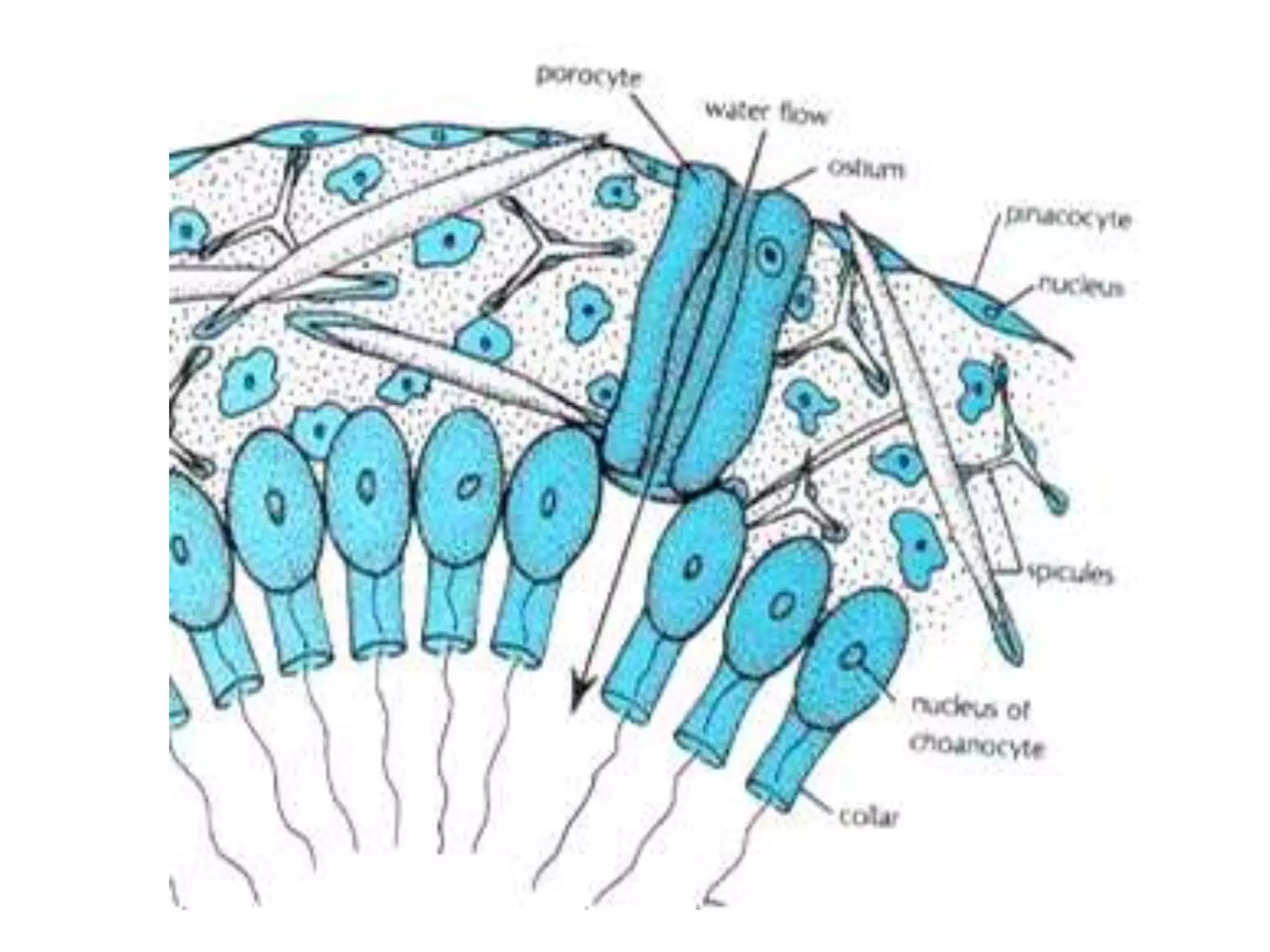
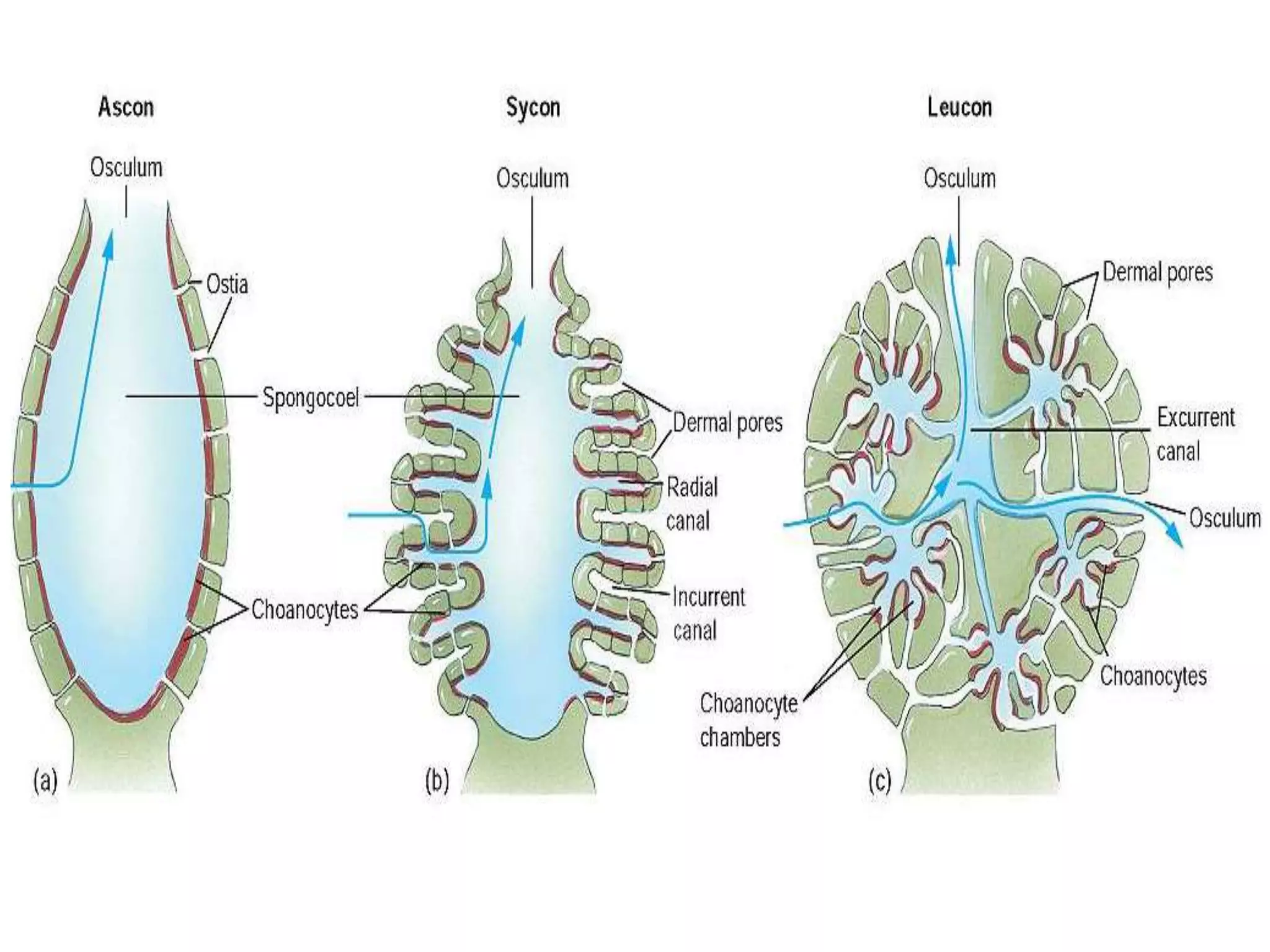
Sponges are multi-cellular aquatic animals that live fixed to the sea floor and filter feed. They come in about 9,000 species divided into three main classes based on their skeleton composition. Sponges lack true tissues and organs. They are composed of three main cell types - pinacocytes, choanocytes, and mesenchyme cells. Choanocytes generate water currents that both capture food and circulate water through the sponge. Sponges reproduce sexually through internal fertilization and larval development or asexually by fragmentation.