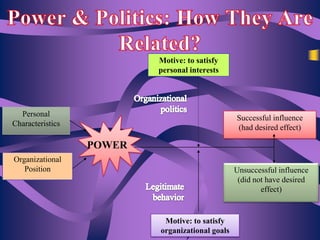
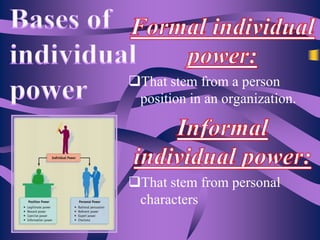
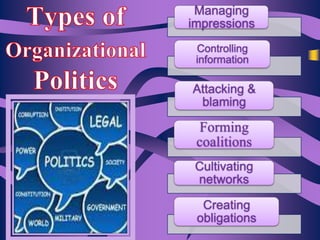
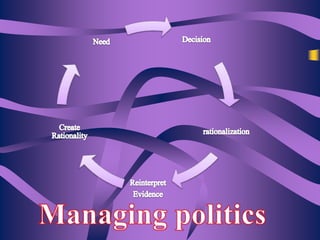
The document discusses the concept of power and influence in organizational behavior, defining how individuals can affect the actions and decisions of others through various means such as personal characteristics and positional authority. It outlines political behaviors that can be beneficial or detrimental to organizations and highlights methods for effectively influencing others while managing relationships. Key tactics include forming coalitions, managing impressions, and leveraging authority to achieve personal or organizational goals.