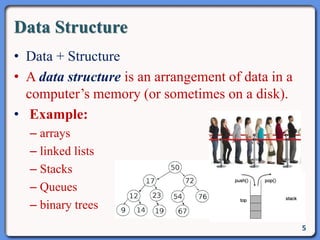
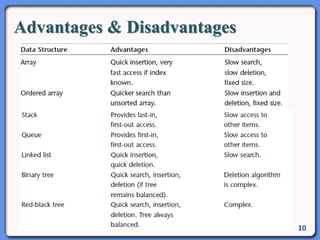
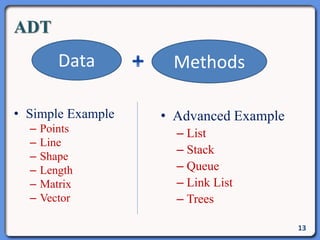
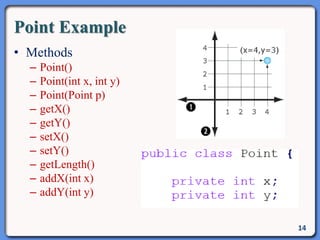
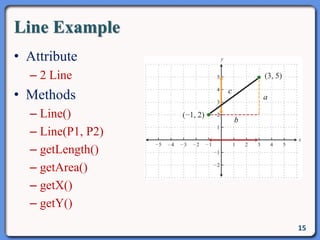
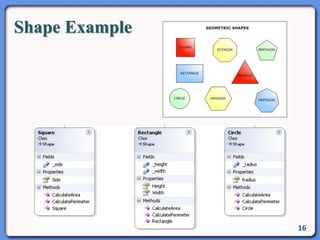
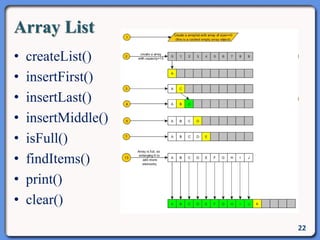
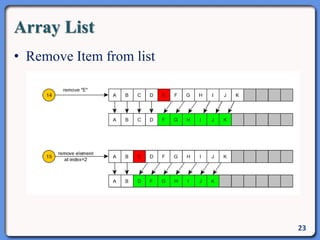
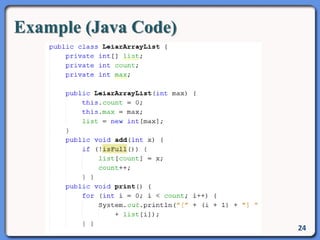
The document outlines the course structure for IT 4043: Data Structures and Algorithms, including lecture and practical hours, assessments, and a syllabus covering topics like abstract data types, list operations, stacks, and algorithms. It also discusses data structures such as arrays, linked lists, and their applications in real-world data storage. Additionally, examples of methods and implementations related to linear lists and abstract data types are provided.