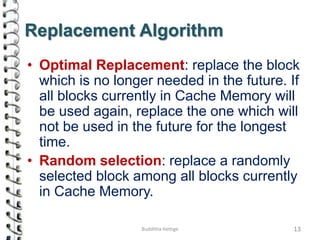
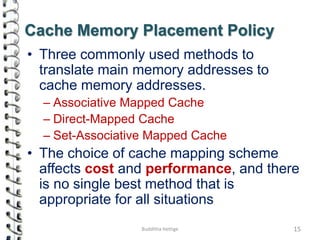
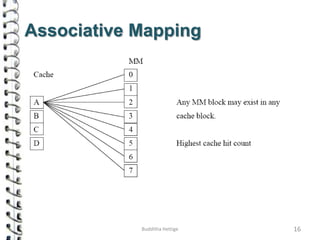
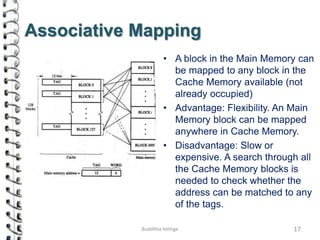
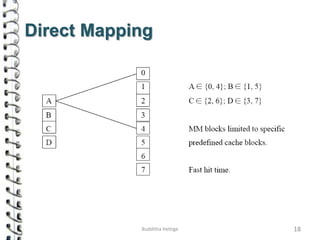
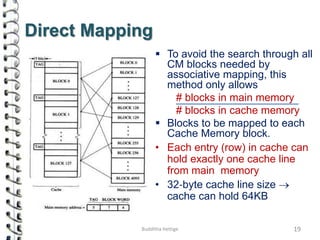
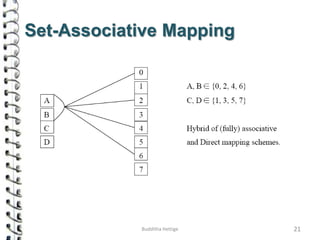
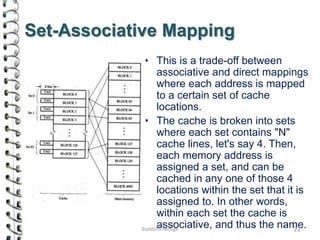
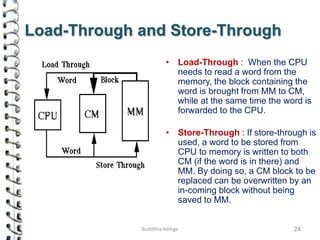
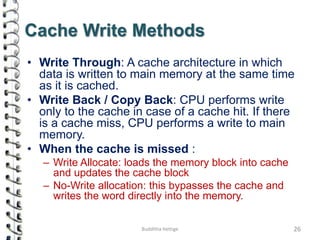
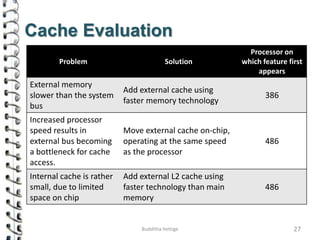
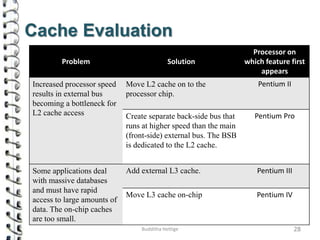
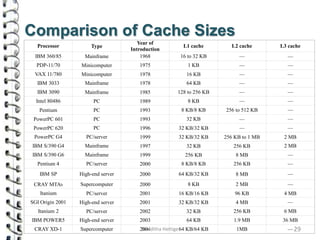
Cache memory is a small, high-speed memory located close to the processor that stores frequently accessed instructions and data. When the CPU requests data, it first checks the cache and if the data is present it is retrieved from cache, otherwise it is retrieved from main memory. There are different types of cache mapping including direct mapping, associative mapping, and set-associative mapping that determine how data is stored in cache. Cache performance is improved through techniques such as write-back caching that only write data to cache on write operations.