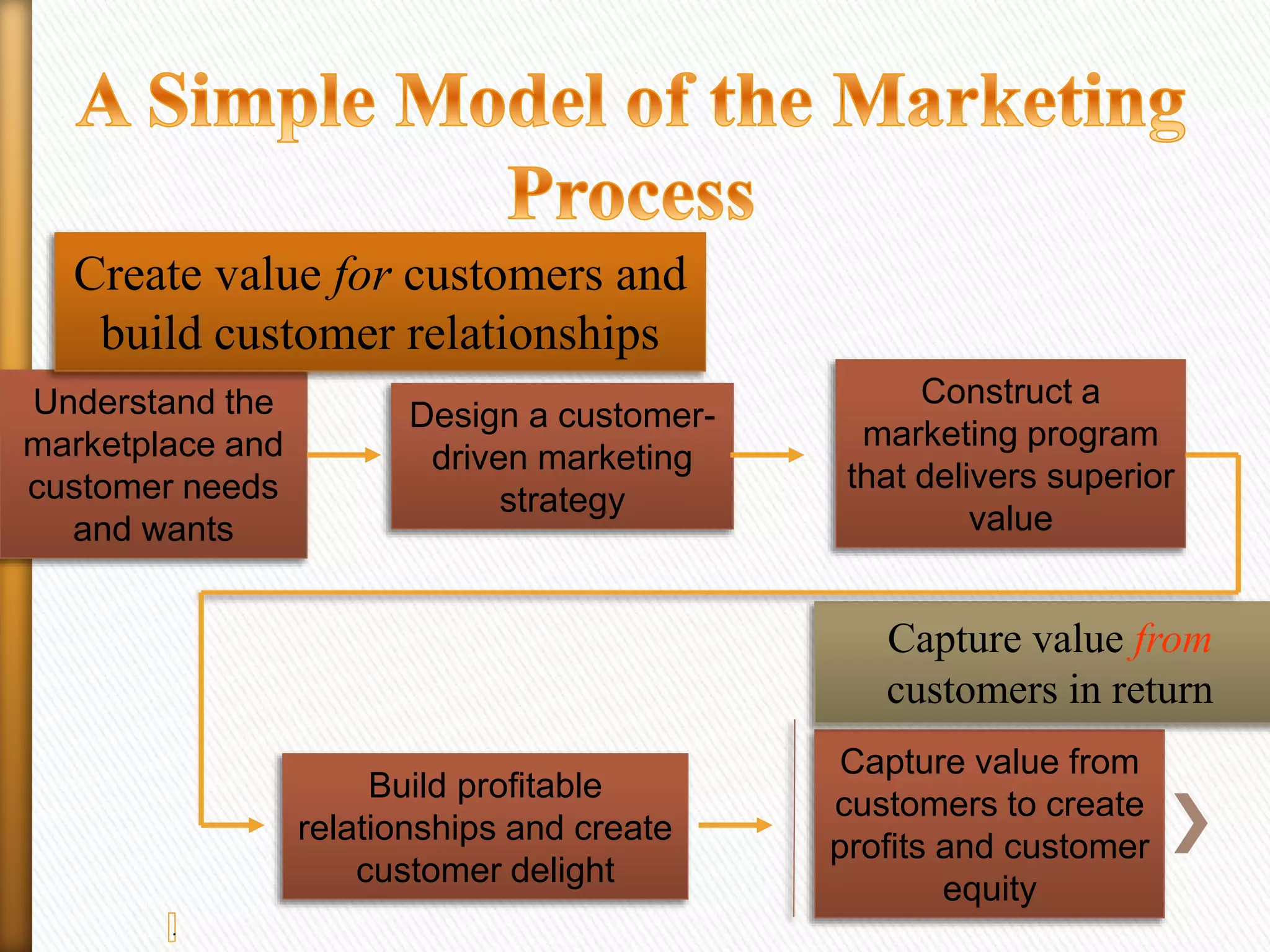
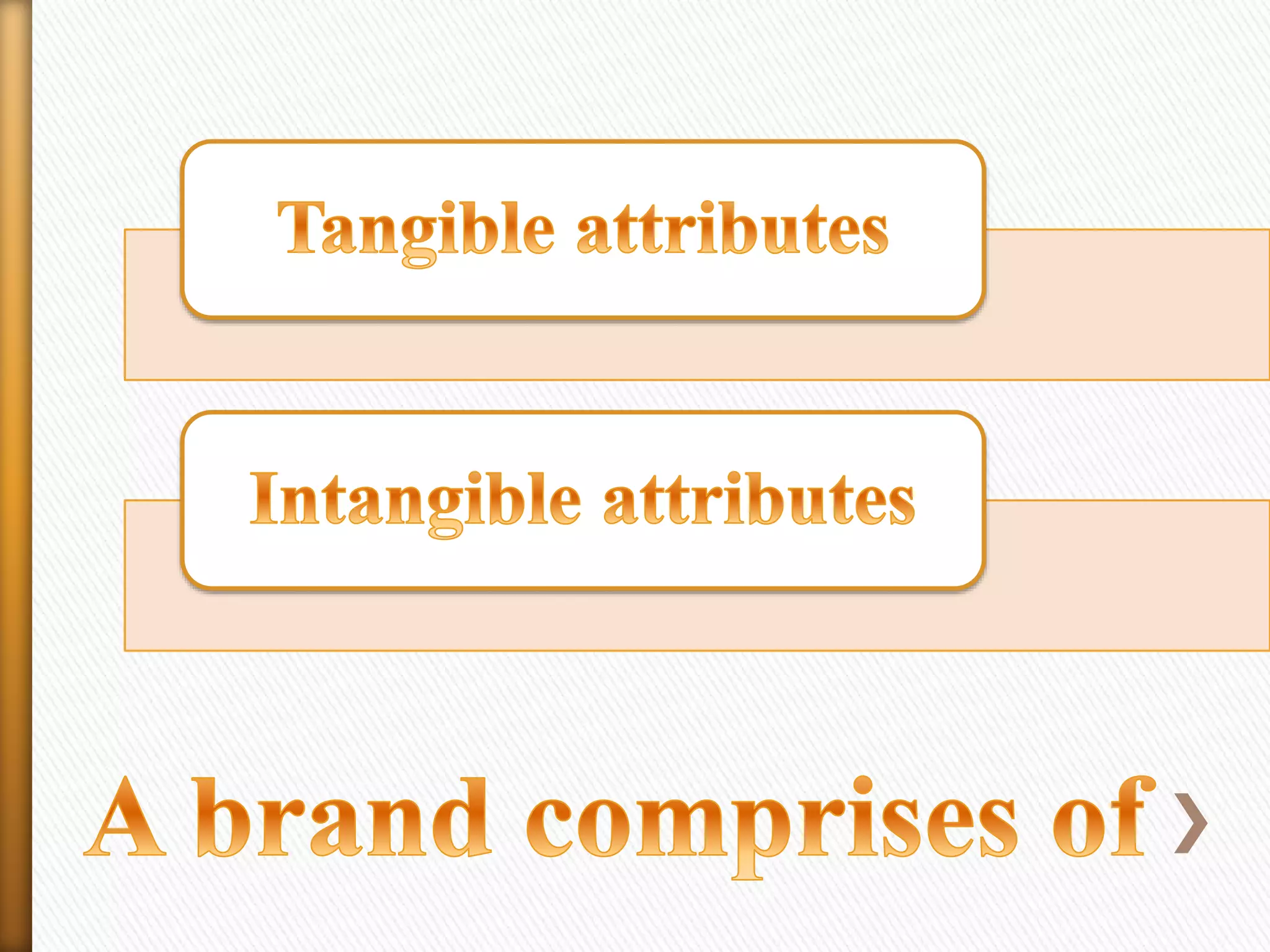
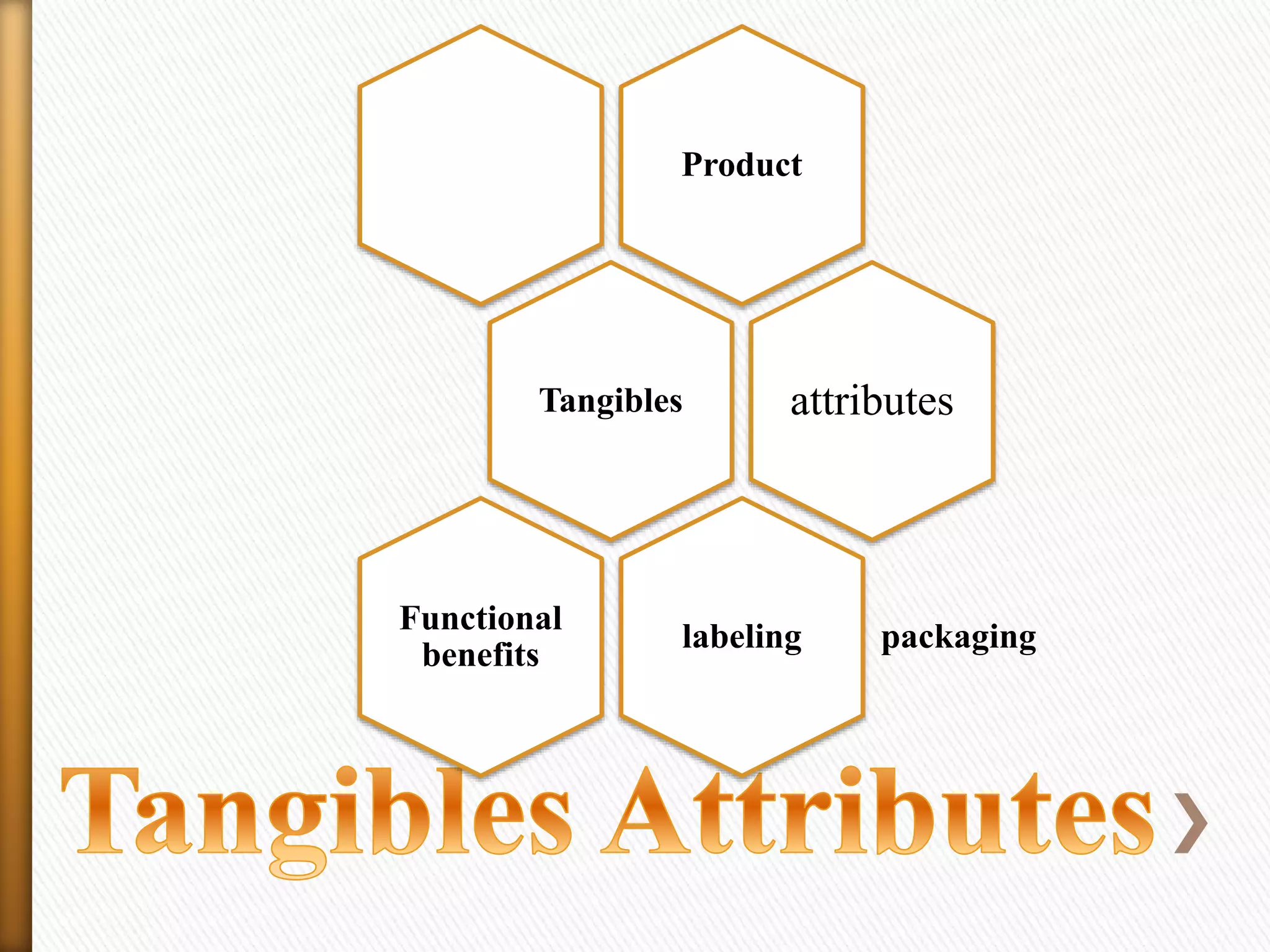
