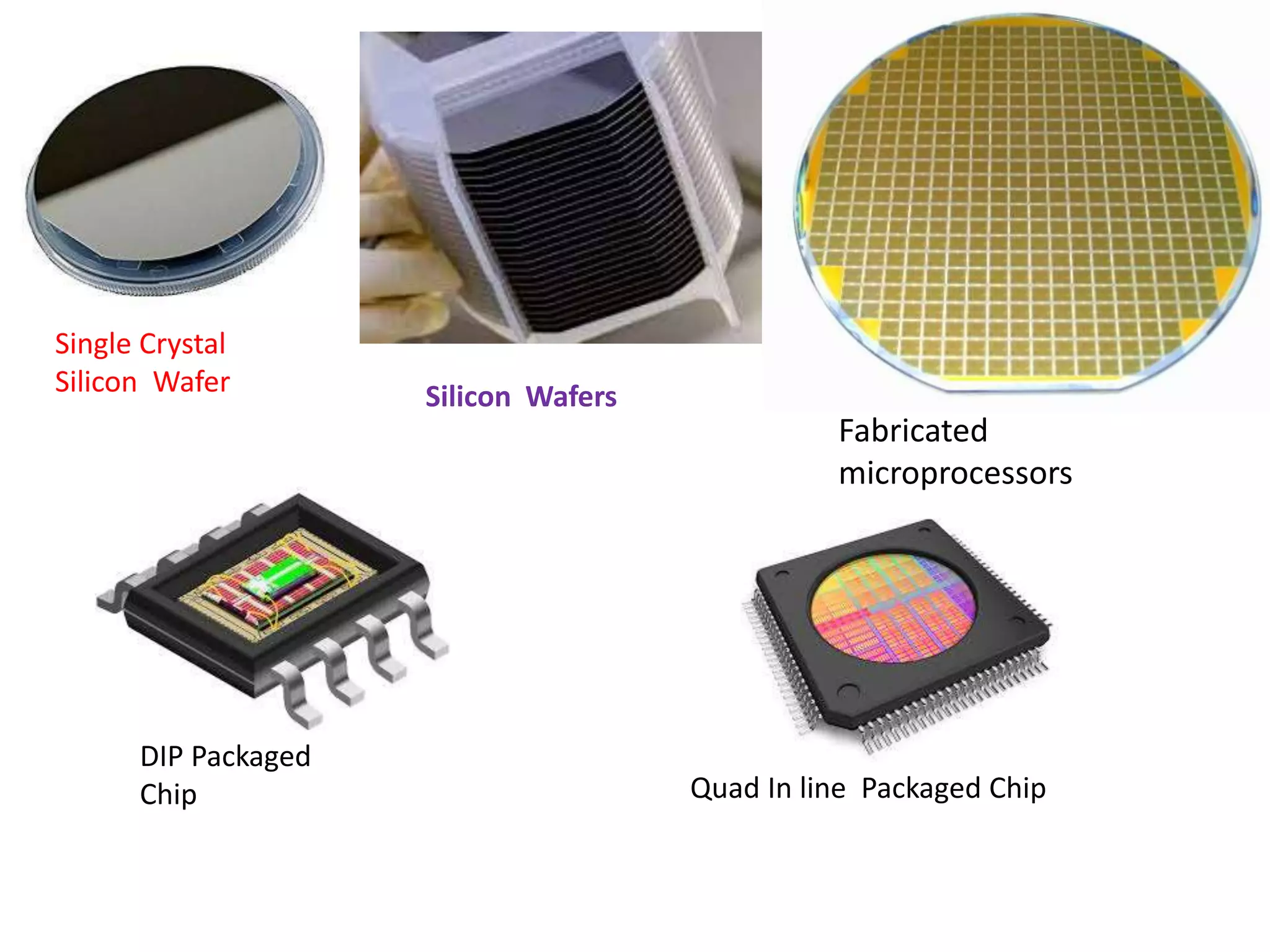
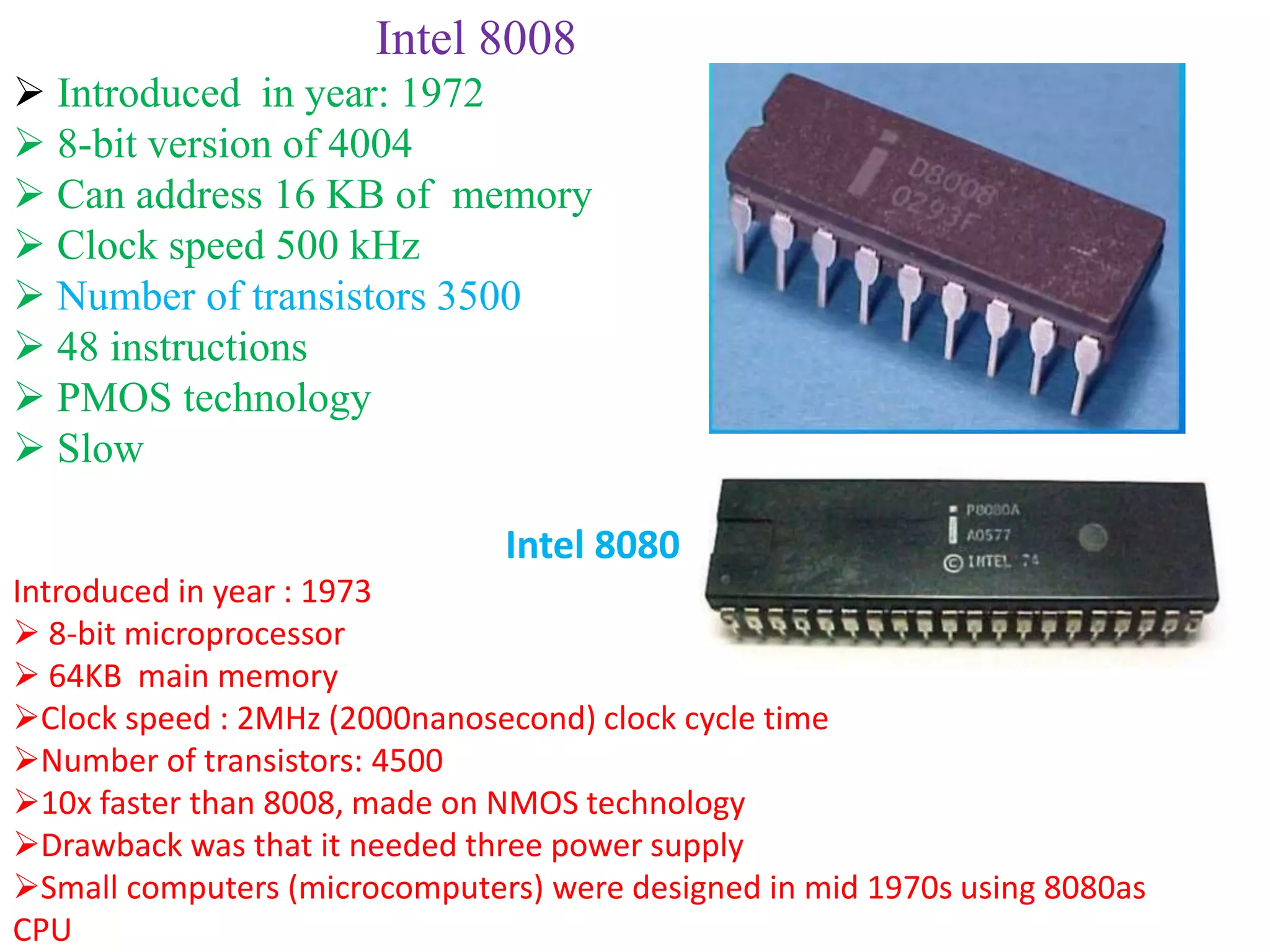
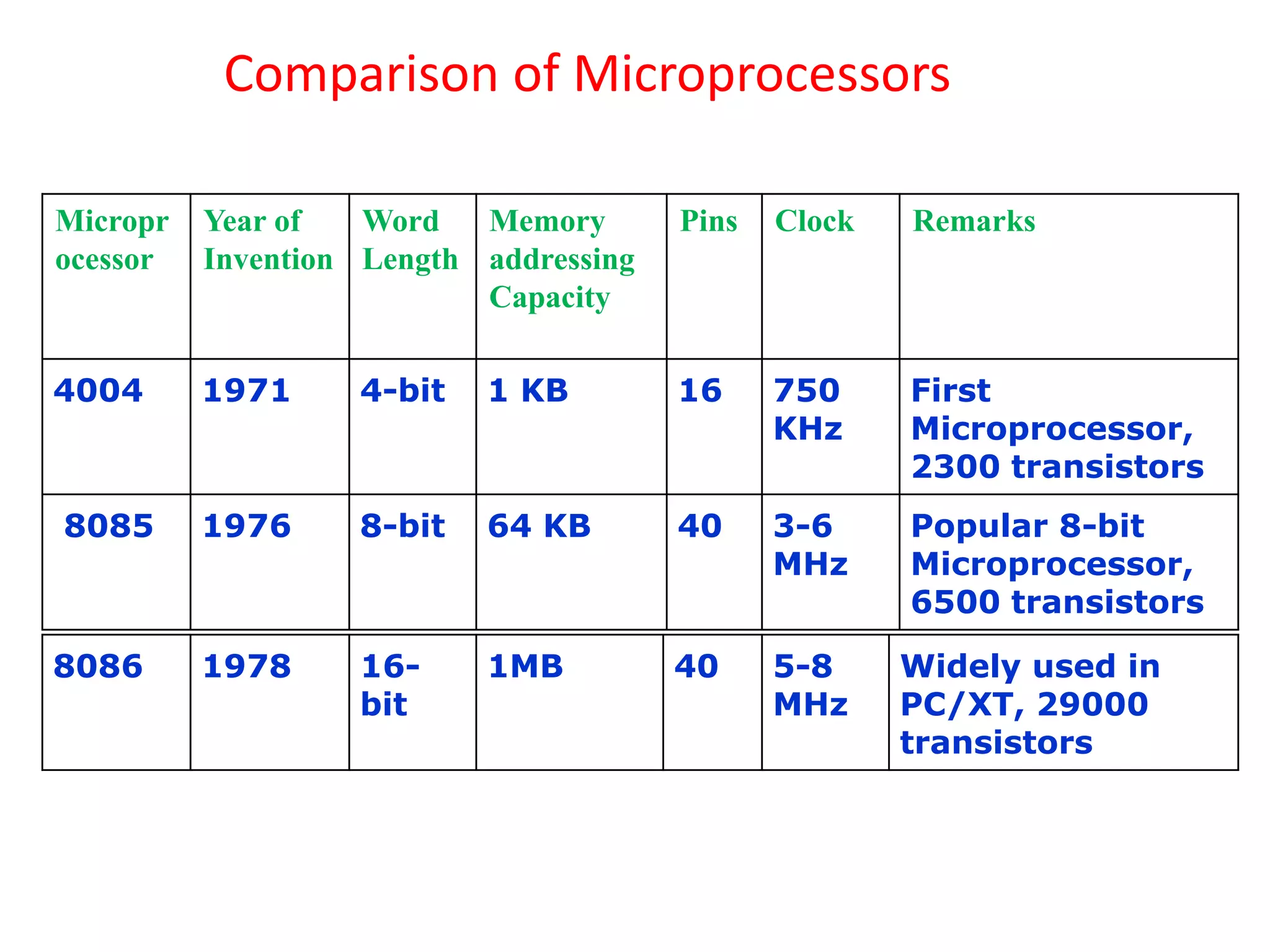
