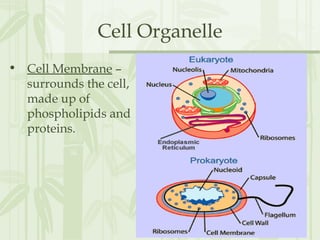
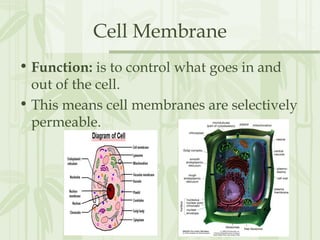
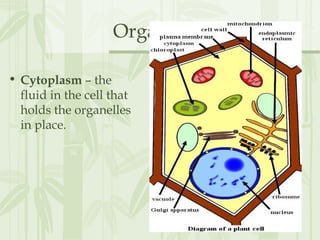
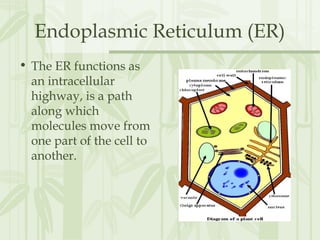
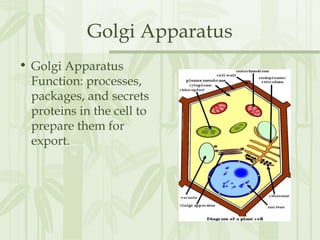
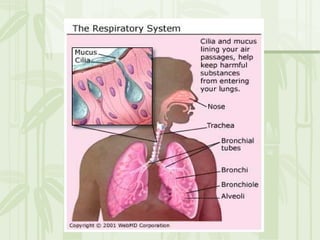
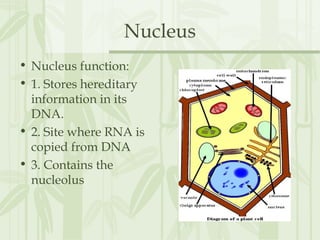
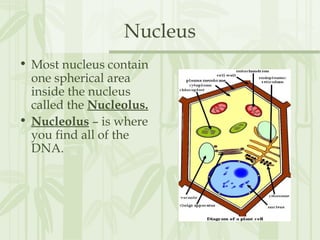
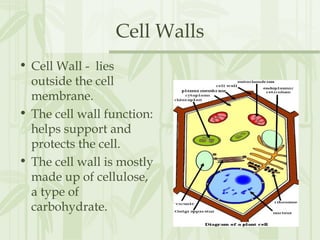
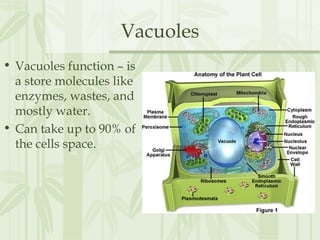
This document provides information on the structures and functions of various cell organelles. It begins by stating that the following slides will review the names and functions of important cell organelles. It then discusses the cell membrane, cytoplasm, mitochondria, ribosomes, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, lysosomes, cilia, flagella, nucleus, and three additional organelles found in plant cells: cell walls, vacuoles, and plastids such as chloroplasts. For each organelle, it provides a brief definition of its name and role within the cell.