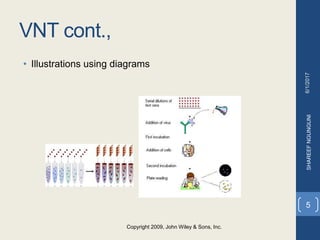
The viral neutralization test is a serological method that detects the presence of viral neutralizing antibodies. It involves mixing dilutions of antibodies with a standardized amount of virus, incubating them, and observing for cytopathic effects in cell cultures. If the antibodies neutralize the virus, no cytopathic effects will be observed as the cells remain intact. While the viral neutralization test is highly sensitive and specific, it is also slow, intensive, and requires skilled technicians. It remains the gold standard method for diagnosing viral infections in the laboratory by comparing other test methods to it.