3. Microscope simple, compound & stereo - Basics
•
3 likes•4,061 views
A simple microscope uses a single lens to magnify objects and forms a virtual image. It provides low magnification and is used to examine things like skin, algae, and soil samples. A compound microscope has two lens systems that provide higher magnification by compounding the magnification of the objective and eyepiece lenses. It allows detailed examination of stained slides and is commonly used in biology labs and medical diagnostics. A stereo microscope uses two separate optical paths and lens systems to provide a three-dimensional view of surfaces. It has lower magnification than compound microscopes and is used for examining things like insects and circuit boards.
Report
Share
Report
Share
Download to read offline
Recommended
Stereo Microscope or Dissecting Miscrscope

GENERAL ASPECTS OF STEREO MICROSCOPE ITS TYPES ,GROUPS AND GENERAL USES
Light microscope

what ids microscopy
light microscopy
principle
types of light microscopy
apllication
Bright field microscope

BRIGHT FIELD MICROSCOPY by SIVASANGARI SHANMUGAM
bRIGHT FIELD MICROSCOPY is also called a compound microscope. The name bright - field is derived from the fact that the specimen is dark and contrasted by the surrounding bright viewing field.
1. MICROSCOPY - introduction + principle (Basics)

Basics only
Microscopy is the technical field that uses microscopes to observe samples which are
not in the resolution range of the normal-unaided eye.
Microscope is a scientific-instrument consisting of magnifying lens that enables an
observer to view the minute features distinctly.
In greek, micro = small
skopein = to view.
Recommended
Stereo Microscope or Dissecting Miscrscope

GENERAL ASPECTS OF STEREO MICROSCOPE ITS TYPES ,GROUPS AND GENERAL USES
Light microscope

what ids microscopy
light microscopy
principle
types of light microscopy
apllication
Bright field microscope

BRIGHT FIELD MICROSCOPY by SIVASANGARI SHANMUGAM
bRIGHT FIELD MICROSCOPY is also called a compound microscope. The name bright - field is derived from the fact that the specimen is dark and contrasted by the surrounding bright viewing field.
1. MICROSCOPY - introduction + principle (Basics)

Basics only
Microscopy is the technical field that uses microscopes to observe samples which are
not in the resolution range of the normal-unaided eye.
Microscope is a scientific-instrument consisting of magnifying lens that enables an
observer to view the minute features distinctly.
In greek, micro = small
skopein = to view.
Bright field microscopy, Principle and applications

Introduction
History
Basic Component of Microscope
Light Microscopy
Types of Light Microscopy
What Are Bright Microscopy
Principle of Bright Microscope
Advantage
Disadvantage
Application
Conclusion
Reference
Microscopy - Magnification, Resolving power, Principles, Types and Applications

Magnification, Resolving power, Principles and Applications of Simple, Compound, Stereozoom, Phase contrast, Fluorescent and Electron microscopes (TEM & SEM).
Microscopy is the technical field that uses microscopes to observe samples which are not in the resolution range of the normal-unaided eye.
Compound microscope

Compound Microscope, Magnification power, Resolving power, Instrumentation of compound microscope, application of compound microscope
DARK FIELD MICROSCOPY

DARK FIELD MICROSCOPY by SIVASANGARI SHANMUGAM
Dark-field microscopy is ideally used to illuminate unstained samples causing them to appear brightly lit against a dark background.
This type of microscope contains a special condenser that scatters light and causes it to reflect off the specimen at an angle
Compound microscope

compound microscope
florescent microscope
DGI
Phase contrast
Electron microscope and its types
TEM
SEM
Fluorescence Microscopy

one of the major light microscopy which is widly use to dedect live imaging cells
Phase contrast microscope

Phase contrast microscope, Types of phase contrast, Parts of Phase contrast microscope, Application of Phase contrast microscope
Numerical aperture and limits of resolution of microscope

Numerical aperture and limits of resolution of microscope
Electron microscope, principle and application

