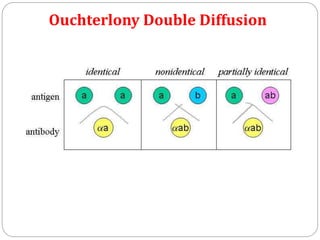
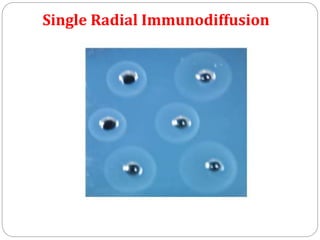
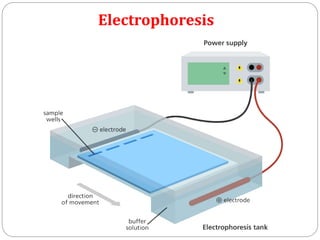
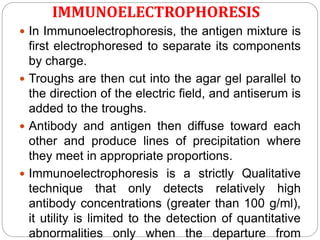
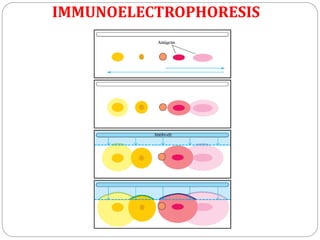
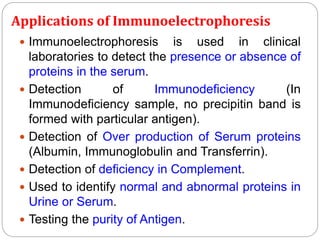
This document discusses various precipitation reactions and immunological techniques used to detect antigens and antibodies, including: Ouchterlony double immunodiffusion, single radial immunodiffusion, immunoelectrophoresis, and rocket electrophoresis. It explains that precipitation reactions involve two soluble reactants forming an insoluble precipitate. These techniques use diffusion and electrophoresis of antigens and antibodies in semi-solid media like agar to form visible precipitin lines, rings, or rockets, allowing detection and sometimes quantification of proteins. The techniques have various applications in medicine and clinical laboratories.