Embed presentation
Downloaded 49 times











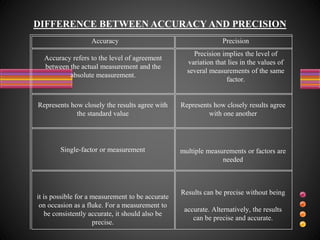


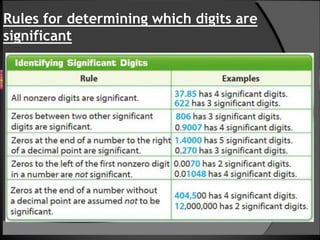




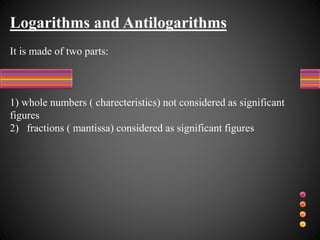
This document defines accuracy, precision, and significant figures in analytical chemistry. Accuracy refers to how close a measurement is to the true value, while precision describes the reproducibility of repeated measurements. A measurement can be precise without being accurate. There are two methods to determine accuracy - absolute and comparative. The absolute method uses samples of known composition, while the comparative method uses secondary standards. Precision is measured by tests of repeatability and reproducibility. The number of significant figures indicates the certainty of a measurement and must be considered when performing calculations to avoid losing accuracy. Rules are provided for determining significant figures in addition, subtraction, multiplication, division and other operations.



