Introduction
History
Resolution &Magnification of
Electron microscope
Types of electron microscope
1) Transmission electron microscope (TEM)
- Structural parts of TEM
- Principle & Working of TEM
- Sample preparation for TEM
- Advantages & disadvantages of TEM
Scanning electron microscope (SEM)
- Structural parts of SEM
- Principle & Working of SEM
- Sample preparation for SEM
- Advantages & disadvantages of SEM
3) Scanning transmission electron microscope (STEM)
Applications of electron microscope
Conclusion
References
Principles and application of light, phase constrast and fluorescence microscope

light microscope, phase contrast microscope, fluorescence microscope, phase contrast ring
Confocal microscope presentation pt

It helps for Bsc first years to understand the basics of Confocal Microscopy
Dark Field microscopy

it will be helpful in understanding dark field microscopy and its advantages and disadvantages.
5. Microsocope ELECTRON MICROSCOPE (TEM & SEM ) - Basics

Basics only
Electron beam is the source of illumination.
Image is produced by magnetic field.
Contrasting features between light microscope and electron microscope are
construction, working principle, specimen preparation, cost-expenses and designed
room (vacuum chamber).
Introducation to Microscopy

In this presentation, I have described the Principle and Application of Light, Phase contrast, Fluorescence.
More Related Content
What's hot
Bright field microscopy, Principle and applications

Introduction
History
Basic Component of Microscope
Light Microscopy
Types of Light Microscopy
What Are Bright Microscopy
Principle of Bright Microscope
Advantage
Disadvantage
Application
Conclusion
Reference
Microscopy - Magnification, Resolving power, Principles, Types and Applications

Magnification, Resolving power, Principles and Applications of Simple, Compound, Stereozoom, Phase contrast, Fluorescent and Electron microscopes (TEM & SEM).
Microscopy is the technical field that uses microscopes to observe samples which are not in the resolution range of the normal-unaided eye.
Compound microscope

Compound Microscope, Magnification power, Resolving power, Instrumentation of compound microscope, application of compound microscope
DARK FIELD MICROSCOPY

DARK FIELD MICROSCOPY by SIVASANGARI SHANMUGAM
Dark-field microscopy is ideally used to illuminate unstained samples causing them to appear brightly lit against a dark background.
This type of microscope contains a special condenser that scatters light and causes it to reflect off the specimen at an angle
Compound microscope

compound microscope
florescent microscope
DGI
Phase contrast
Electron microscope and its types
TEM
SEM
Fluorescence Microscopy

one of the major light microscopy which is widly use to dedect live imaging cells
Phase contrast microscope

Phase contrast microscope, Types of phase contrast, Parts of Phase contrast microscope, Application of Phase contrast microscope
Numerical aperture and limits of resolution of microscope

Numerical aperture and limits of resolution of microscope
Electron microscope, principle and application

Introduction
History
Resolution &Magnification of
Electron microscope
Types of electron microscope
1) Transmission electron microscope (TEM)
- Structural parts of TEM
- Principle & Working of TEM
- Sample preparation for TEM
- Advantages & disadvantages of TEM
Scanning electron microscope (SEM)
- Structural parts of SEM
- Principle & Working of SEM
- Sample preparation for SEM
- Advantages & disadvantages of SEM
3) Scanning transmission electron microscope (STEM)
Applications of electron microscope
Conclusion
References
Principles and application of light, phase constrast and fluorescence microscope

light microscope, phase contrast microscope, fluorescence microscope, phase contrast ring
Confocal microscope presentation pt

It helps for Bsc first years to understand the basics of Confocal Microscopy
Dark Field microscopy

it will be helpful in understanding dark field microscopy and its advantages and disadvantages.
5. Microsocope ELECTRON MICROSCOPE (TEM & SEM ) - Basics

Basics only
Electron beam is the source of illumination.
Image is produced by magnetic field.
Contrasting features between light microscope and electron microscope are
construction, working principle, specimen preparation, cost-expenses and designed
room (vacuum chamber).
What's hot (20)
Bright field microscopy, Principle and applications

Bright field microscopy, Principle and applications
Microscopy - Magnification, Resolving power, Principles, Types and Applications

Microscopy - Magnification, Resolving power, Principles, Types and Applications
Lecture 3 Unit-I Bright-field & Dark-field Microscopy.pdf

Lecture 3 Unit-I Bright-field & Dark-field Microscopy.pdf
Numerical aperture and limits of resolution of microscope

Numerical aperture and limits of resolution of microscope
Principles and application of light, phase constrast and fluorescence microscope

