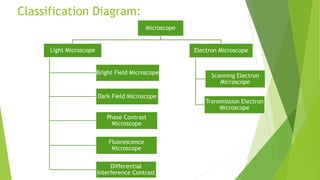
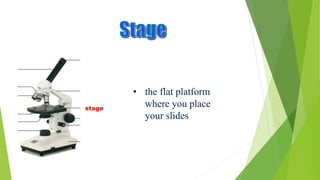
This document defines microscopy and describes the main types and parts of microscopes. It discusses that a microscope is an instrument that uses magnification to see small objects. There are two main types of microscopes - light microscopes, which use visible light and can magnify up to 400x, and electron microscopes, which use electron beams and have higher magnification. Light microscopes are further divided into brightfield, darkfield, fluorescence, phase contrast, and differential interference contrast microscopes. Electron microscopes are divided into scanning electron microscopes and transmission electron microscopes. The document also includes diagrams labeling the main parts of a light microscope like the eyepiece, stage, objective lenses, light source, and diaphragm.