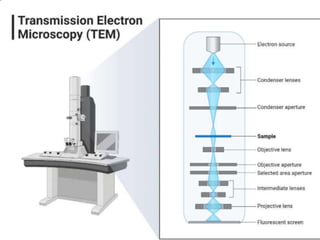
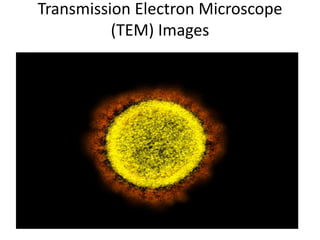
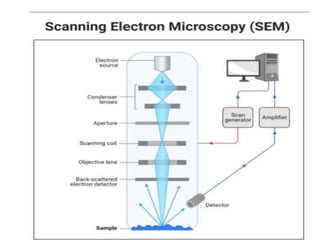
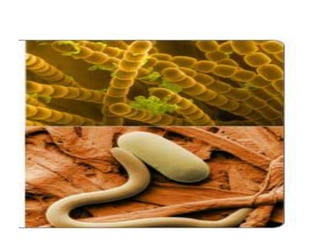
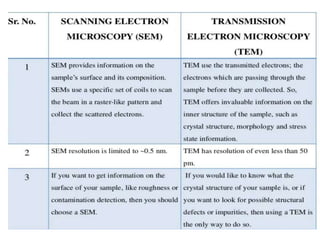
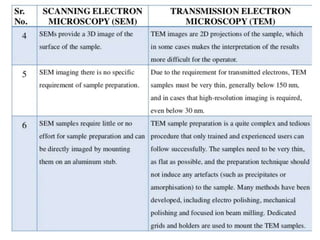
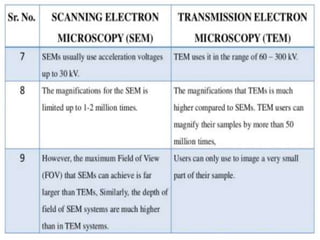
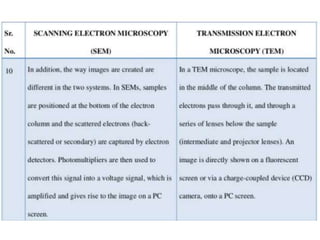
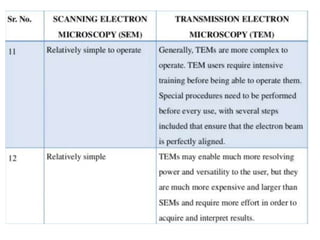
The document summarizes electron microscopes. It describes that Ernst Ruska invented the first electron microscope in 1931, which uses a beam of electrons instead of light to magnify objects. It has three main parts - an electron gun that generates electrons, electromagnetic lenses that focus the electron beam, and a specimen holder. Electron microscopes can magnify objects up to two million times, allowing visualization of structures at the nanoscale. There are two main types - transmission electron microscopes (TEM), which produce highly detailed images but require thin specimens, and scanning electron microscopes (SEM) which scan surfaces and provide 3D topographic information.