Principles and application of light, phase constrast and fluorescence microscope
5. Microsocope ELECTRON MICROSCOPE (TEM & SEM ) - Basics

5. Microsocope ELECTRON MICROSCOPE (TEM & SEM ) - Basics
Similar to 3. Microscope simple, compound & stereo - Basics
Introducation to Microscopy

In this presentation, I have described the Principle and Application of Light, Phase contrast, Fluorescence.
Types of Light Microscopes used in Histological Studies.pptx

Light microscopes relies on glass lenses and visible light to magnify tissue samples. It was
invented in XVII century, and has been improved over the years, resulting in the powerful
modern light microscopes. As individual cellular structures are too small to be seen by the
human eye, microscopy techniques have played a key role in the development of
histological techniques.
Types of Microscopes with their applications

Types of Microscopes with their applications - Microbiologynote.com
https://microbiologynote.com/types-of-microscopes-with-their-applications/
Youtube Lecture Video:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=nuJZtXohFFQ&ab_channel=MicrobiologyNote
Electron Microscope: Definition, Types, Parts, Application, Advantages, Disad...

Electron Microscope: Definition, Types, Parts, Application, Advantages, Disadvantages
Note link: https://microbiologynote.com/category/microbiology/microscope/
Youtube Video Link:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=E6-jgJedGDU&ab_channel=MicrobiologyNote
Principles of microscopy: A microscope is an instrument that produces an accu...

A microscope (from the Ancient Greek: micro- "small“ and scope-"to look") is an instrument used to see objects that are too small for the naked eye
Compound microscope

Compound microscope is the highly used instrument for the purpose to watch / observed any micro organism. It is the basic instrument for the analysis of the micro object.It used in the various fields such as biology, physics, chemistry,forensic science,geology etc.
Microscope and Microscopy

Microscope and Microscopy
Principal , Function & Difference of various types of Light & Electron microscope.Microscopy is the technical field of using microscopes to view samples & objects that cannot be seen with the unaided eye (objects that are not within the resolution range of the normal eye).
Microscopists explore the relationships between structures & properties for a very wide variety of materials ranging from soft to very hard, from inanimate materials to living organisms, in order to better understand it. Zachariaz Janssen 1585 Robert Hooks 1665
Joseph Jackson Lister1830
Microscopy - Study

Microscopy is the technique of using microscopes to observe and analyze objects that are too small to be seen by the naked eye. Microscopes are instruments that magnify and resolve the details of objects, allowing scientists and researchers to study the structure, composition, and behavior of materials and specimens at a microscopic level
Microscopy - Study

Microscopy is the technique of using microscopes to observe and analyze objects that are too small to be seen by the naked eye. Microscopes are instruments that magnify and resolve the details of objects, allowing scientists and researchers to study the structure, composition, and behavior of materials and specimens at a microscopic level
Microscopy (Principle, structure, types and abilities of microscope)

Microscopy is the technical field of using microscopes to view objects and areas of objects that cannot be seen with the naked eye (objects that are not within the resolution range of the normal eye).
In this file principle, structure, types and abilities of microscope is discussed.
Microscopy all types of microscope

In this file all the types of microscope along with their resolution are present.
Review the slide for better understanding.
Like and comment below either its useful or not?
Similar to 3. Microscope simple, compound & stereo - Basics (20)
Types of Light Microscopes used in Histological Studies.pptx

Types of Light Microscopes used in Histological Studies.pptx
Electron Microscope: Definition, Types, Parts, Application, Advantages, Disad...

Electron Microscope: Definition, Types, Parts, Application, Advantages, Disad...
Principles of microscopy: A microscope is an instrument that produces an accu...

