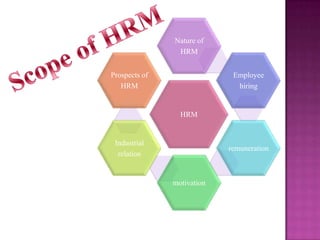
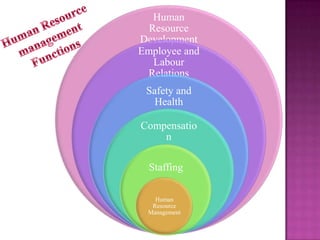
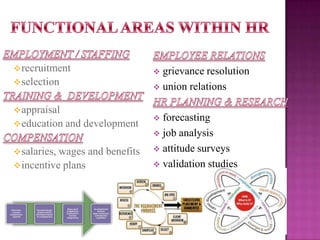
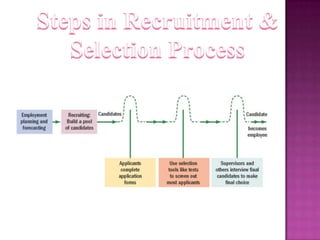
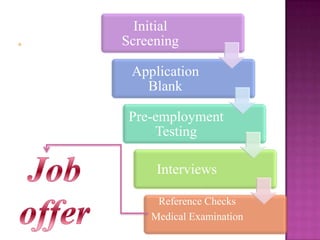
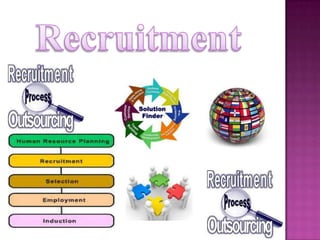
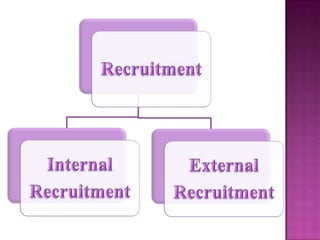
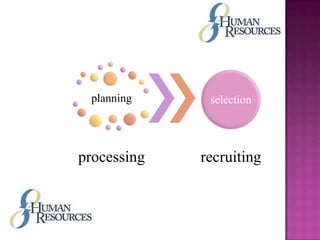
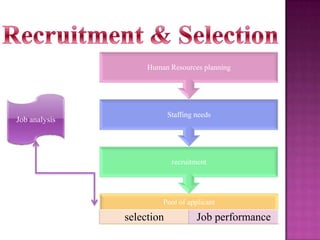
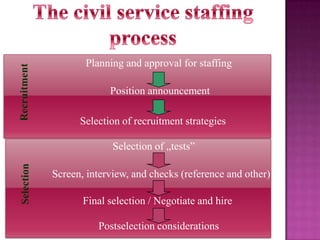
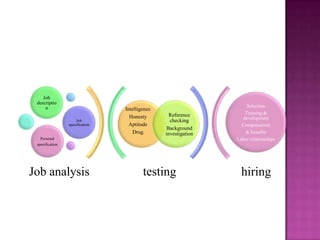
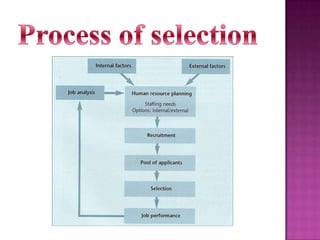
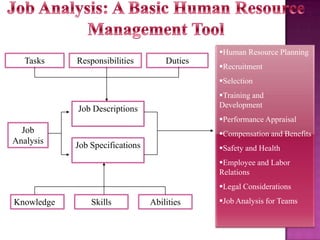
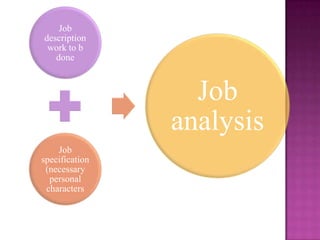
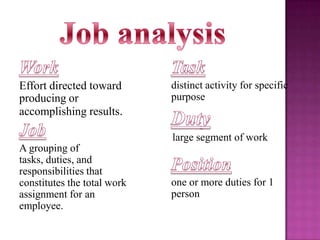
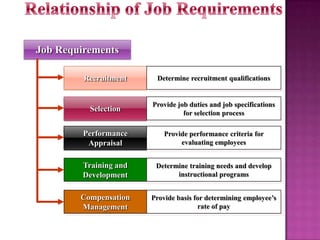
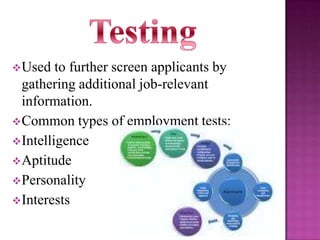
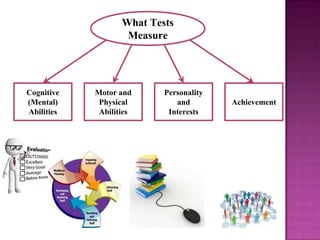
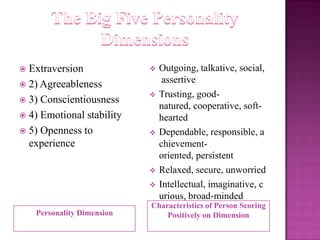
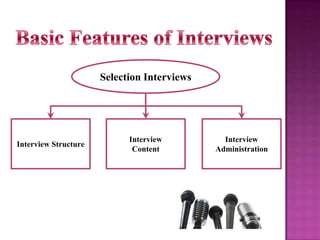
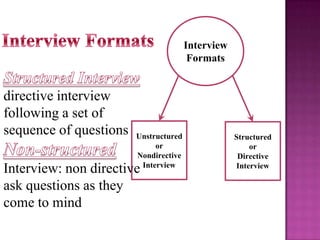
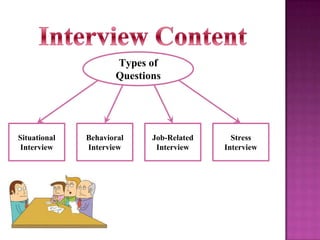
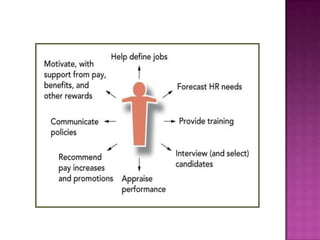
The document outlines the definition, functions, and scope of Human Resource Management (HRM), emphasizing its critical role in planning, organizing, staffing, leading, and controlling within organizations. It covers key aspects like recruitment, employee development, compensation, and the significance of managing human capital for organizational success. Additionally, it highlights the connection between employee productivity, motivation, and economic growth, while discussing various HR practices and policies essential for effective personnel management.