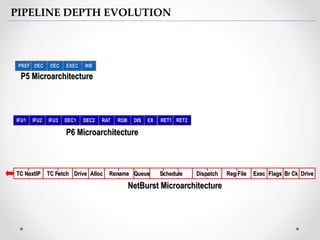
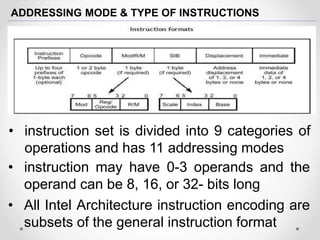
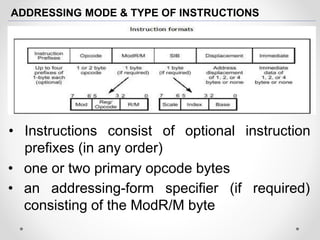
The document provides an overview of the Pentium processor family developed by Intel, detailing its history, architecture, and evolution since its introduction in 1993. It discusses key technical features such as superscalar architecture, various modes of operation, instruction set categories, and trends in microprocessor technology. Additionally, it highlights advancements in semiconductor technology and the increasing specialization of processors for diverse applications.