Principles of microscopy: A microscope is an instrument that produces an accu...
Microscopy (Principle, structure, types and abilities of microscope)

Microscopy (Principle, structure, types and abilities of microscope)
More from Nethravathi Siri
Human genetics and holistic health

This presentation was live on July 8th 2020, here is the link for YouTube https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=2DvAot_L2QU
LIVE AND LET IVE
QUANTITATIVE INHERITANCE - KERNEL COLOR IN WHEAT

Nilsson-Ehle (1909) and East (1910, 1916) documented first significant evidence of
quantitative inheritance by their individual works in wheat.
Their analysis started from one-locus control which continued to two locus control
and concluded at three-locus control.
Evolutionary genetics - Theories, 

Overview
In simpler terms, Evolutionary Genetics is the study to understand how genetic
variation leads to evolutionary change.
Evolutionary Genetics attempts to account for evolution in terms of changes in gene
and genotype frequencies within populations and the processes that convert the
variation with populations into more or less permanent variation between species.
The central challenge of Evolutionary Genetics is to describe how the evolutionary
forces shape the patterns of biodiversity.
Evolutionary Genetics majorly deals with;
a. Evolution of genome structure
b. The genetic basis of speciation and adaptation
c. Genetic change in response to selection within populations
Upstream processing 

Overview
Industrial fermentations comprise both upstream (USP) and downstream processing
(DSP) stages. USP involves all factors and processes leading to and including the
fermentation. It consists of three main areas: the producer organism, the medium
and the fermentation process.
Retro copia transposons

Basics of Undergraduate/university fellows
RNA TRANSPOSABLE ELEMENTS (COPIA) IN Drosophila
within host genomes.
As TEs comprise more than 40% of the human genome and are linked to
numerous diseases, understanding their mechanisms of mobilization and
regulation is important.
Drosophila melanogaster is an ideal model organism for the study of eukaryotic
TEs as its genome contains a diverse array of active TEs.
Also referred to as “jumping genes,” TEs move, or transpose, to different locations
throughout the genomes in which they reside.
Eukaryotic transcription 

Basics of Undergraduate/university fellows
Transcription is more complicated in eukaryotes than in prokaryotes because
eukaryotes possess three different classes of RNA polymerases and because of the
way in which transcripts are processed to their functional forms.
More proteins and transcription factors are involved in eukaryotic transcription.
Holliday model of crossing over

One of the first plausible models to account for the preceding observations was
formulated by Robin Holliday.
The key features of the Holliday model are the formation of heteroduplex DNA; the
creation of a cross bridge; its migration along the two heteroduplex strands,
termed branch migration; the occurrence of mismatch repair; and the
subsequent resolution, or splicing, of the intermediate structure to yield different
typesof recombinant molecules.
Vitamins - Basics

A Vitamin is an organic compound by an organism as a vital nutrient in limited
amounts.
• We need vitamins in our diet, because our bodies can’t synthesize them quickly
enough to meet our daily needs.
• The term vitamin was derived from ‘vitamine’ meaning vital and amine.
• It was coined by K FUNK (1912).
3. Special chromosome - B chromosome 

Basics of Undergraduate/university fellows
Supernumerary chromosomes are the additional or extra chromosomal set present in a
cell, which are dissimilar to normal A-Chromosomal set in the species.
They are also called as Accessory Chromosomes and lack homologous chromosome part.
In wild populations, around 100 animal species, 600 plant species especially fungi
contain supernumerary / B-chromosomes
3. Special chromosomes - Lampbrush chromosomes 

Basics of Undergraduate/university fellows
Paired chromosome in meiosis in immature amphibian eggs, in which the chromatin
forms large stiff loops extending out from the linear axis of the chromosome
The lampbrush chromosomes derive their name from the lateral loops that extrude from
the chromomeres at certain point.
They are very transcriptionally active DNA, where loops of DNA emerging from an
apparently continuous chromosomal axis are coated with RNA polymerase.
2. Special chromosomes - Polytene chromosomes

Basics of Undergraduate/university fellows
Since, these chromosomes were discovered in the salivary gland cells, they are called
as "Salivary Gland Chromosomes".
The present name polytene chromosome was suggested by kollar due to the
occurrence of many chromonemata (DNA) in them.
Bridges (~1936) 1st constructed a salivary chromosome map of D melanogaster and
found 5000 special bands in polytene chromosomes.
1. Special chromosomes - Introduction