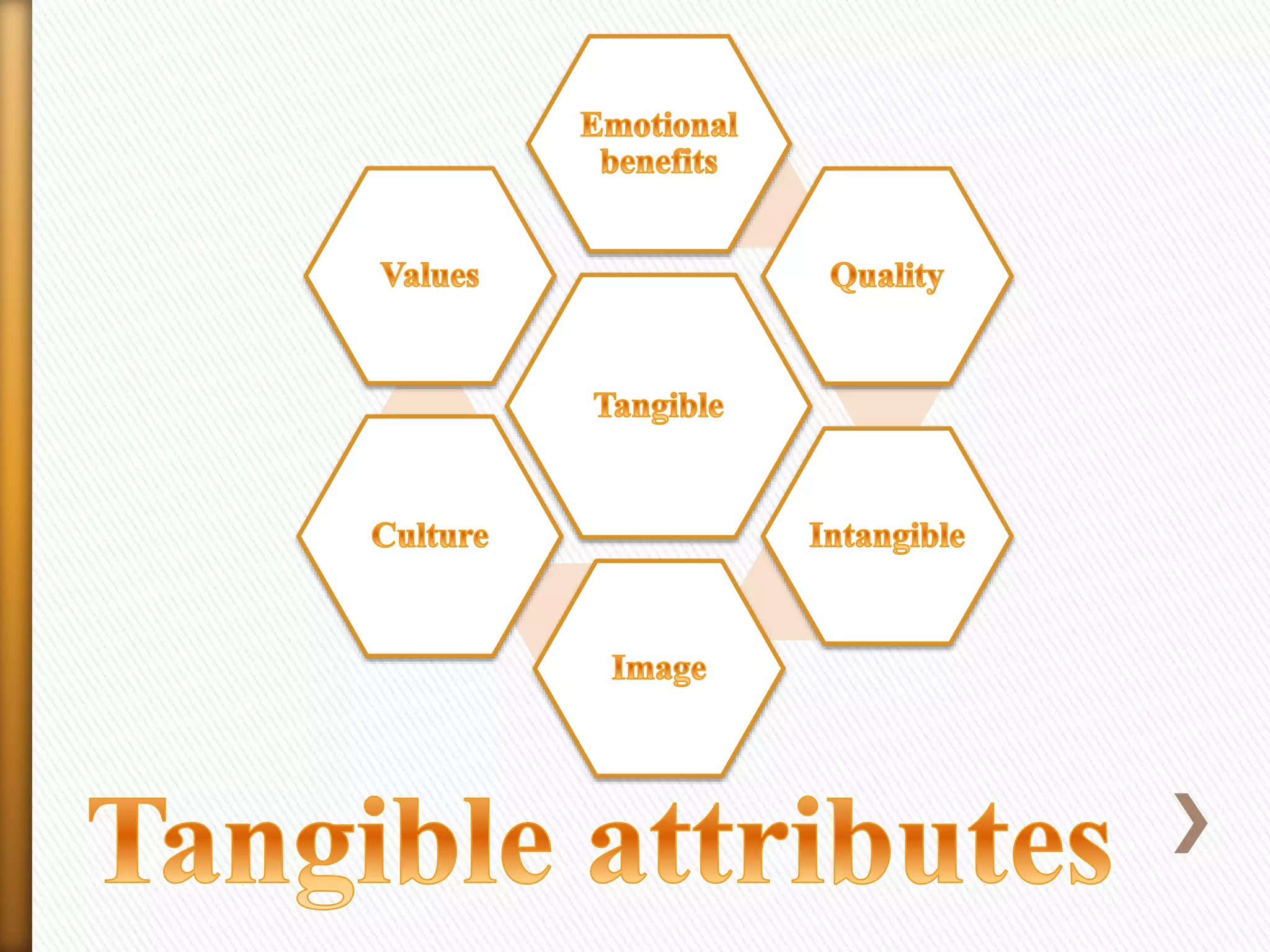
Branding is the process of creating a unique name and image for a product in the minds of consumers. It involves designing a recognizable name, logo, symbol, or design to identify and differentiate products from competitors. Marketing aims to understand customer needs and create value for customers through a strategy that builds relationships and delivers superior value.