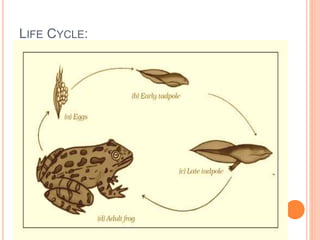
Amphibians evolved from fish during the Devonian period and diversified during the Carboniferous period. They undergo metamorphosis from an aquatic larval stage to a terrestrial adult stage. Amphibians have a three-chambered heart, lungs for respiration, and porous skin that also aids gas exchange. They reproduce through external fertilization, with the eggs developing into larvae that breathe through gills before transforming into air-breathing adults. The major orders of amphibians are salamanders, frogs and toads, and caecilians.