Basics of Undergraduate/university fellows
In some organisms, there are special tissues in which chromosomes undergo structural
specializations.
Such specialized chromosomes are generally termed as SPECIAL TYPES OF
CHROMOSOMES
Measurement of Radioactivity - Geiger Muller [GM] Counter & SCINTILLATION COU...![Measurement of Radioactivity - Geiger Muller [GM] Counter & SCINTILLATION COU...](data:image/gif;base64,R0lGODlhAQABAIAAAAAAAP///yH5BAEAAAAALAAAAAABAAEAAAIBRAA7)
![Measurement of Radioactivity - Geiger Muller [GM] Counter & SCINTILLATION COU...](data:image/gif;base64,R0lGODlhAQABAIAAAAAAAP///yH5BAEAAAAALAAAAAABAAEAAAIBRAA7)
Basics of Undergraduate/university fellows
It is not in range of human senses or un-aided detection for measurement.
Crossing over basics

Basics of Undergraduate/university fellows
Crossing over is exchange of strictly homologous segments of a genome between their
respective non-sister chromatids during cell division, which results in chromosomal
recombinations of linked genes in daughter cells.
NUCLEOSOME MODEL OF CHROMOSOME

Basics of Undergraduate/university fellows
Nucleosome model of chromosome is proposed by ROGER KORNBERG (son of Arthur
Kornberg) in 1974.
It was confirmed and crystalised by P. Oudet et al., (1975).
Nucleosome is the lowest level of Chromosome organization in eukaryotic cells.
Nucleosome model is a scientific model which explains the organization of DNA and
associated proteins in the chromosomes.
Nucleosome model also explains the exact mechanism of the folding of DNA in
thenucleus.
It is the most accepted model of chromatin organization.
4. Gene interaction - Epistasis - Dominant & Recessive, Non-epistatsis

Basics of Undergraduate/university fellows
Epistasis is a Greek word that means standing over.
BATESON used term epistasis to describe the masking effect in 1909
The term epistasis describes a certain relationship between genes, where an allele of
one gene hides or masks the visible output or phenotype of another gene.
When two different genes which are not alleles, both affect the same character in such
a way that the expression of one masks (inhibits or suppresses) the expression of the
other gene, the phenomenon is said to be epistasis.
The gene that suppresses other gene expression is known as Epistatic gene.
The gene that is suppressed or remain obscure is called Hypostatic gene
The classical phenotypic ratio of 9:3:3:1 F2 ratio becomes modified by epistasis.
3. Gene interaction - supplementary

Basics of Undergraduate/university fellows
In supplementary gene action, the dominant allele of one gene is essential for the
development of the concerned phenotype, while the other gene modifies the expression of the first gene.
2. Gene interaction - complementary

Basics of Undergraduate/university fellows
Complementation between two non-allelic genes (C and P) are essential for production
of a particular or special phenotype i.e., complementary factor.
Two genes involved in a specific pathway and their functional products are required
for gene expression, then one recessive allelic pair at either allelic pair would result in
the mutant phenotype.
When Dominant alleles are present together, they complement each other to yield
complementary factor resulting in a special phenotype.
They are called complementary genes.
When either of gene loci have homozygous recessive alleles (i.e., genotypes of ccPP,
ccPp, CCpp, Ccpp and ccpp), they produce identical phenotypes and change F2 ratio
to 9:7.
1. Gene interaction - Introduction

Basics for undergraduate/university students
The phenomenon of two or more genes affecting the expression of each other in various
ways in the development of a single character of an organism is known as GENE
INTERACTION.
Comparative account on different types of microscopes

Basics
SIMPLE
MICROSCOPE
BRIGHTFIELD
MICROSCOPE
DARK-FIELD
MICROSCOPE
STEREO
ZOOM
MICROSCOPE
PHASE
CONTRAST
MICROSCOPE
FLUORESCENT
MICROSCOPE
TRANSMISSION
ELECTRON
MICROSCOPE
SCANNING
ELECTRON
MICROSCOPE
SOURCE OF ILLUMINATION
SAMPLEVISUALIZATION
CONDENSER
ADDITIONAL SUPPORT SYSTEM
SPECIMEN STAINING
MAGNIFICATION POWER
RESOLUTION
APPLICATION
More from Nethravathi Siri (20)
Measurement of Radioactivity - Geiger Muller [GM] Counter & SCINTILLATION COU...![Measurement of Radioactivity - Geiger Muller [GM] Counter & SCINTILLATION COU...](data:image/gif;base64,R0lGODlhAQABAIAAAAAAAP///yH5BAEAAAAALAAAAAABAAEAAAIBRAA7)
![Measurement of Radioactivity - Geiger Muller [GM] Counter & SCINTILLATION COU...](data:image/gif;base64,R0lGODlhAQABAIAAAAAAAP///yH5BAEAAAAALAAAAAABAAEAAAIBRAA7)
Measurement of Radioactivity - Geiger Muller [GM] Counter & SCINTILLATION COU...
4. Gene interaction - Epistasis - Dominant & Recessive, Non-epistatsis

