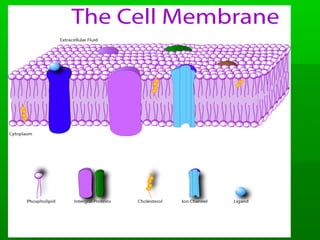
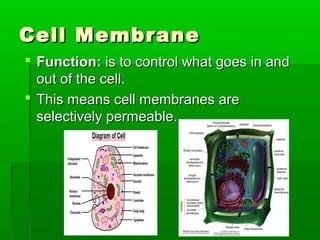
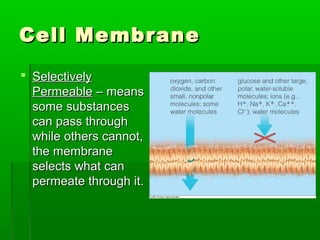
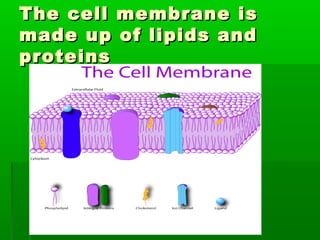
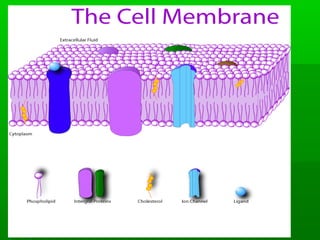
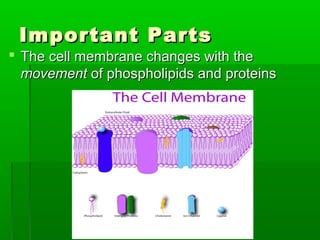
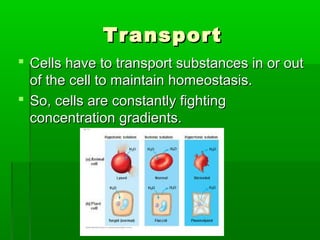
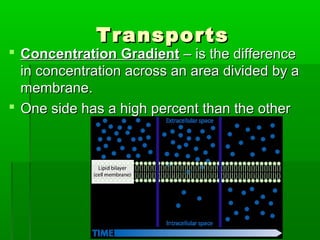
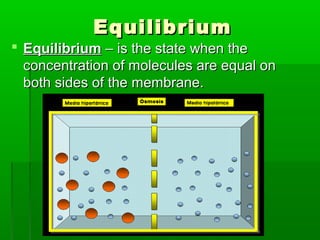
Cell membranes allow molecules to pass in and out of cells through passive or active transport in order to maintain homeostasis. Passive transport involves molecules moving down their concentration gradient through the cell membrane without requiring energy. Active transport moves molecules against their concentration gradient by using energy. This allows cells to regulate the movement of substances and control what passes through the selectively permeable cell membrane.