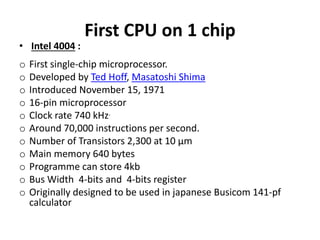
The document discusses the history and development of microprocessors from the Intel 4004 in 1971 to Intel dual core processors in 2006. It provides details on key processors such as the 8008, 8080, 8086, 8088, 80386, 80486, Pentium, Pentium Pro, Pentium II, Pentium III, Pentium IV, and dual core/Core 2 processors. It describes features such as clock speed, number of transistors, cache memory, and architecture of various processors over time.