4. Gene interaction - Epistasis - Dominant & Recessive, Non-epistatsis
Comparative account on different types of microscopes

Comparative account on different types of microscopes
Recently uploaded
Predicting property prices with machine learning algorithms.pdf

This is a report about predicting property prices using SVM, random forest and gradient boosting machine
Citrus Greening Disease and its Management

Citrus Greening was one of the major causes of decline in the citrus production. So, effective management cultural practices should be incorporated
Richard's entangled aventures in wonderland

Since the loophole-free Bell experiments of 2020 and the Nobel prizes in physics of 2022, critics of Bell's work have retreated to the fortress of super-determinism. Now, super-determinism is a derogatory word - it just means "determinism". Palmer, Hance and Hossenfelder argue that quantum mechanics and determinism are not incompatible, using a sophisticated mathematical construction based on a subtle thinning of allowed states and measurements in quantum mechanics, such that what is left appears to make Bell's argument fail, without altering the empirical predictions of quantum mechanics. I think however that it is a smoke screen, and the slogan "lost in math" comes to my mind. I will discuss some other recent disproofs of Bell's theorem using the language of causality based on causal graphs. Causal thinking is also central to law and justice. I will mention surprising connections to my work on serial killer nurse cases, in particular the Dutch case of Lucia de Berk and the current UK case of Lucy Letby.
(May 29th, 2024) Advancements in Intravital Microscopy- Insights for Preclini...

(May 29th, 2024) Advancements in Intravital Microscopy- Insights for Preclini...Scintica Instrumentation
Intravital microscopy (IVM) is a powerful tool utilized to study cellular behavior over time and space in vivo. Much of our understanding of cell biology has been accomplished using various in vitro and ex vivo methods; however, these studies do not necessarily reflect the natural dynamics of biological processes. Unlike traditional cell culture or fixed tissue imaging, IVM allows for the ultra-fast high-resolution imaging of cellular processes over time and space and were studied in its natural environment. Real-time visualization of biological processes in the context of an intact organism helps maintain physiological relevance and provide insights into the progression of disease, response to treatments or developmental processes.
In this webinar we give an overview of advanced applications of the IVM system in preclinical research. IVIM technology is a provider of all-in-one intravital microscopy systems and solutions optimized for in vivo imaging of live animal models at sub-micron resolution. The system’s unique features and user-friendly software enables researchers to probe fast dynamic biological processes such as immune cell tracking, cell-cell interaction as well as vascularization and tumor metastasis with exceptional detail. This webinar will also give an overview of IVM being utilized in drug development, offering a view into the intricate interaction between drugs/nanoparticles and tissues in vivo and allows for the evaluation of therapeutic intervention in a variety of tissues and organs. This interdisciplinary collaboration continues to drive the advancements of novel therapeutic strategies.
SCHIZOPHRENIA Disorder/ Brain Disorder.pdf

This pdf is about the Schizophrenia.
For more details visit on YouTube; @SELF-EXPLANATORY;
https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCAiarMZDNhe1A3Rnpr_WkzA/videos
Thanks...!
Structures and textures of metamorphic rocks

It is useful for the Under Graduating students for easy understanding and it's useful for the exam preparations.
Structural Classification Of Protein (SCOP)

A brief information about the SCOP protein database used in bioinformatics.
The Structural Classification of Proteins (SCOP) database is a comprehensive and authoritative resource for the structural and evolutionary relationships of proteins. It provides a detailed and curated classification of protein structures, grouping them into families, superfamilies, and folds based on their structural and sequence similarities.
Multi-source connectivity as the driver of solar wind variability in the heli...

