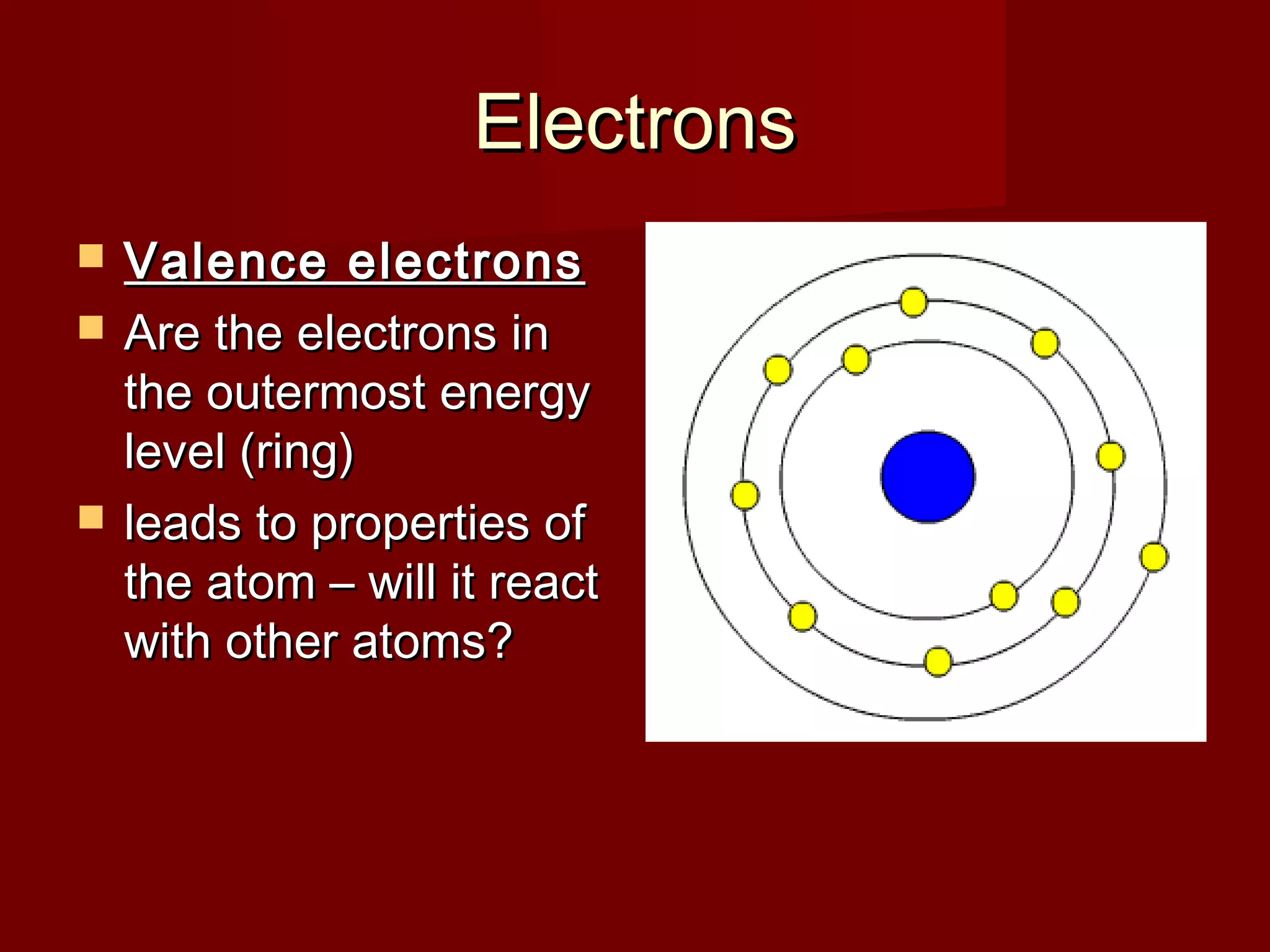
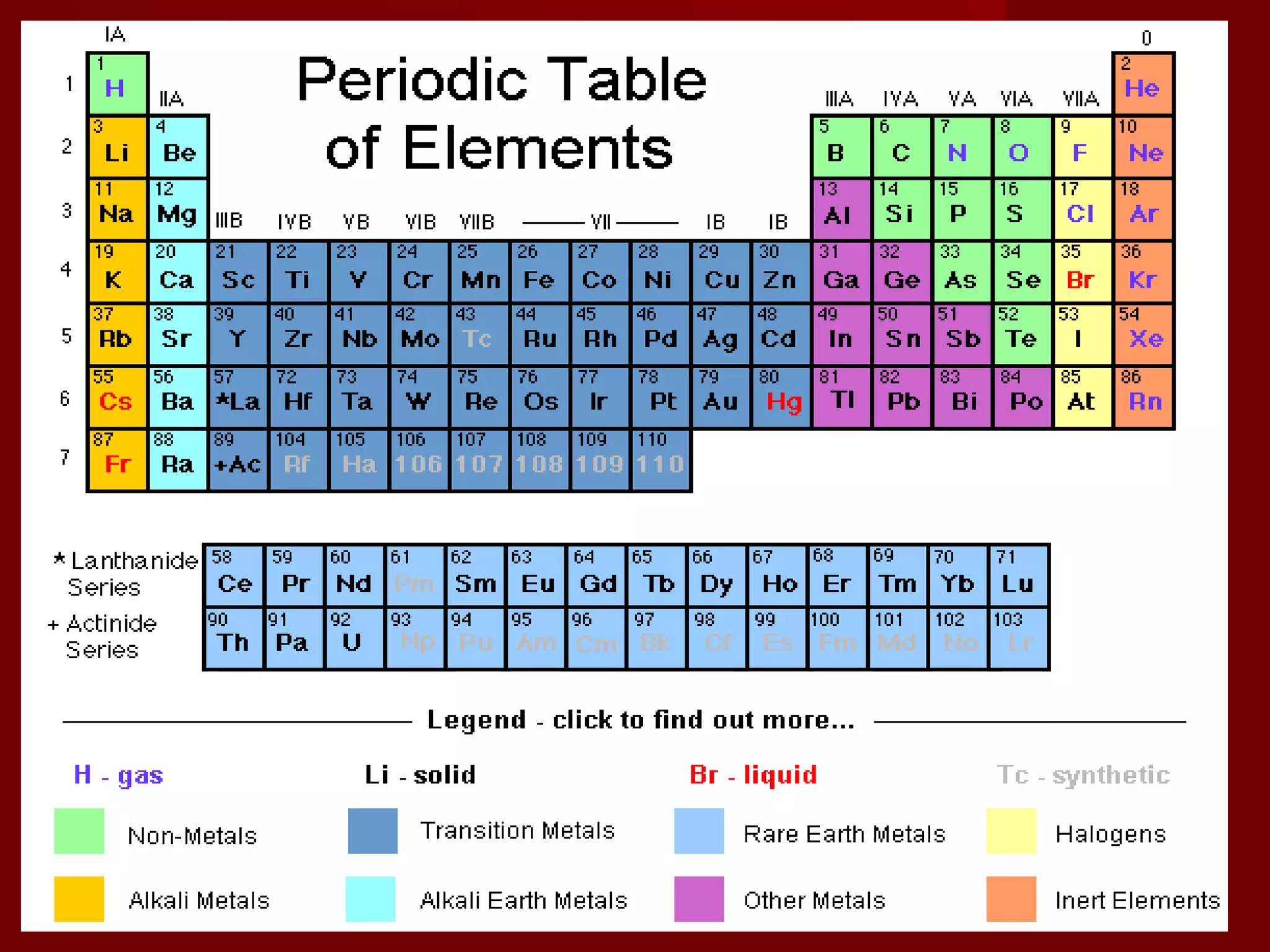
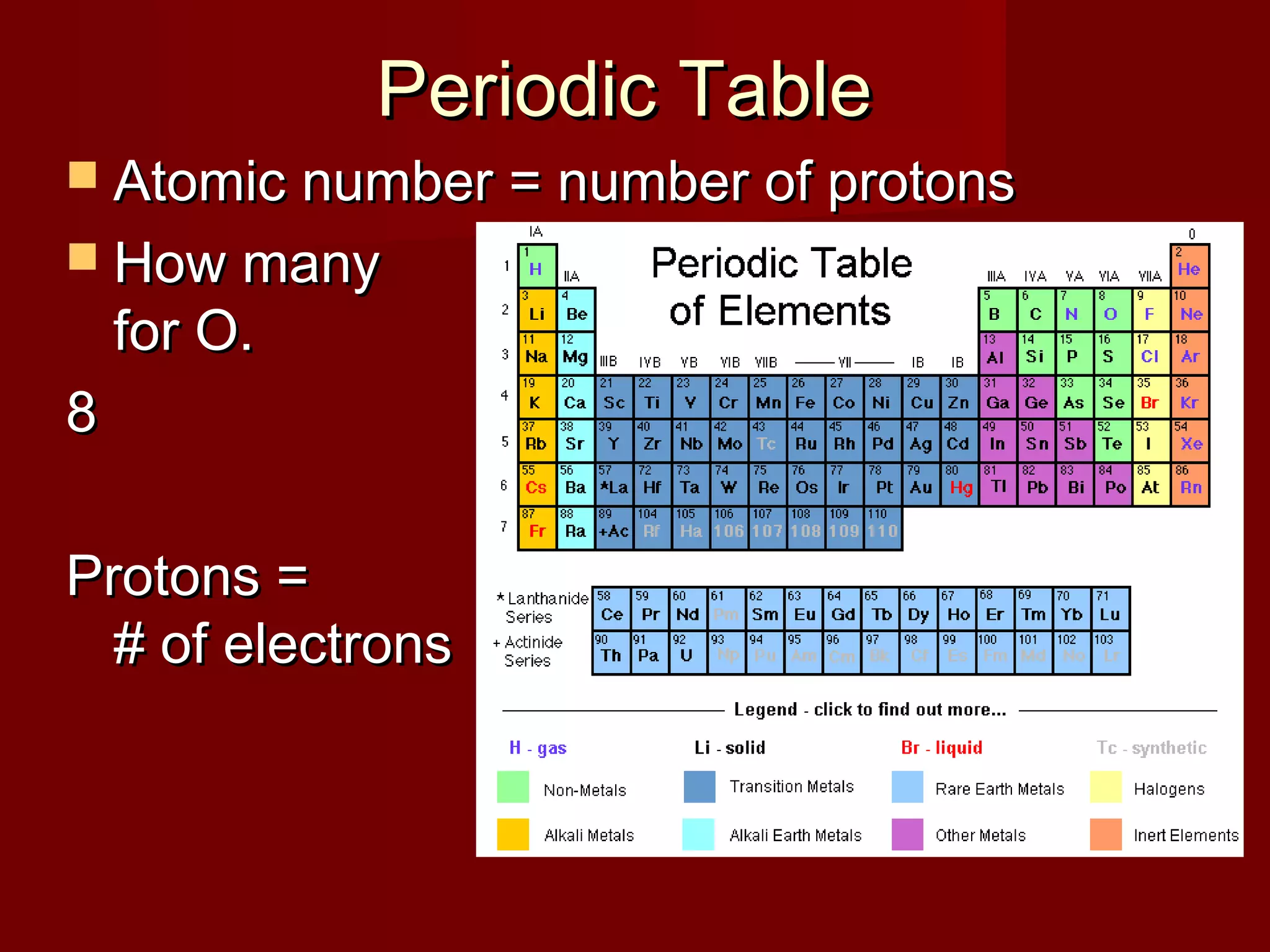
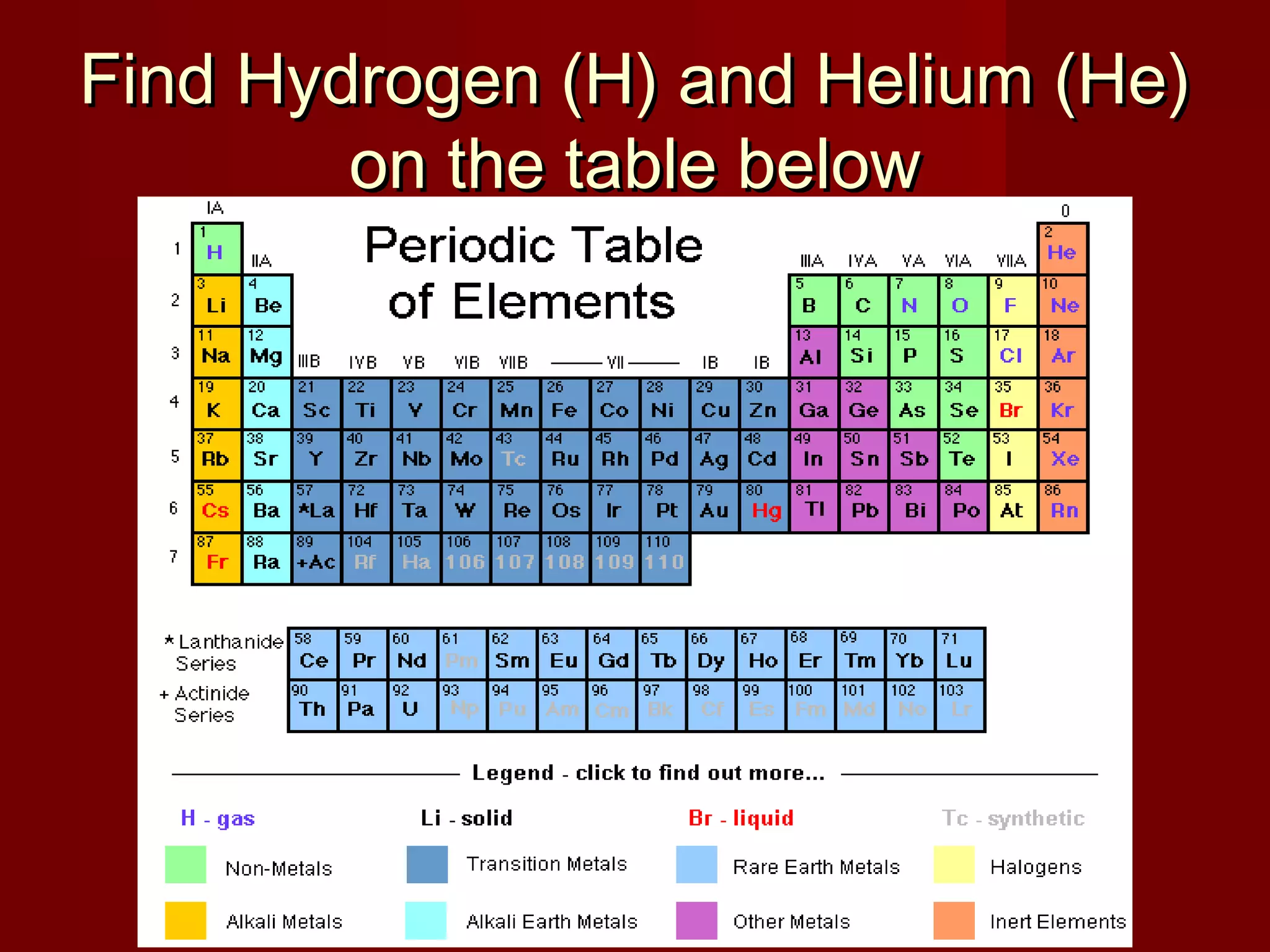
Chemistry is important in biology because the structure and function of living things are governed by chemical laws. All living things are composed of six main elements: carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, phosphorus, and sulfur. Atoms of these elements form bonds and combine to create molecules and compounds through chemical reactions. Carbon is unique in that it can form four bonds, allowing it to make complex molecules with different shapes that are essential for life.