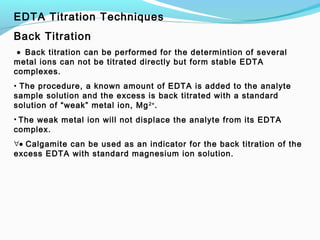
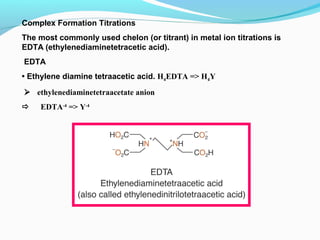
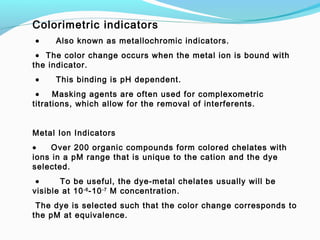
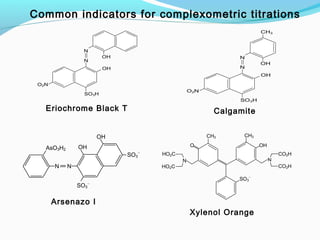
The document provides an overview of complexometric titrations, which involve the formation of coordination complexes between metal ions and ligands. It discusses the role of chelating agents like EDTA, the formation of colored complexes as indicators, and various titration techniques such as direct titration, back titration, and displacement titration. Additionally, it highlights the importance of maintaining pH levels and the use of specific indicators for accurate titration results.






![[ ]
[ ] [ ]-4
4)-(n
MY
YM
MY
K
+
=
EDTA Titration
EDTA combined with the metal ion (1 : 1) to form complex.
For a +1 cation: Ag+
+ Y4−
→ Ag Y3−
For a +2 cation: Hg2+
+ Y4−
→ Hg Y2−
For a +3 cation: Fe3+
+ Y4−
→ Fe Y−
For a + n ion: Mn+
+ Y4−
→ MY(n – 4)+
The Formation Constant,](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/complexometrictitrations-150115042231-conversion-gate01/85/Complexometric-titrations-10-320.jpg)