The ambient solar wind that flls the heliosphere originates from multiple
sources in the solar corona and is highly structured. It is often described
as high-speed, relatively homogeneous, plasma streams from coronal
holes and slow-speed, highly variable, streams whose source regions are
under debate. A key goal of ESA/NASA’s Solar Orbiter mission is to identify
solar wind sources and understand what drives the complexity seen in the
heliosphere. By combining magnetic feld modelling and spectroscopic
techniques with high-resolution observations and measurements, we show
that the solar wind variability detected in situ by Solar Orbiter in March
2022 is driven by spatio-temporal changes in the magnetic connectivity to
multiple sources in the solar atmosphere. The magnetic feld footpoints
connected to the spacecraft moved from the boundaries of a coronal hole
to one active region (12961) and then across to another region (12957). This
is refected in the in situ measurements, which show the transition from fast
to highly Alfvénic then to slow solar wind that is disrupted by the arrival of
a coronal mass ejection. Our results describe solar wind variability at 0.5 au
but are applicable to near-Earth observatories.
The ASGCT Annual Meeting was packed with exciting progress in the field advan...

The ASGCT Annual Meeting was packed with exciting progress in the field advancing efforts to deliver highly promising therapies to more patients.
Unveiling the Energy Potential of Marshmallow Deposits.pdf

Unveiling the Energy Potential of Marshmallow Deposits: A Revolutionary
Breakthrough in Sustainable Energy Science
Seminar of U.V. Spectroscopy by SAMIR PANDA

Spectroscopy is a branch of science dealing the study of interaction of electromagnetic radiation with matter.
Ultraviolet-visible spectroscopy refers to absorption spectroscopy or reflect spectroscopy in the UV-VIS spectral region.
Ultraviolet-visible spectroscopy is an analytical method that can measure the amount of light received by the analyte.
Recently uploaded (20)
Predicting property prices with machine learning algorithms.pdf

Predicting property prices with machine learning algorithms.pdf
Body fluids_tonicity_dehydration_hypovolemia_hypervolemia.pptx

Body fluids_tonicity_dehydration_hypovolemia_hypervolemia.pptx
In silico drugs analogue design: novobiocin analogues.pptx

In silico drugs analogue design: novobiocin analogues.pptx
(May 29th, 2024) Advancements in Intravital Microscopy- Insights for Preclini...

(May 29th, 2024) Advancements in Intravital Microscopy- Insights for Preclini...
Multi-source connectivity as the driver of solar wind variability in the heli...

Multi-source connectivity as the driver of solar wind variability in the heli...
The ASGCT Annual Meeting was packed with exciting progress in the field advan...

The ASGCT Annual Meeting was packed with exciting progress in the field advan...
Unveiling the Energy Potential of Marshmallow Deposits.pdf

Unveiling the Energy Potential of Marshmallow Deposits.pdf
Circulatory system_ Laplace law. Ohms law.reynaults law,baro-chemo-receptors-...

Circulatory system_ Laplace law. Ohms law.reynaults law,baro-chemo-receptors-...
platelets- lifespan -Clot retraction-disorders.pptx

