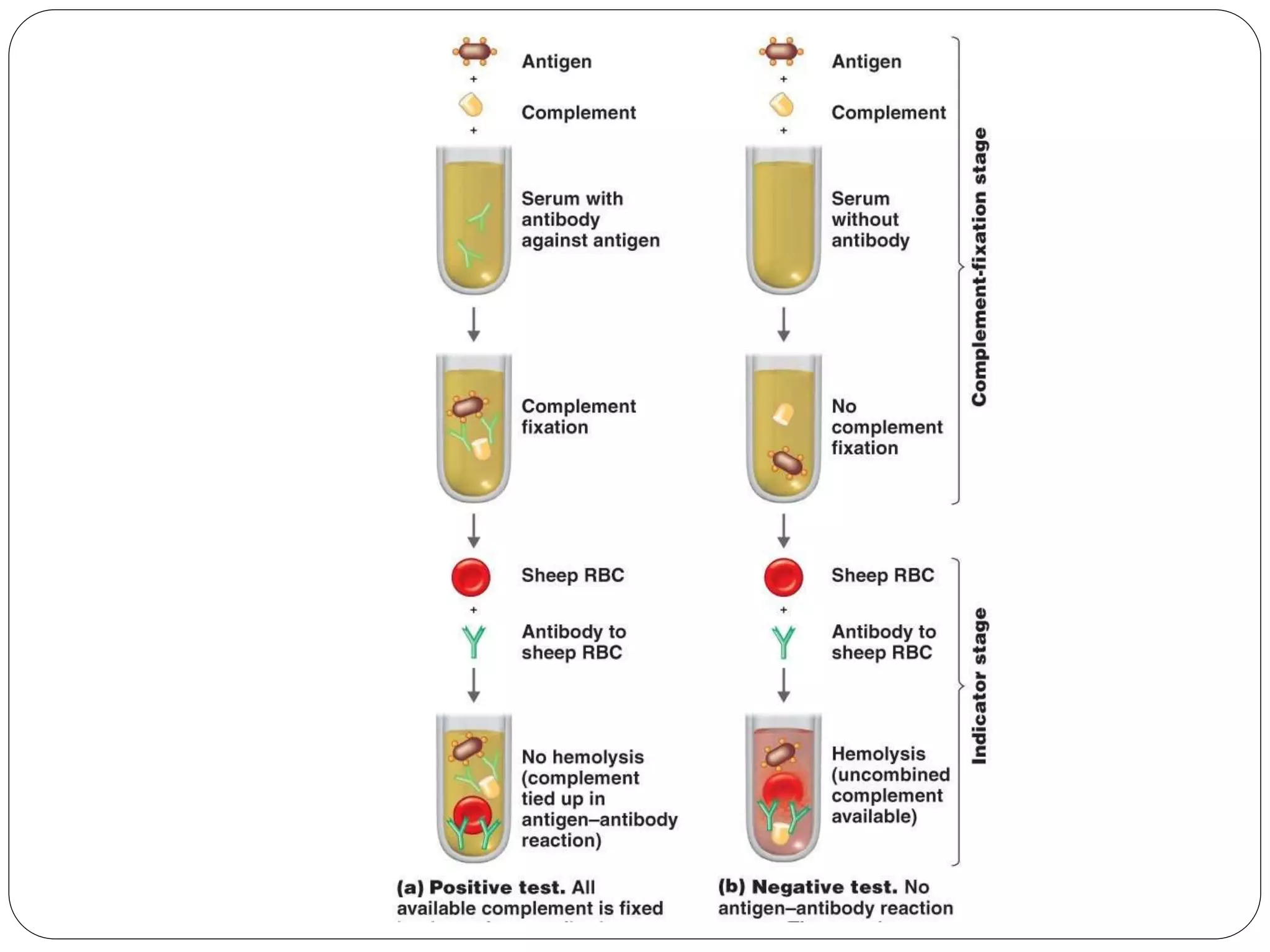
The complement fixation test is a traditional test used to detect the presence of specific antigens or antibodies. It involves incubating a patient's serum sample with a known antigen, then checking if any complement was activated and "fixed" or bound by the formation of antigen-antibody complexes. If complexes formed, the complement is fixed and will not react with indicator cells, showing a positive result. If no complexes formed, free complement will react with the indicators, showing a negative result. While economical for screening multiple infections, it is not very sensitive and can produce non-specific results.