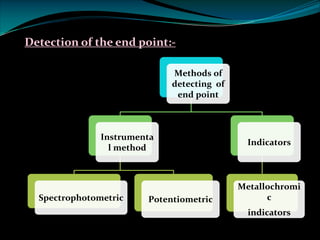
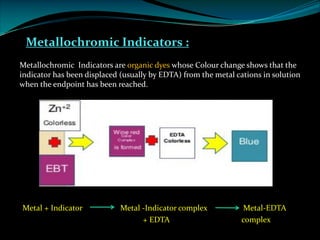
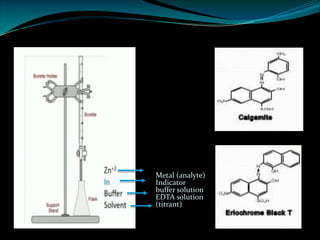
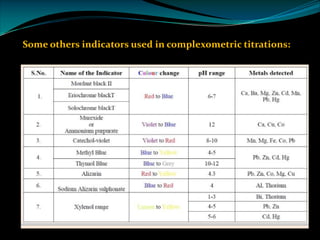
Complexometric titrations involve the titration of a metal ion with a complexing agent or chelating agent such as EDTA. EDTA is a hexadentate ligand that forms very stable 1:1 complexes with metal ions. It is often used as the titrant in complexometric titrations due to the stability of the metal-EDTA complexes formed. The endpoint of the titration can be detected using metallochromic indicators that change color when the metal ion is completely bound to EDTA instead of the indicator. Complexometric titrations have many applications such as determining water hardness and analyzing metals in pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, urine and other samples.








![EDTA Structure:
EDTA Stands For: ethylenediaminetetraaceti cacid.
Ø EDTA is a chelating agent or sequestering agent as it binds the metal ion through several
coordinate bonds.
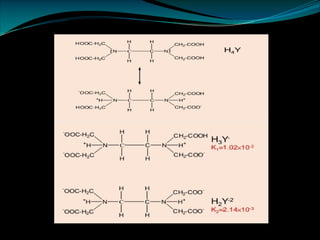
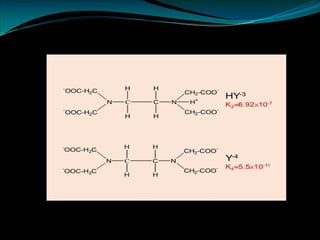
Ø EDTA is a tetrabasic acid that has six potential sites for bonding with a metal ion, four
carboxyl groups and the two amino groups so it is a Hexadentate ligand.
Ø EDTA reacts with any metal ion
Ø within the ratio of 1:1
Ø regardless of the charge on
Ø the cation, thus EDTA is not
Ø a selective reagent.
Ø e.g. Ag+ + EDTA [Ag-EDTA]3-
Al3+ + EDTA [Al-EDTA]-](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/complexometrictitration1-221006164526-8d7d0ab8/85/Complexometric-Titration1-pdf-12-320.jpg)

![Ø EDTA is slightly soluble in water so its disodium salt (Na2H2Y) is commonly
used instead as a titrant.
Ø The reaction between metal ion and EDTA is usually written as:
Mn+ + H2Y2- [MY]n-4 + 2H+
Ø EDTA is produced as several salts such as :
Disodium EDTA
Sodium Calcium edetate (Used to treat lead poisoning).
Tetrasodium EDTA.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/complexometrictitration1-221006164526-8d7d0ab8/85/Complexometric-Titration1-pdf-17-320.jpg)





![EDTA Titration Curve:
Ø A titration is performed by adding the chelating agent to the sample.
Ø Take EDTA Conc. in mL on x-axis and metal Conc. on y-axis.
Ø We report metal conc. In pM, where
pM=_log[Mgn+]
e.g pCA2+ = _ log[Ca2+].
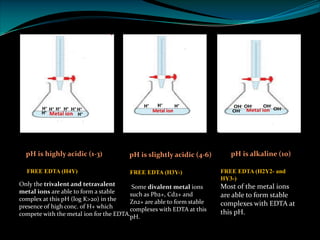
§ In region 1 excess of metal ion present.
We added EDTA some react but most of the
metal left behind
§ In region 2 at equivalence point
we added enough EdTA to form complex
with all of the metal ions left over.
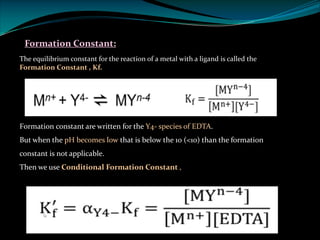
So the conditional formation constant is :
The Kf' = Ca2+ = EDTA.
§ In region 3 we have of EDTA
which will complex with all of the metal ions
that are left over. So
The Kf' = Ca2+ = EDTA
We could calculate [EDTA] and [Mn+] at
every point in the titration curve.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/complexometrictitration1-221006164526-8d7d0ab8/85/Complexometric-Titration1-pdf-25-320.jpg)