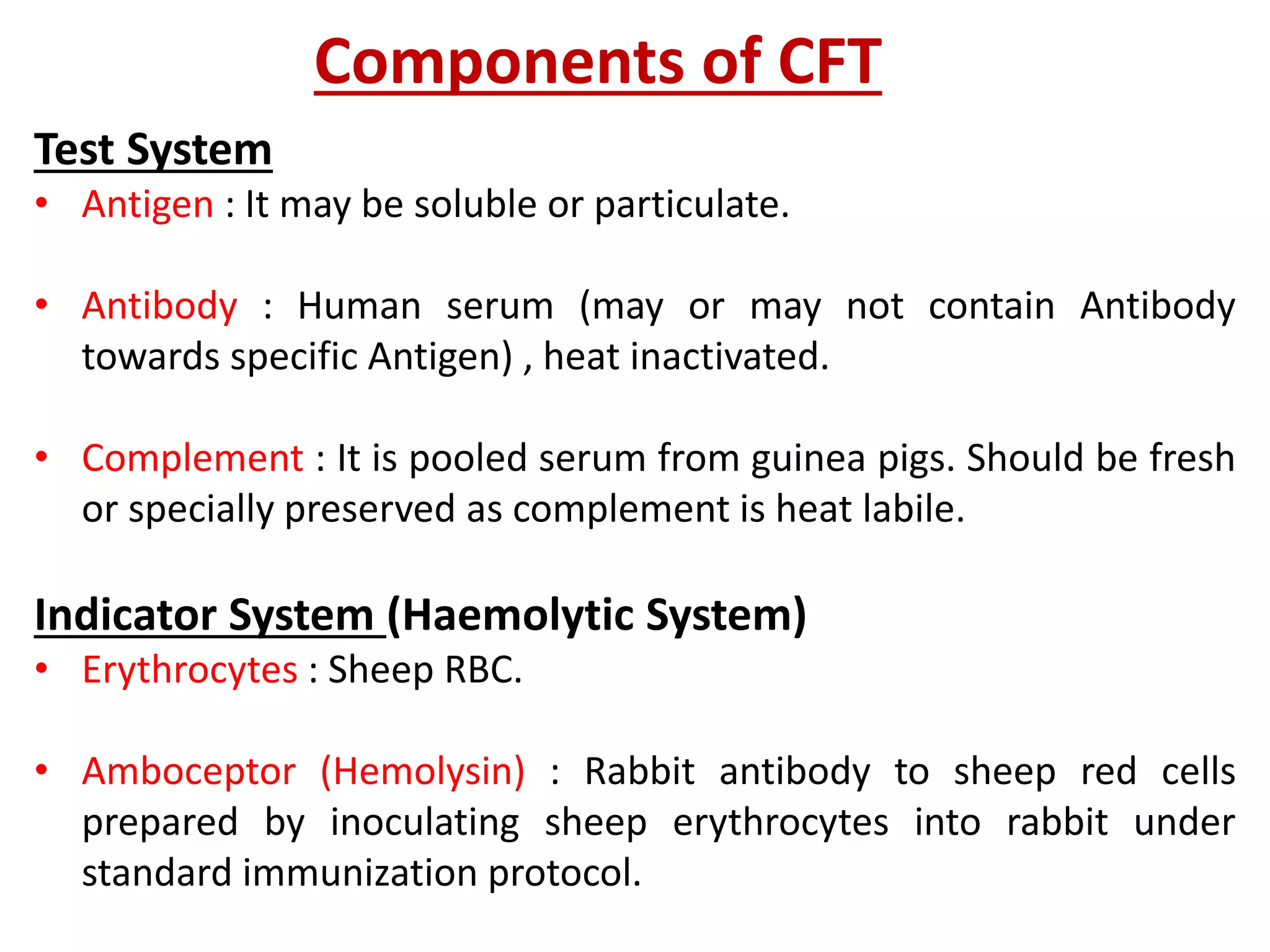
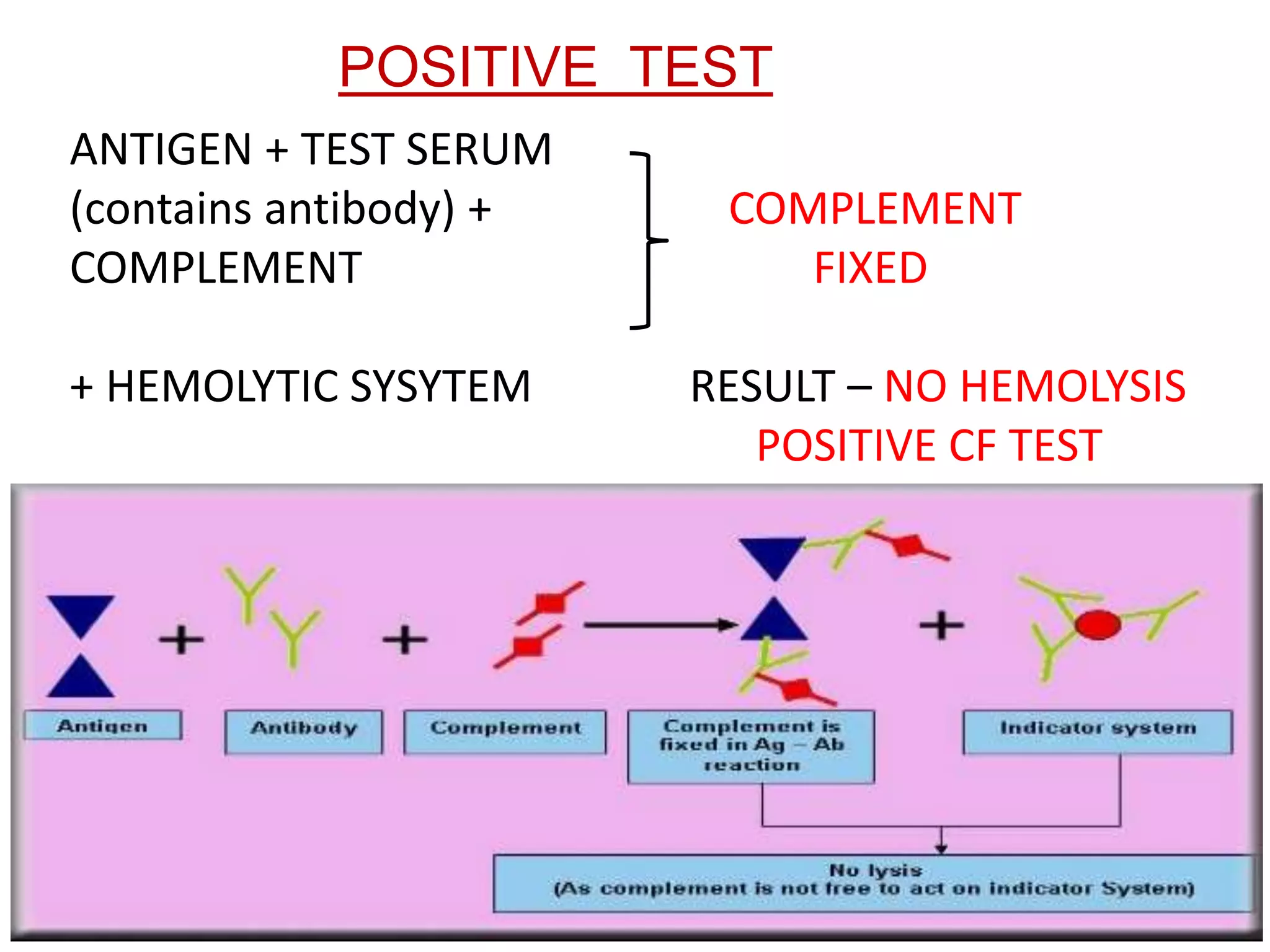
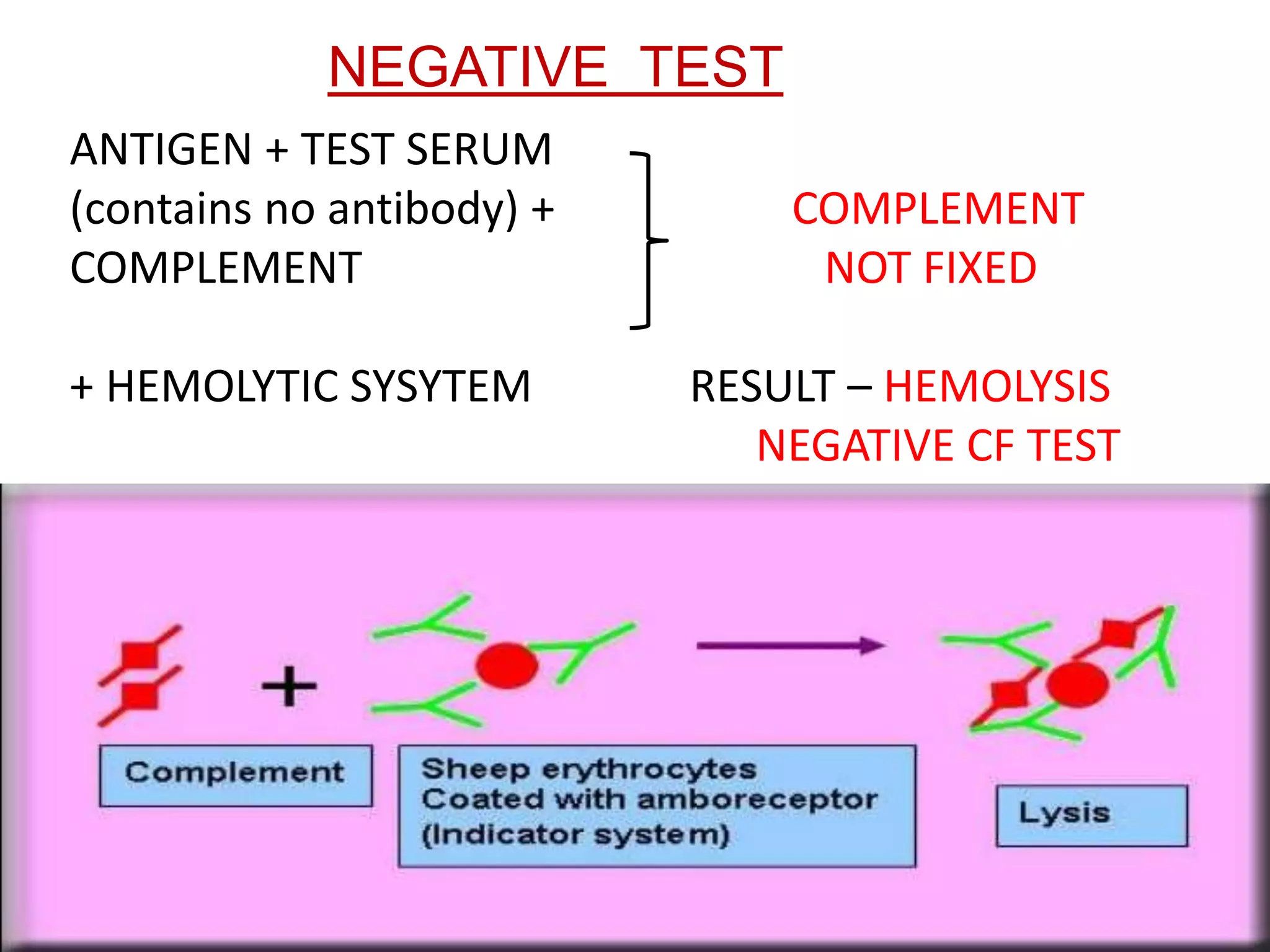
