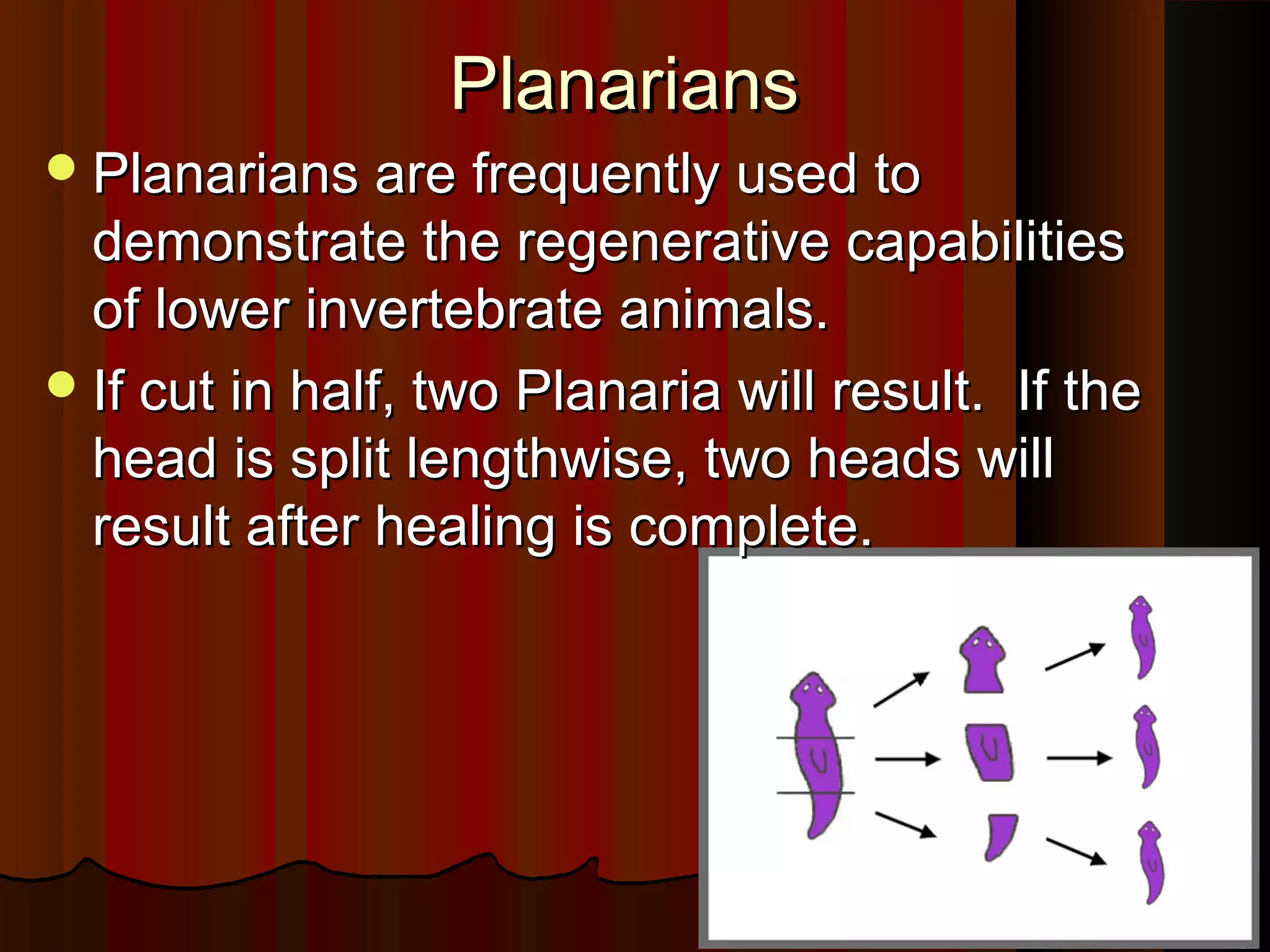
- Class Turbellaria contains free-living flatworms that can be found in three habitats: freshwater like planaria, marine like sea slugs, and terrestrial like ribbon worms.
- Planarians are commonly studied due to their remarkable regenerative abilities - they can regrow entire bodies from fragments.
- Planarians have eyespots, a ganglion brain, and bilateral symmetry, representing an early stage in the evolution of heads and body organization in animals.