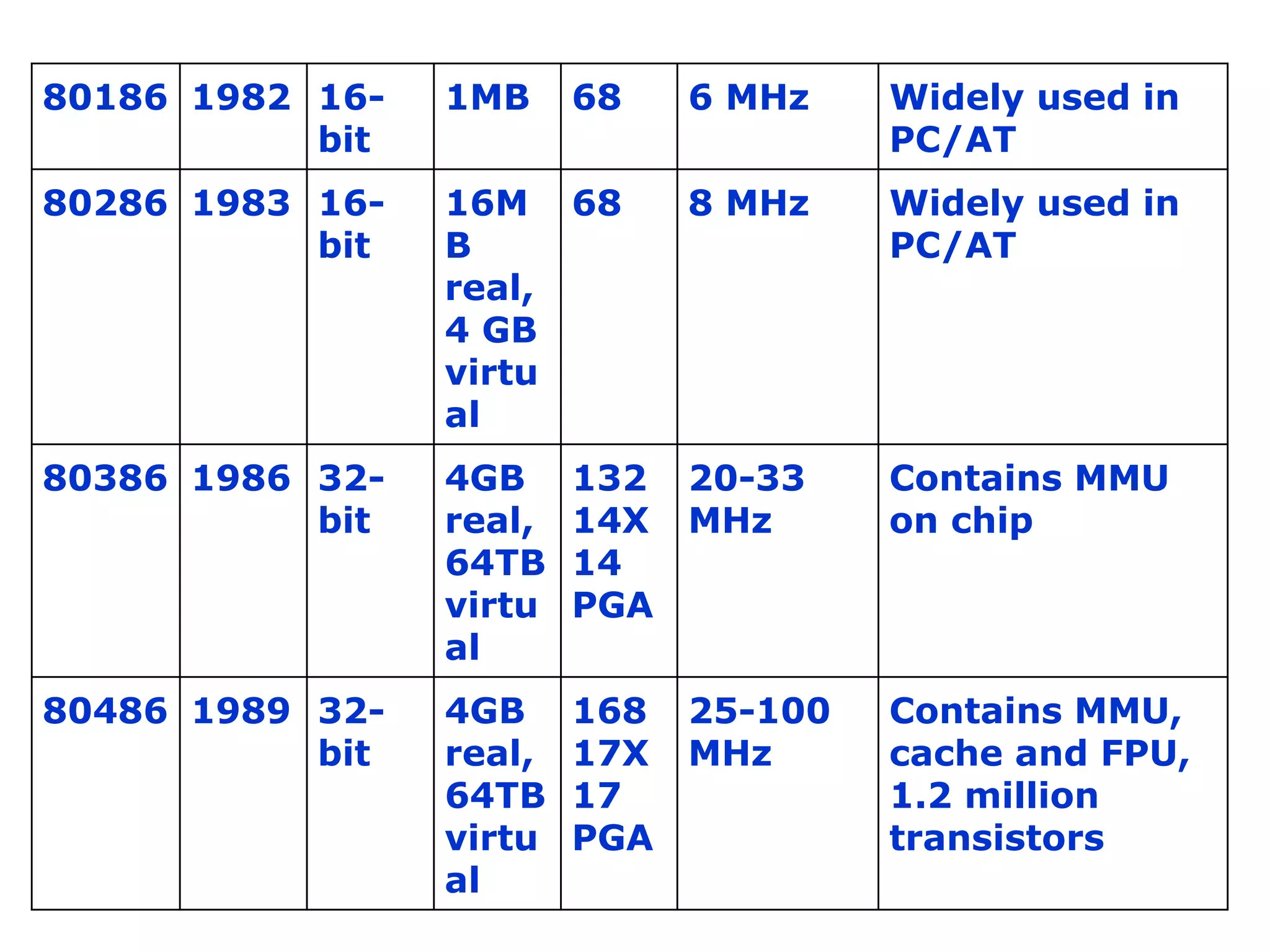
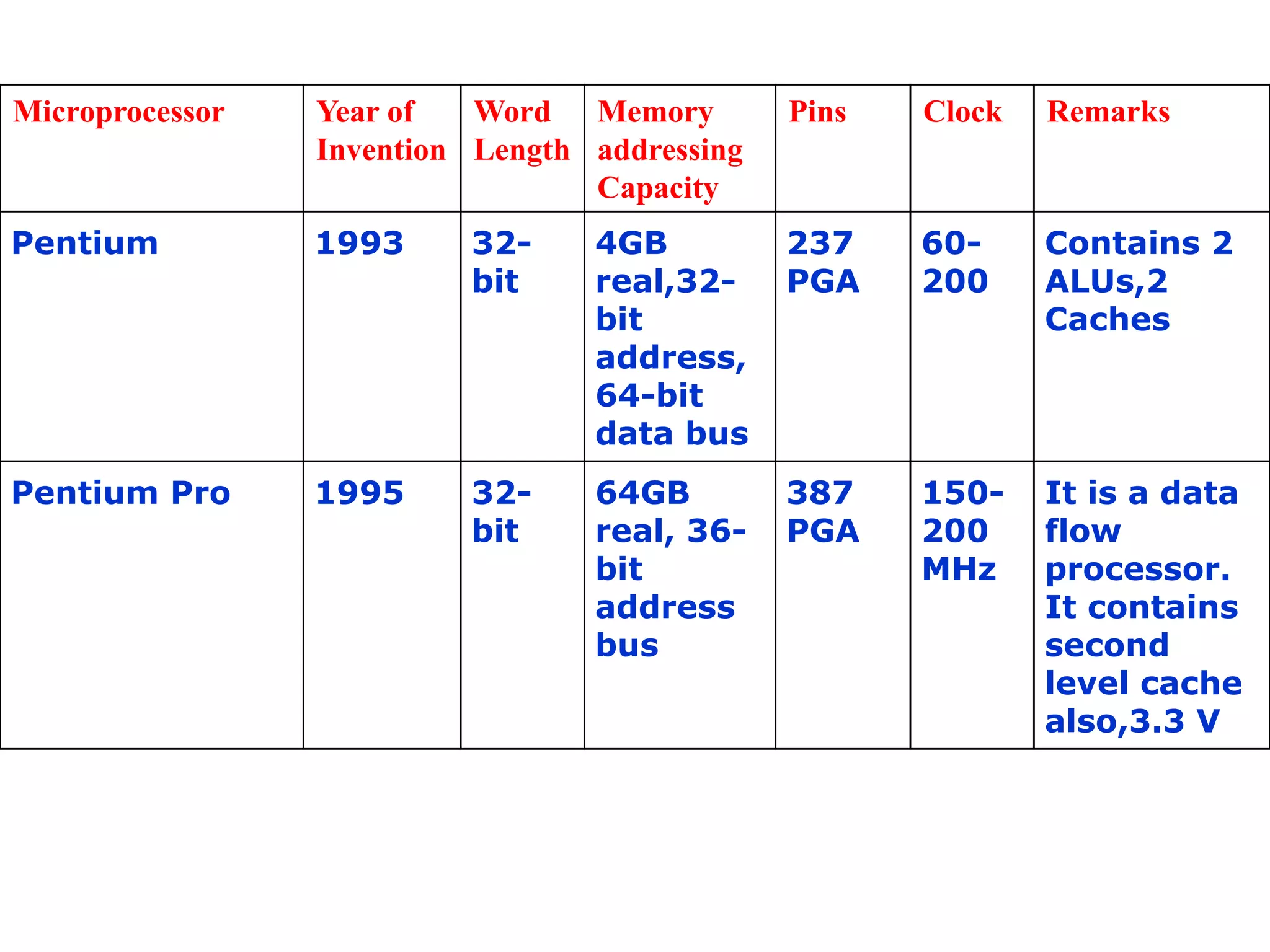
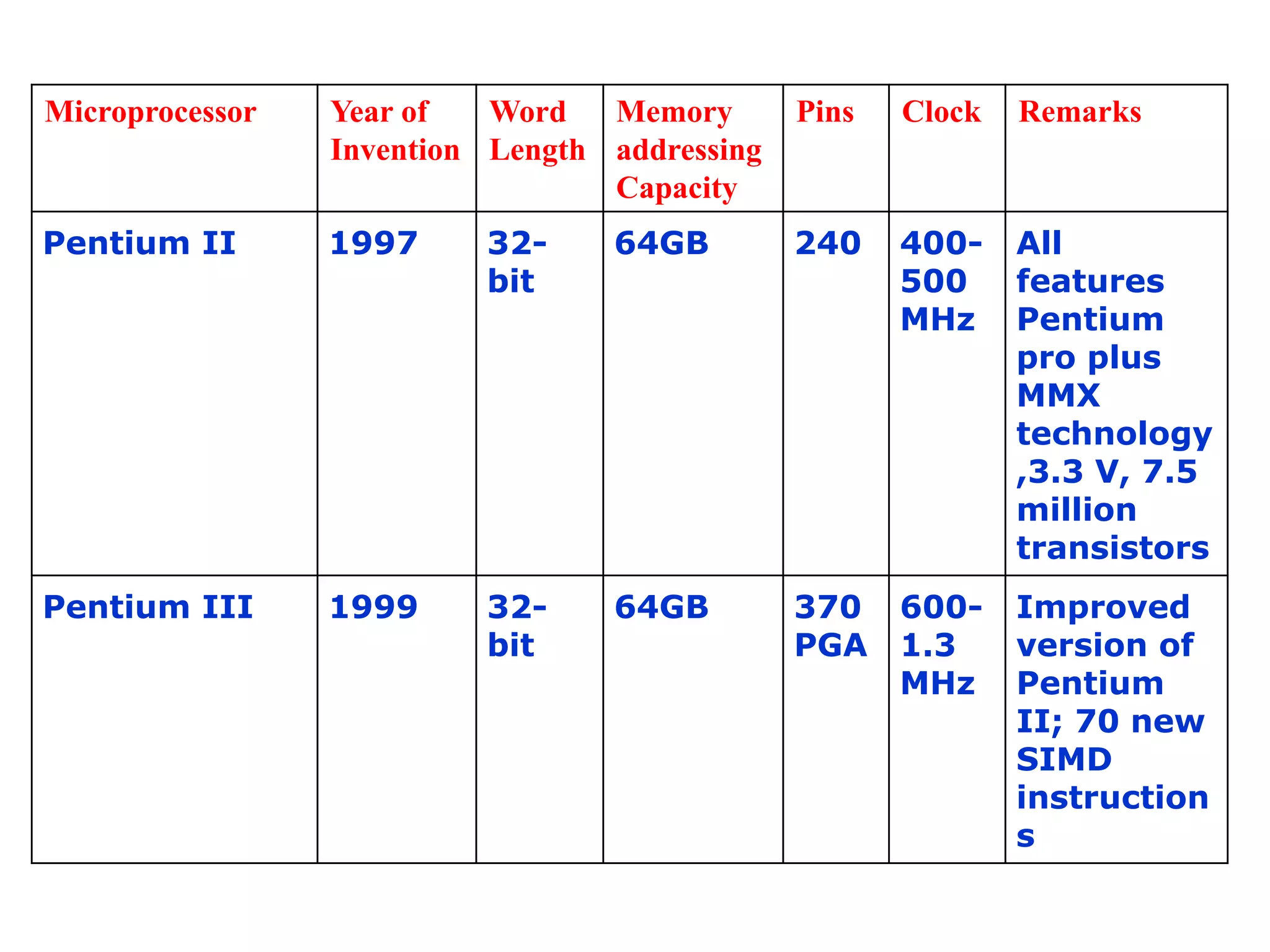