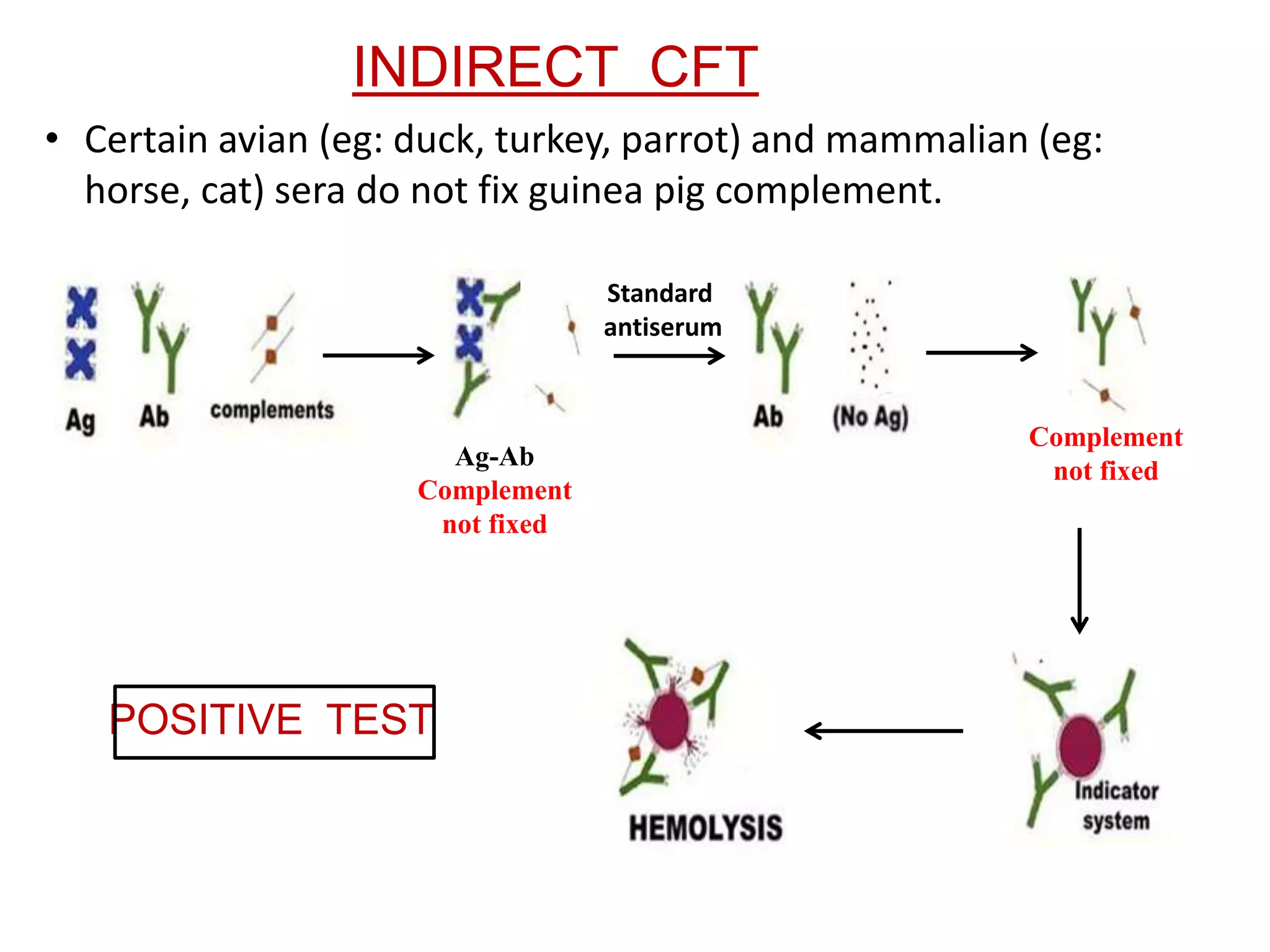
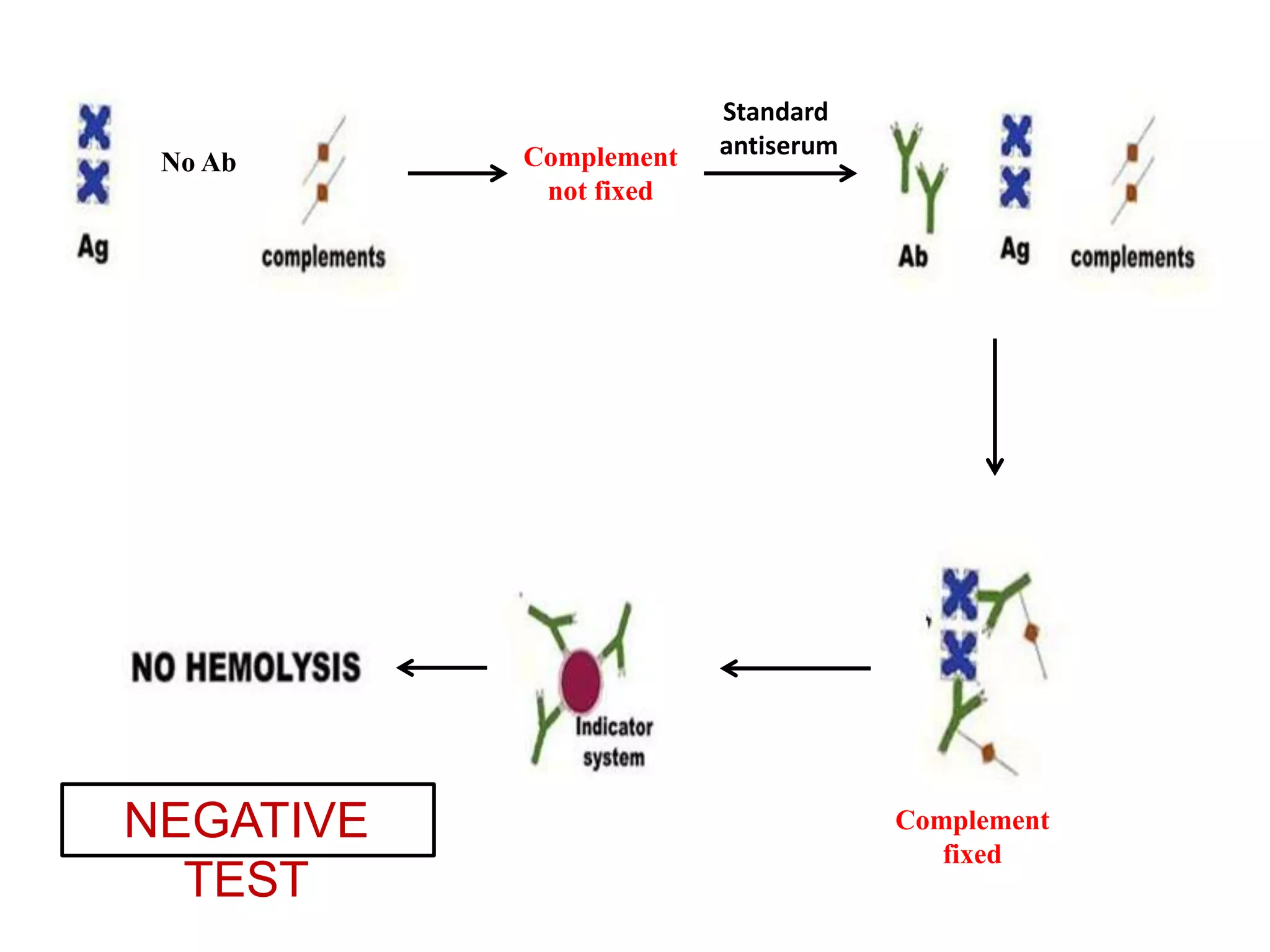
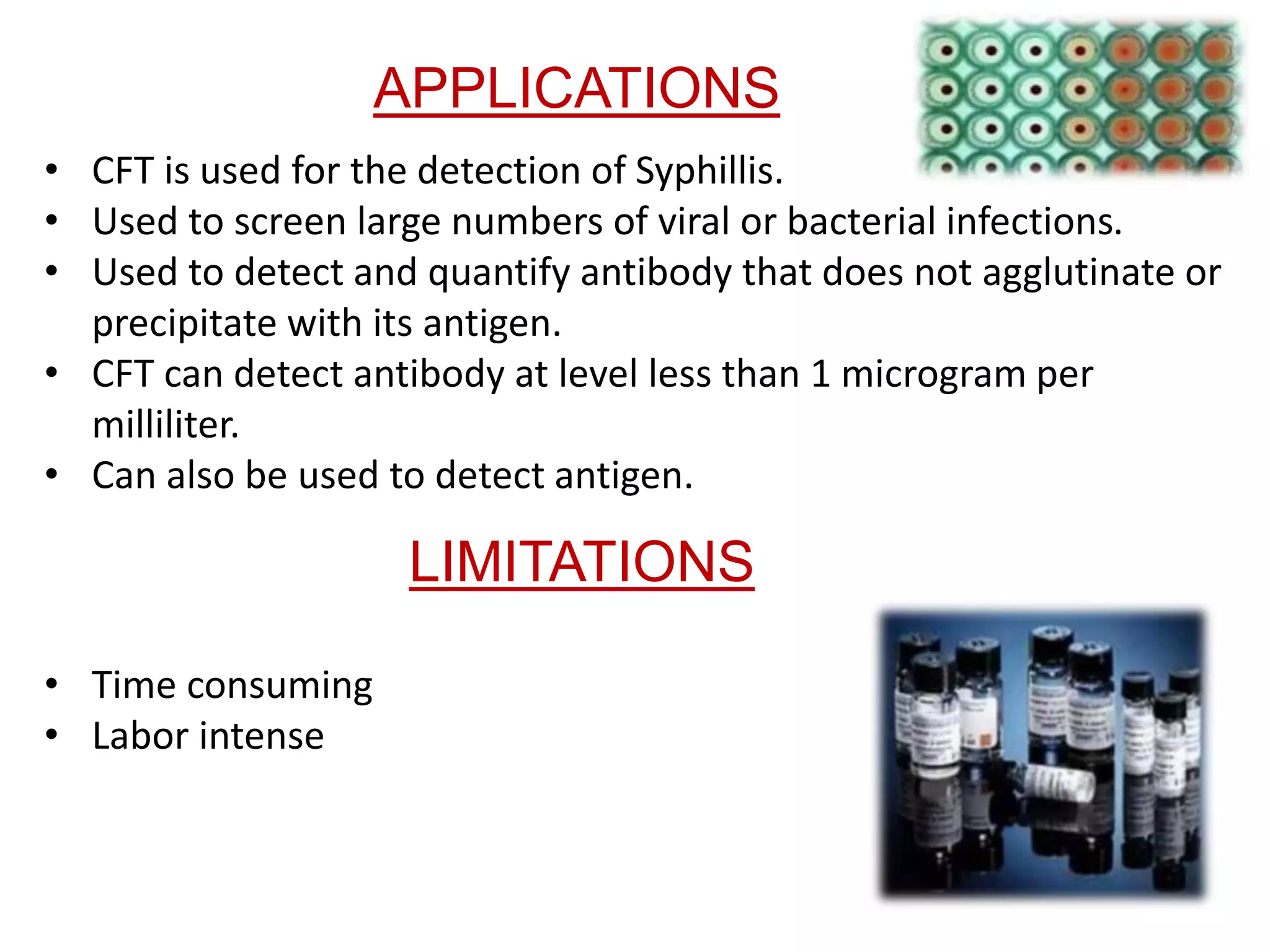
The complement fixation test (CFT) involves mixing antigen, antibody, and complement. If the antibody is specific to the antigen, it will bind and "fix" the complement, preventing it from lysing red blood cells. In a positive test, lysis does not occur, while a negative test results in lysis. CFT is used to detect antibodies against pathogens like syphilis, and can detect antibody levels below 1 microgram/ml. It has limitations like being time-consuming and labor-intensive. Variations involve using different complement sources or detection methods depending on the pathogen.