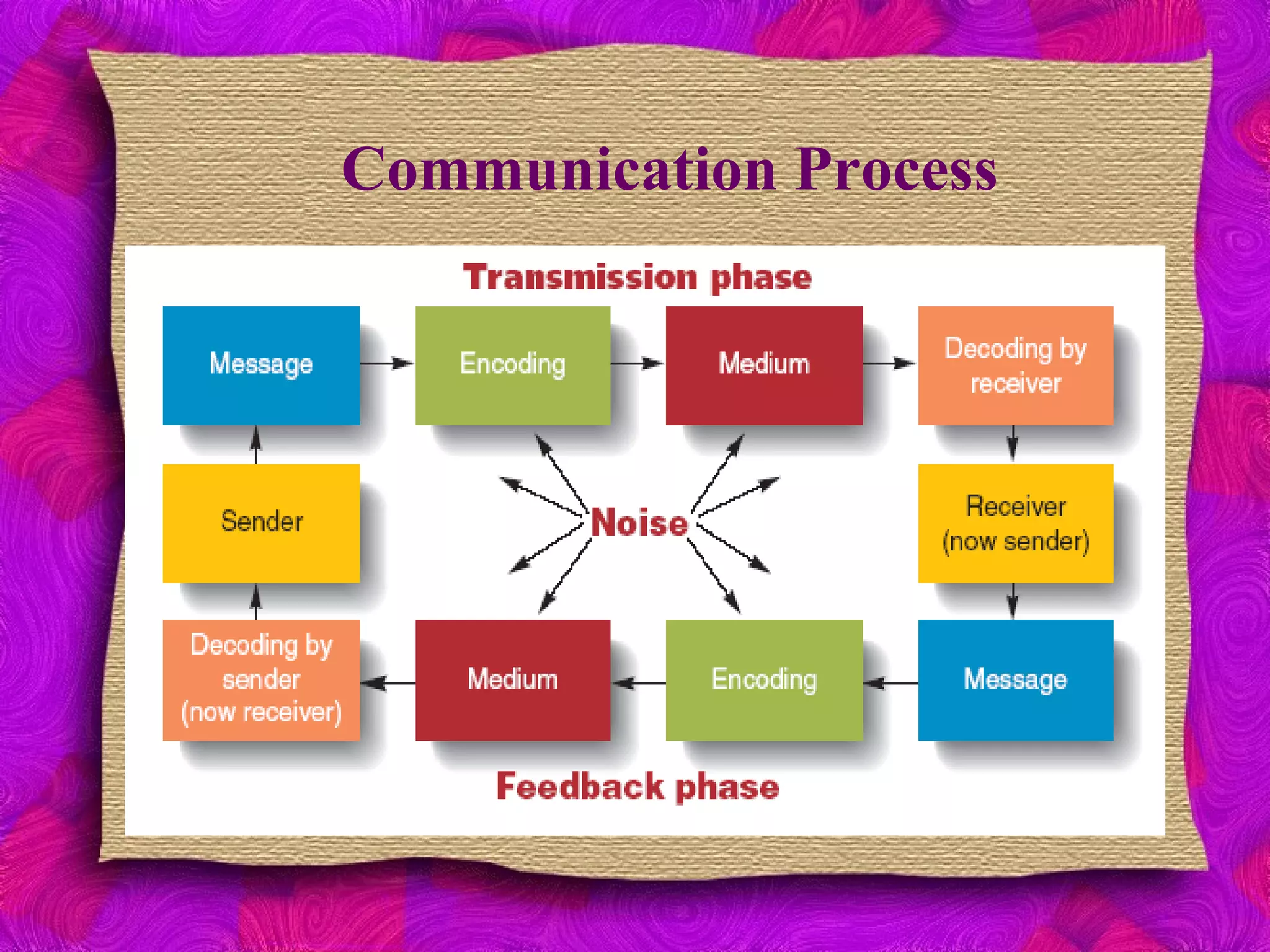
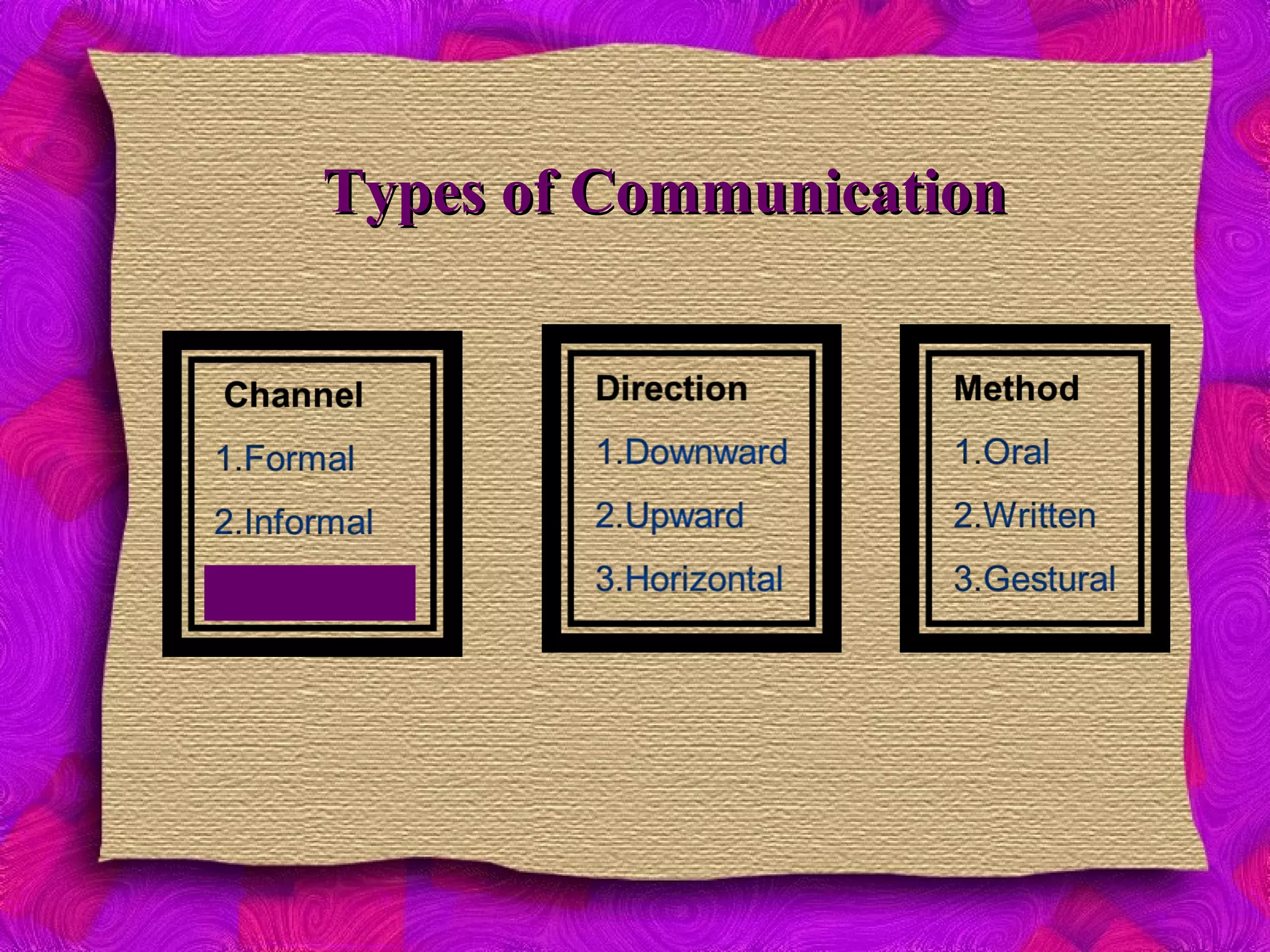
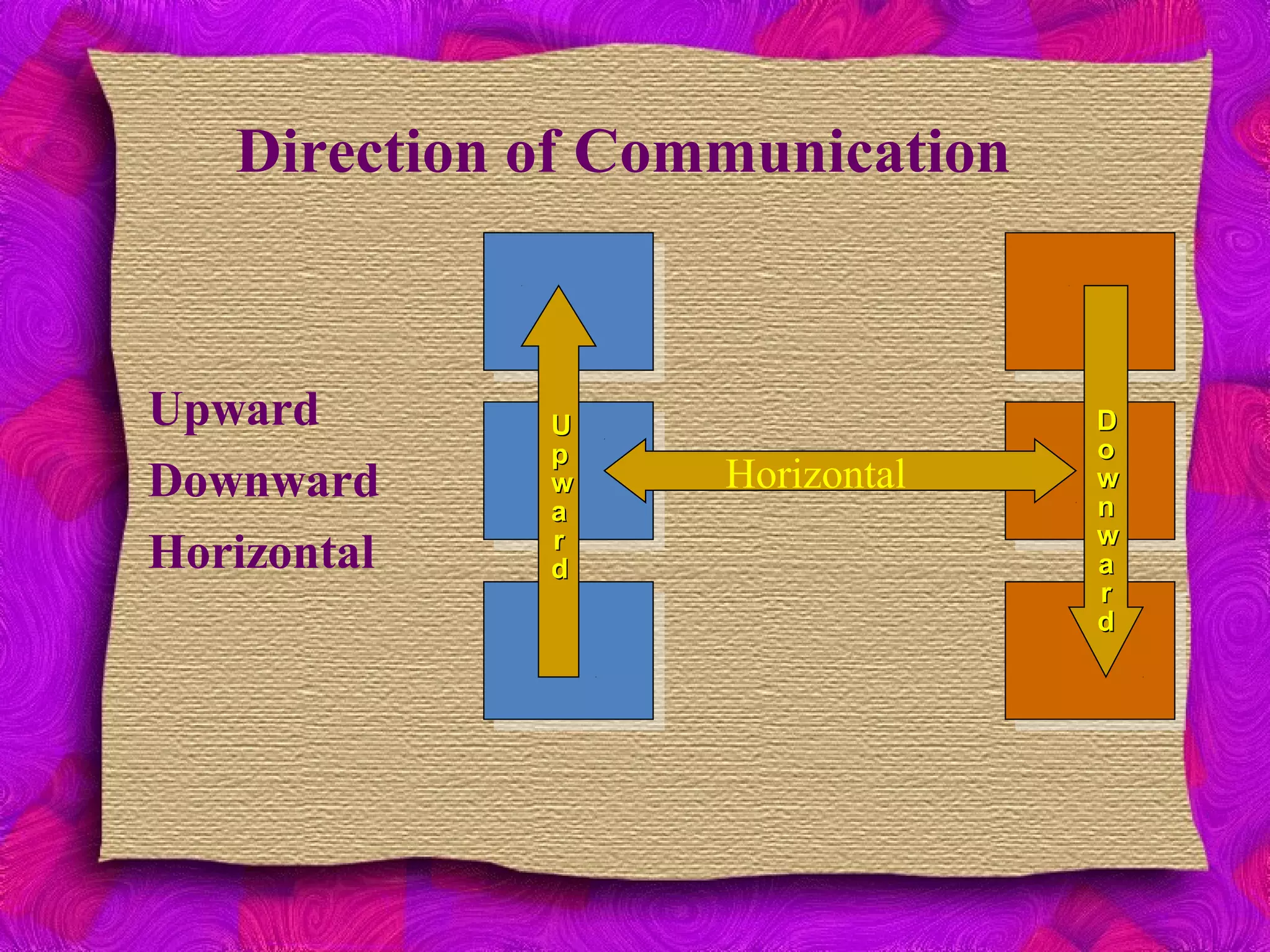
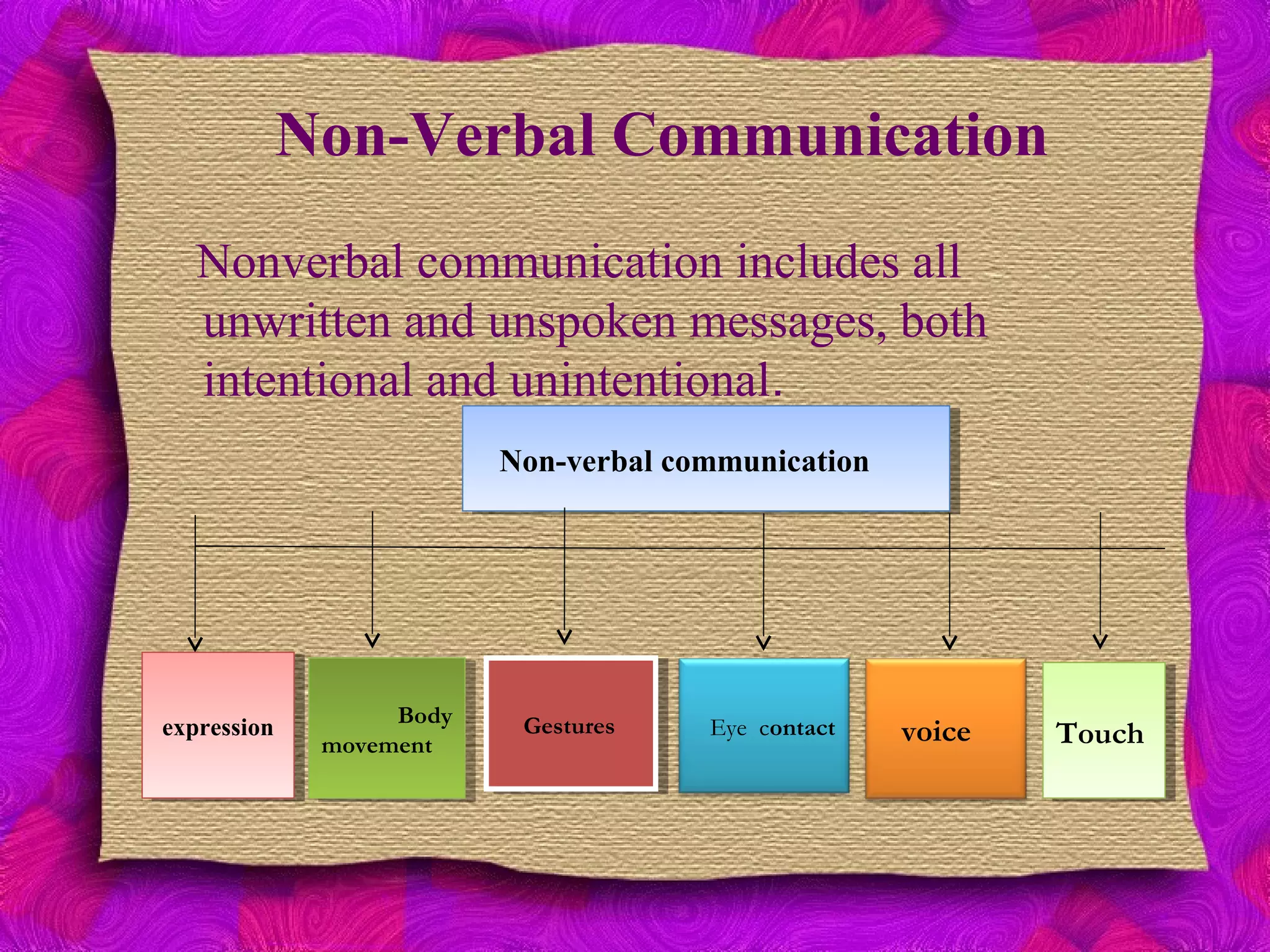
The document discusses various aspects of communication, including its definition, functions, types, and barriers. It outlines the communication process, emphasizing the roles of the communicator, message, encoding, medium, decoding, feedback, and noise. The content also highlights different communication methods and identifies barriers such as language, physical location, and cultural differences that can hinder effective communication.