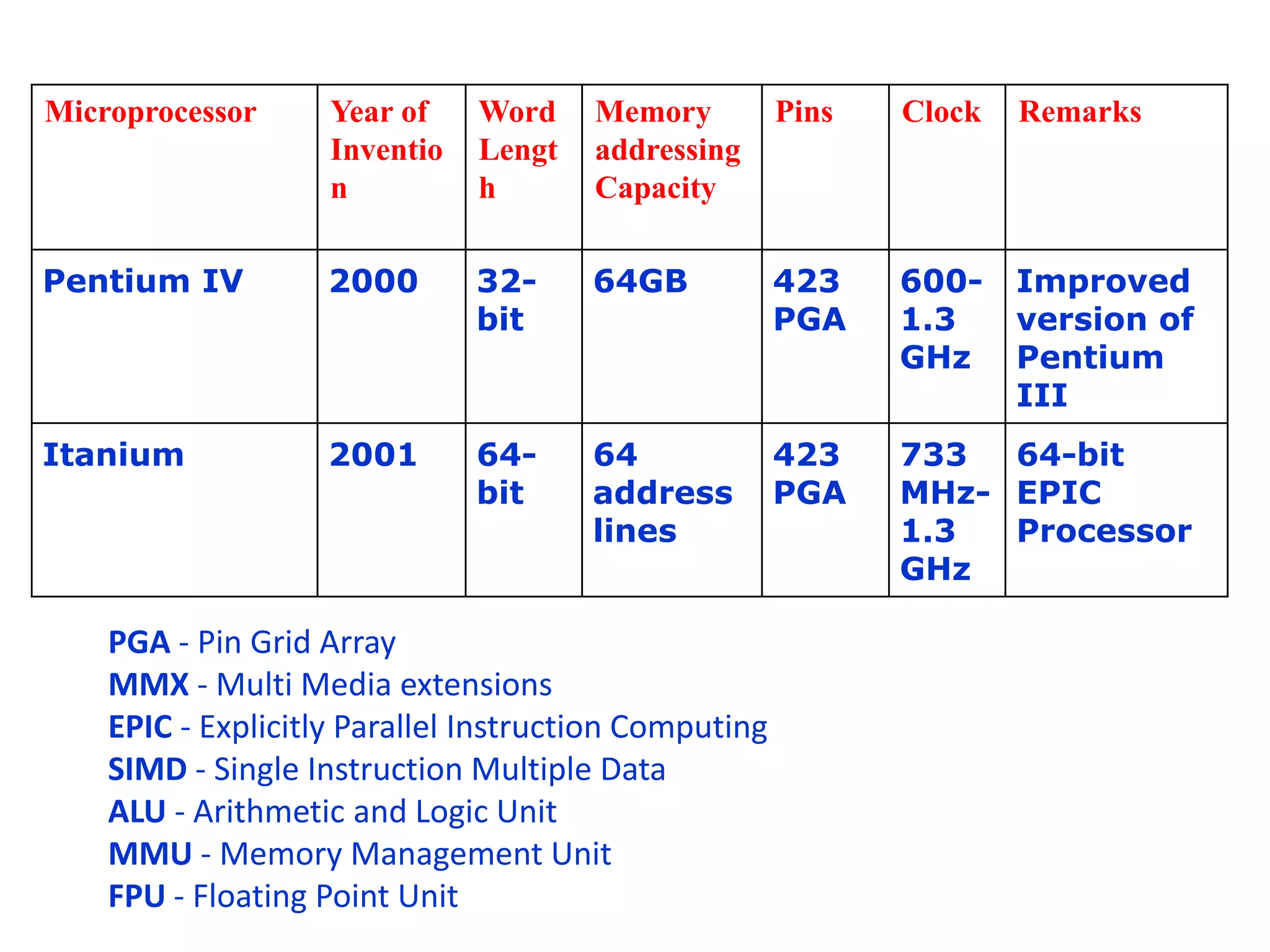
The document summarizes the evolution of microprocessors from Intel Corporation's founding in 1968 to the development of 64-bit processors like the Itanium in the early 2000s. It traces the progression from early 4-bit processors like the 4004 and the 8080, to widely used 16-bit processors like the 8086 and 80286, to 32-bit processors such as the 80386 and Pentium, and finally to multi-core 64-bit designs including the Core i7. Each new generation brought improvements like increased processing power, additional features, and support for larger memory addressing. This helped enable new classes of computers and applications.