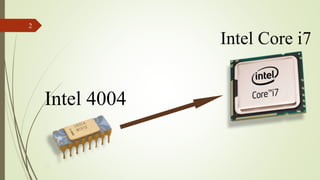
The document traces the evolution of Intel processors from 4-bit to modern 64-bit processors. It discusses the key developments including the 4004 (1971), the first commercial microprocessor, the 8086 (1978) which introduced the x86 architecture, the 80386 (1985) which was the first 32-bit processor, and the Core i7 (2008) which is one of Intel's top consumer processors today. The document highlights increasing transistor counts, clock speeds, memory addressing and capabilities with each generation to show Intel's leadership in driving the advancement of microprocessor technology over the past 50 years.