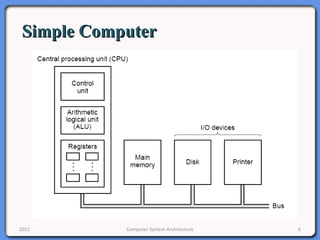
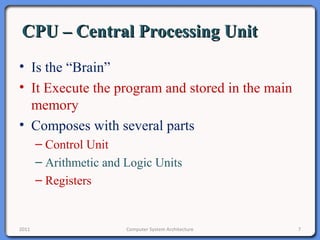
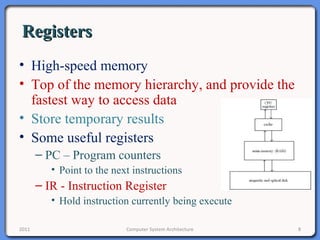
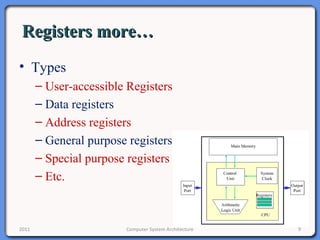
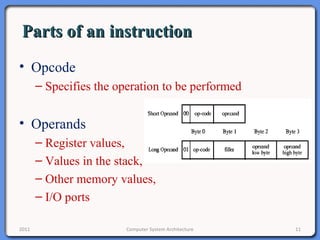
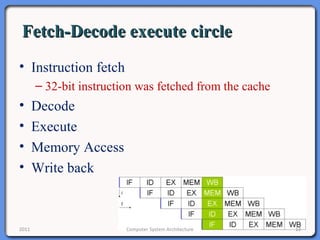
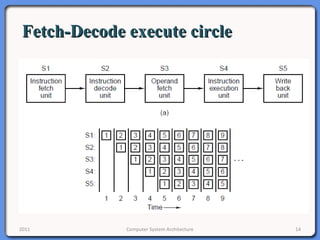
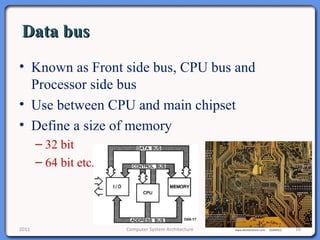
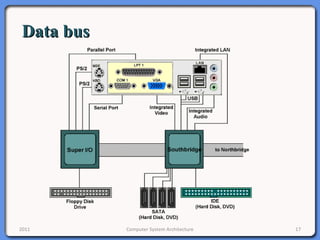
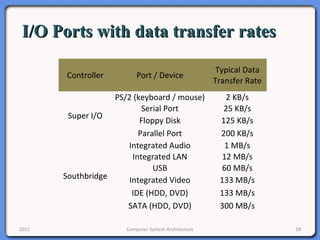
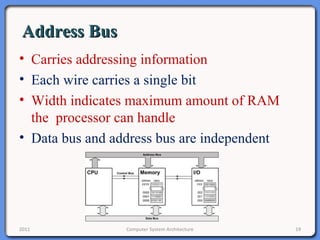
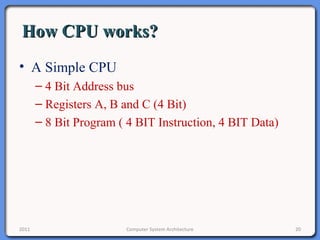
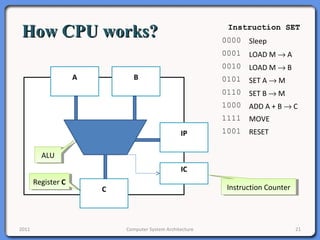
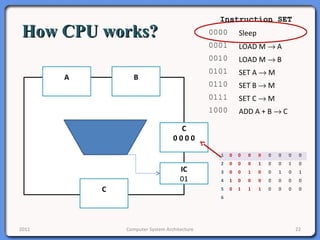
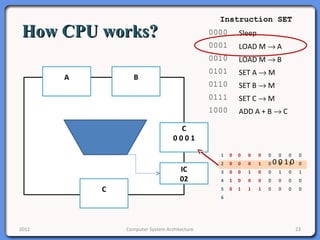
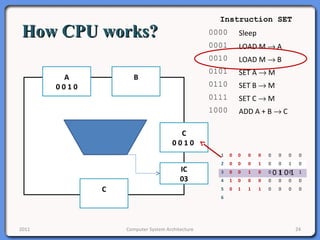
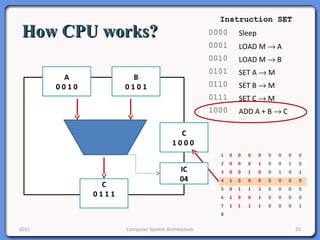
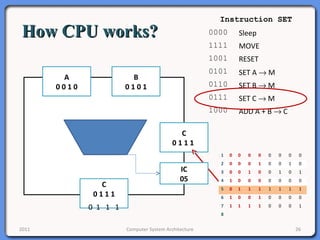
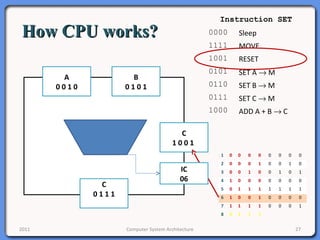
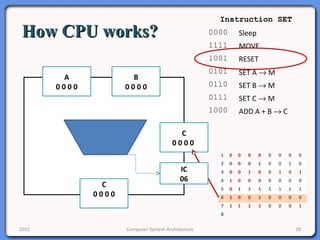
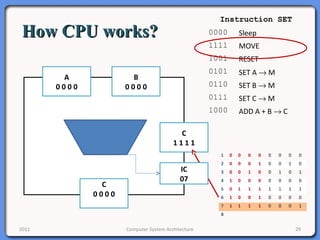
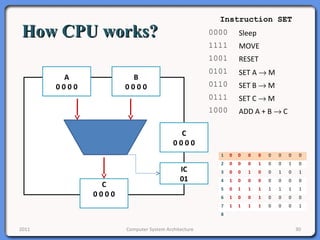
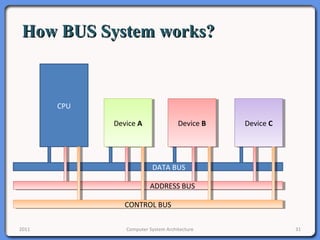
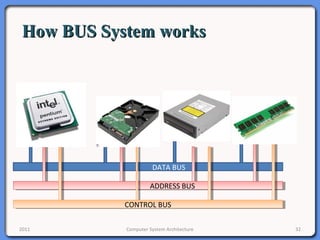
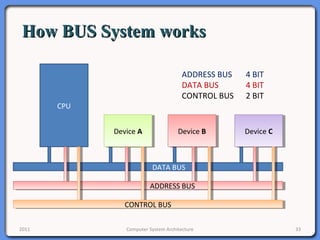
