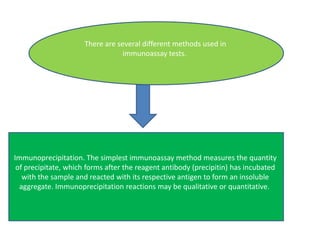
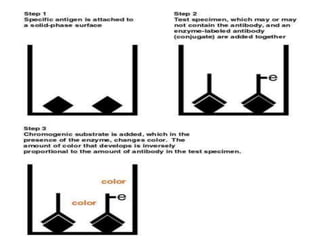
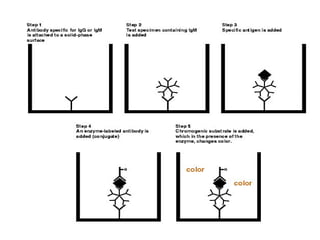
This document discusses various serological and immune assay techniques. It begins by defining serological assays and immune assays. It then describes different types of serological reactions including agglutination (direct, indirect, conglutination, latex agglutination) and precipitation (ring precipitation test, slide precipitation, gel diffusion precipitation, immunoelectrophoresis, countercurrent immunoelectrophoresis). The document also discusses immune assays including principles, qualitative vs quantitative assays, and different methods like immunoprecipitation, particle immunoassays, immunonephelometry, radioimmunoassay, enzyme immunoassay, fluorescent immunoassay, and chemiluminescent immunoassay. It provides examples of using these techniques to detect antigens and antibodies.