platelets- lifespan -Clot retraction-disorders.pptx
3. Microscope simple, compound & stereo - Basics
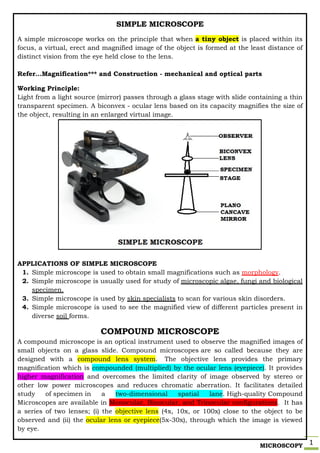
- 1. MICROSCOPY 1 SIMPLE MICROSCOPE A simple microscope works on the principle that when a tiny object is placed within its focus, a virtual, erect and magnified image of the object is formed at the least distance of distinct vision from the eye held close to the lens. Refer…Magnification*** and Construction - mechanical and optical parts Working Principle: Light from a light source (mirror) passes through a glass stage with slide containing a thin transparent specimen. A biconvex - ocular lens based on its capacity magnifies the size of the object, resulting in an enlarged virtual image. APPLICATIONS OF SIMPLE MICROSCOPE 1. Simple microscope is used to obtain small magnifications such as morphology. 2. Simple microscope is usually used for study of microscopic algae, fungi and biological specimen. 3. Simple microscope is used by skin specialists to scan for various skin disorders. 4. Simple microscope is used to see the magnified view of different particles present in diverse soil forms. COMPOUND MICROSCOPE A compound microscope is an optical instrument used to observe the magnified images of small objects on a glass slide. Compound microscopes are so called because they are designed with a compound lens system. The objective lens provides the primary magnification which is compounded (multiplied) by the ocular lens (eyepiece). It provides higher magnification and overcomes the limited clarity of image observed by stereo or other low power microscopes and reduces chromatic aberration. It facilitates detailed study of specimen in a two-dimensional spatial lane. High-quality Compound Microscopes are available in Monocular, Binocular, and Trinocular configurations. It has a series of two lenses; (i) the objective lens (4x, 10x, or 100x) close to the object to be observed and (ii) the ocular lens or eyepiece(5x-30x), through which the image is viewed by eye.
- 2. MICROSCOPY 2 Compound microscopy classified based on the field observed; 1. Bright-field microscopes 2. Dark-field microscopes 1. BRIGHTFIELD MICROSCOPES The bright-field microscope is the simplest optical microscope and is popularly employed. The object to be inspected is normally placed on a clear glass slide, and light is transmitted though the object. This makes the object appear dark against a bright background, hence the term Bright-field. WORKING PRINCIPLE Light from the illumination (light) source from the base of the Microscope stand is aimed at sub-stage condenser lens. The sub-stage condenser lens focuses light through slit in the stage onto the sample. The sample absorbs some amount of light based on stain, pigmentation or thickness. The projected light from the sample is collected by objective lens and is magnified according to its capacity, creating a primary image. The primary image is magnified by ocular lens (eye piece), which also act as magnifying glass by allowing the observer to view virtual and magnified image of the sample. APPLICATIONS Widely used for stained or naturally pigmented or highly contrasted specimens mounted on a glass microscope slide. Used in biology classrooms (mitosis & meiosis, etc.) and clinical laboratories. Used in pathology to view fixed tissue sections or cell smears / smears.
- 3. MICROSCOPY 3 2. DARKFIELD MICROSCOPES Used to observe unstained – transparent specimens. Samples having very close refractive indices value as that of surroundings are difficult to observe with conventional bright-field microscopes, such samples are ideal for observation with dark background. Example: small aquatic organisms, oocytes and other thin-transparent materials with Refractive Index from 1.2 to 1.4 WORKING PRINCIPLE Light from the illumination (light) source from the base of the Microscope stand is aimed at dark-field ring. Dark-field ring is an opaque disk blocks the central rays of the light. The marginal/peripheral light rays are directed to sub-stage dark-field condenser lens. The specimen on the stage is illuminated only with the peripheral oblique rays. As a result of this, the field appears dark. The scattered ray from bright specimen is collected by objective lens and is magnified according to its capacity, creating a primary image. The primary image is magnified by ocular lens (eye piece), which also act as magnifying glass by allowing the observer to view virtual and magnified image of the sample. APPLICATIONS Used for examination of live sample. Unstained or lightly stained specimen or fluids could also be observed. Useful for diagnosis of disease. The bacterial motility can be studied. Precious stones are viewed.
- 4. MICROSCOPY 4 STEREO MICROSCOPE The stereo microscope, also called a Dissecting microscope, as it allows the operator to manipulate/dissect the specimen while it is being observed through the microscope. It provides relatively lower magnification usually below 100x. They provide a close-up, 3-Dimensional view of objects surface textures. Stereo microscopes are used for large biological samples ( insects, leaf, tissues…) and medical science applications as well as in the electronics industry, such as by those who make circuit boards or watches. WORKING PRINCIPLE The Optical binocular stereo microscope consists of two objective lens and two ocular lens. Two spatially separated optical path focuses sample on the same point from slightly different angles. The laterally correct, upright-erect image is obtained. ADVANTAGES They can have a single fixed magnification, several discrete magnifications, or a zoom magnification system. Many stereo microscopes are modular in design. It does not require a slide preparation. It enables to switch from bright-field to dark-field and vice-versa.
