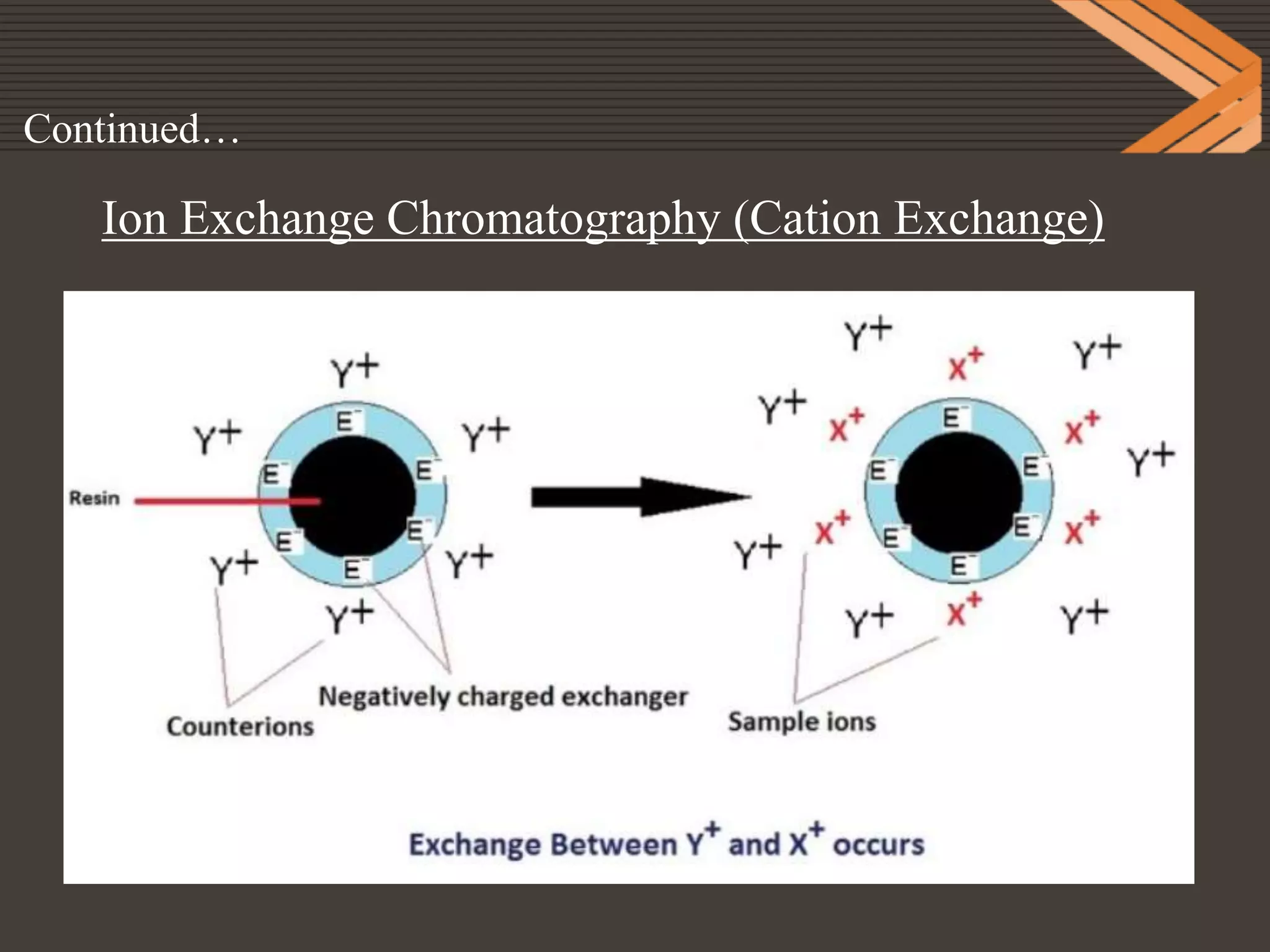
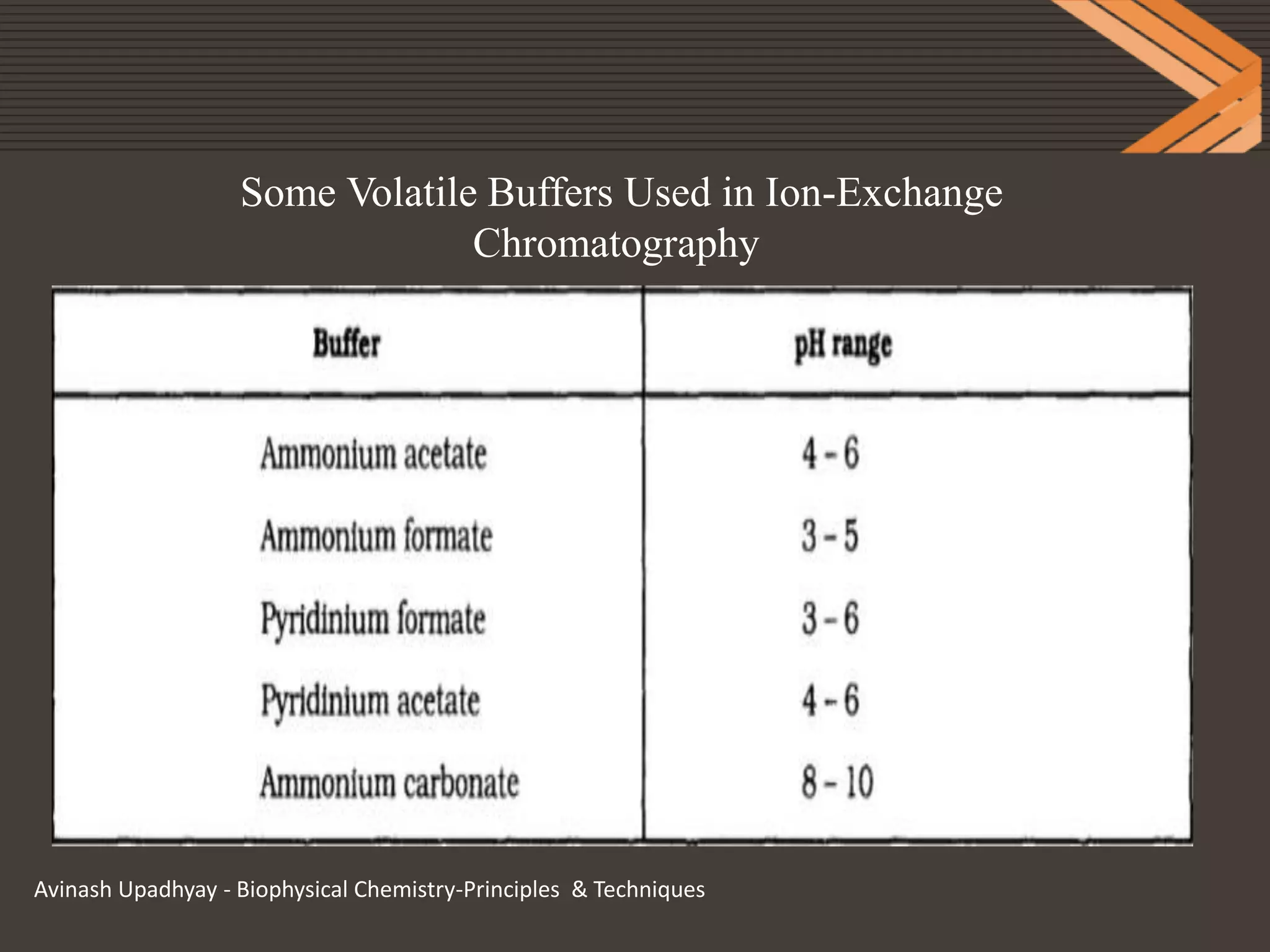
This document provides information on ion exchange chromatography. It begins by describing Michael Tswett who first separated plant pigments using chromatography in 1906. It then discusses how chromatography can be used to separate mixtures with similar properties. The document outlines the basic principles of ion exchange chromatography, including that it relies on reversible exchange between ions in solution and ions bound to an insoluble stationary phase. It provides details on cation and anion exchangers, preparation of ion exchangers, choice of buffers, applications, advantages and disadvantages of ion exchange chromatography.