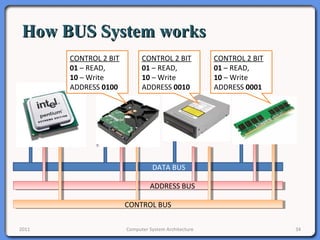
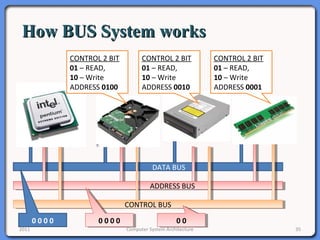
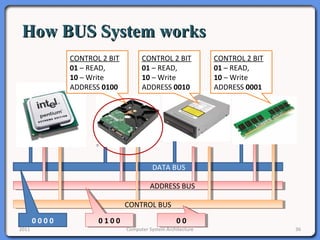
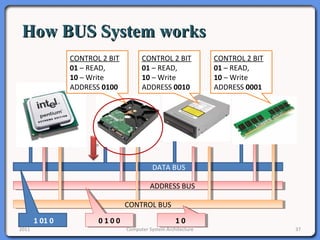
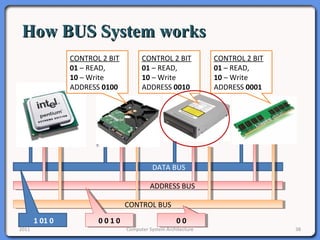
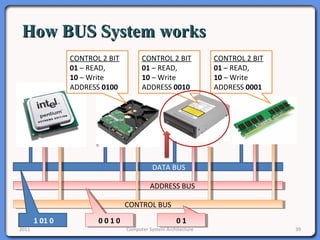
The document provides an overview of computer system architecture. It begins by defining computer architecture as the set of data types, operations, and features that are visible to a computer's users at a particular level of abstraction. The document then discusses why computer architecture is important for optimizing performance within cost constraints. It describes the basic components of a simple computer system, including the CPU, memory, I/O devices, and bus. The document explains in detail the role of the CPU, including its main components like the control unit, ALU, and registers. It provides examples of how a simple CPU would execute instructions on a 4-bit system. Finally, it illustrates how the bus is used to connect the CPU and other devices to allow