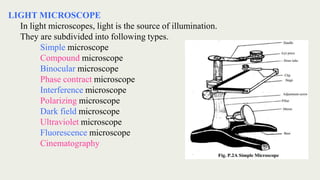
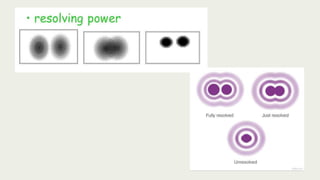
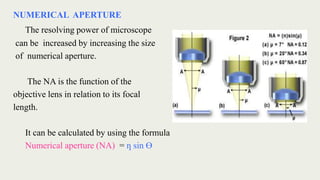
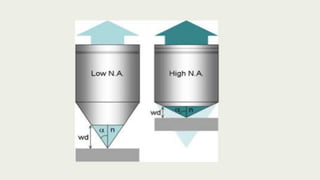
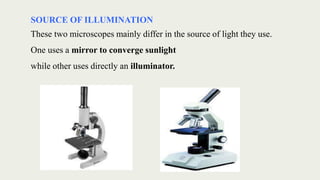
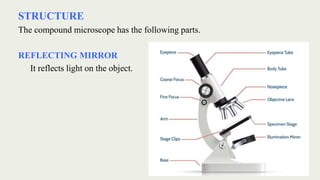
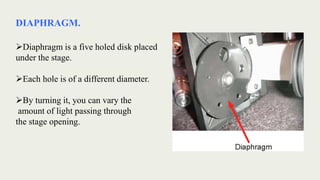
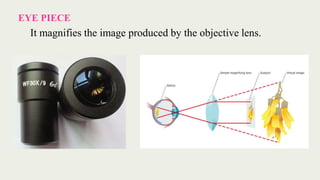
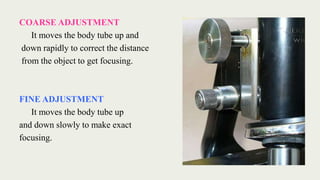
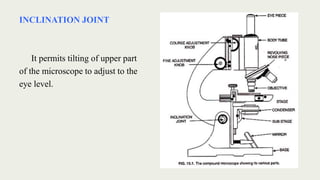
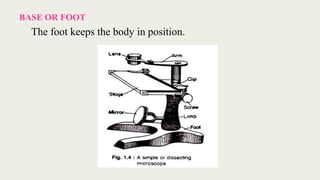
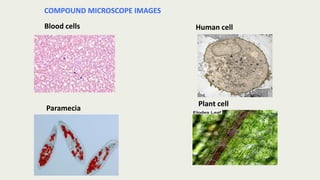
The document discusses microscopes, focusing on their definition, types, and usage in clinical and research laboratories. It details various types of microscopes, including light and compound microscopes, and explains the principles of magnification and resolving power. Additionally, it outlines the structure and components of a compound microscope and its applications in fields like pathology and forensics.