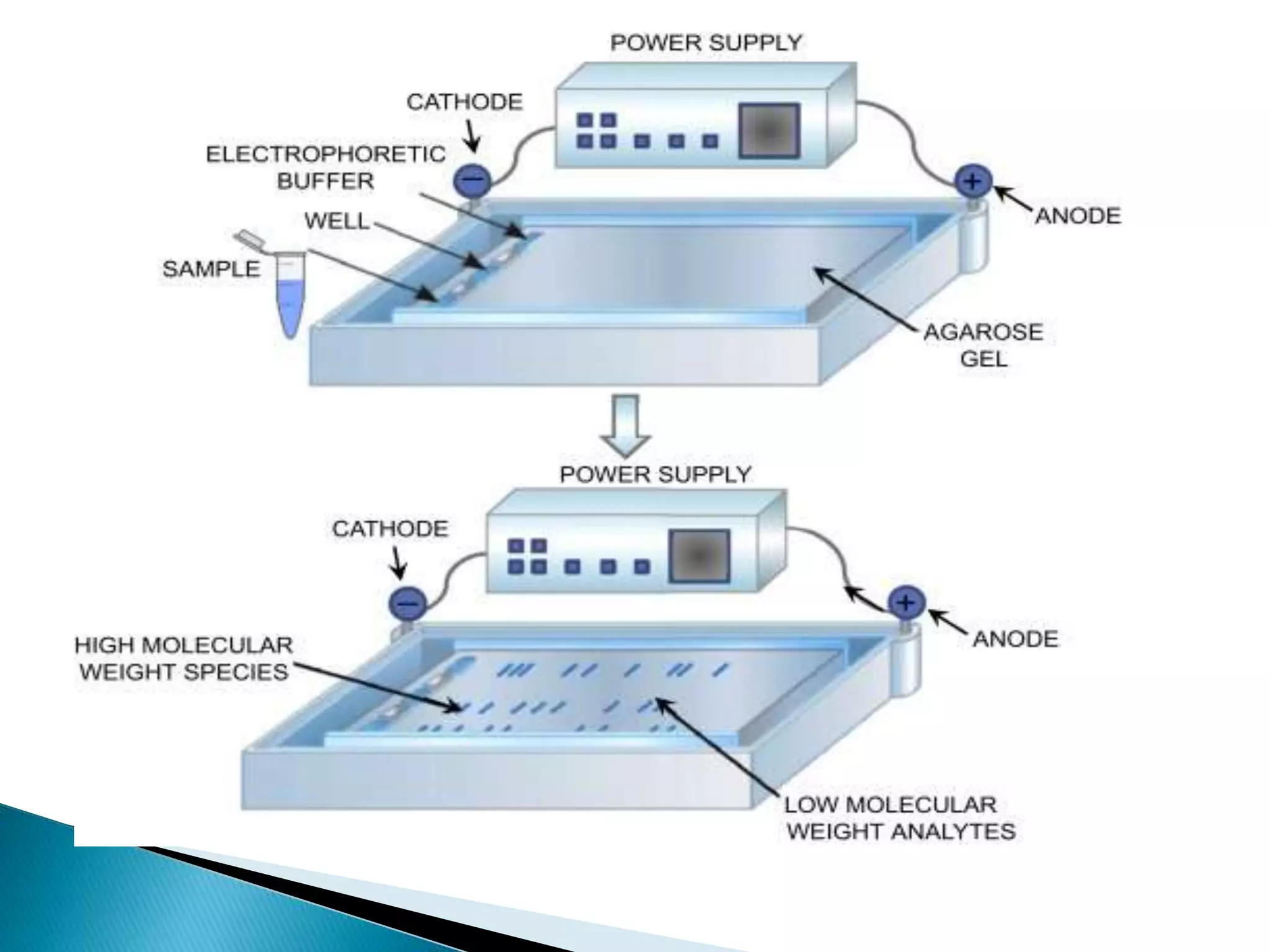
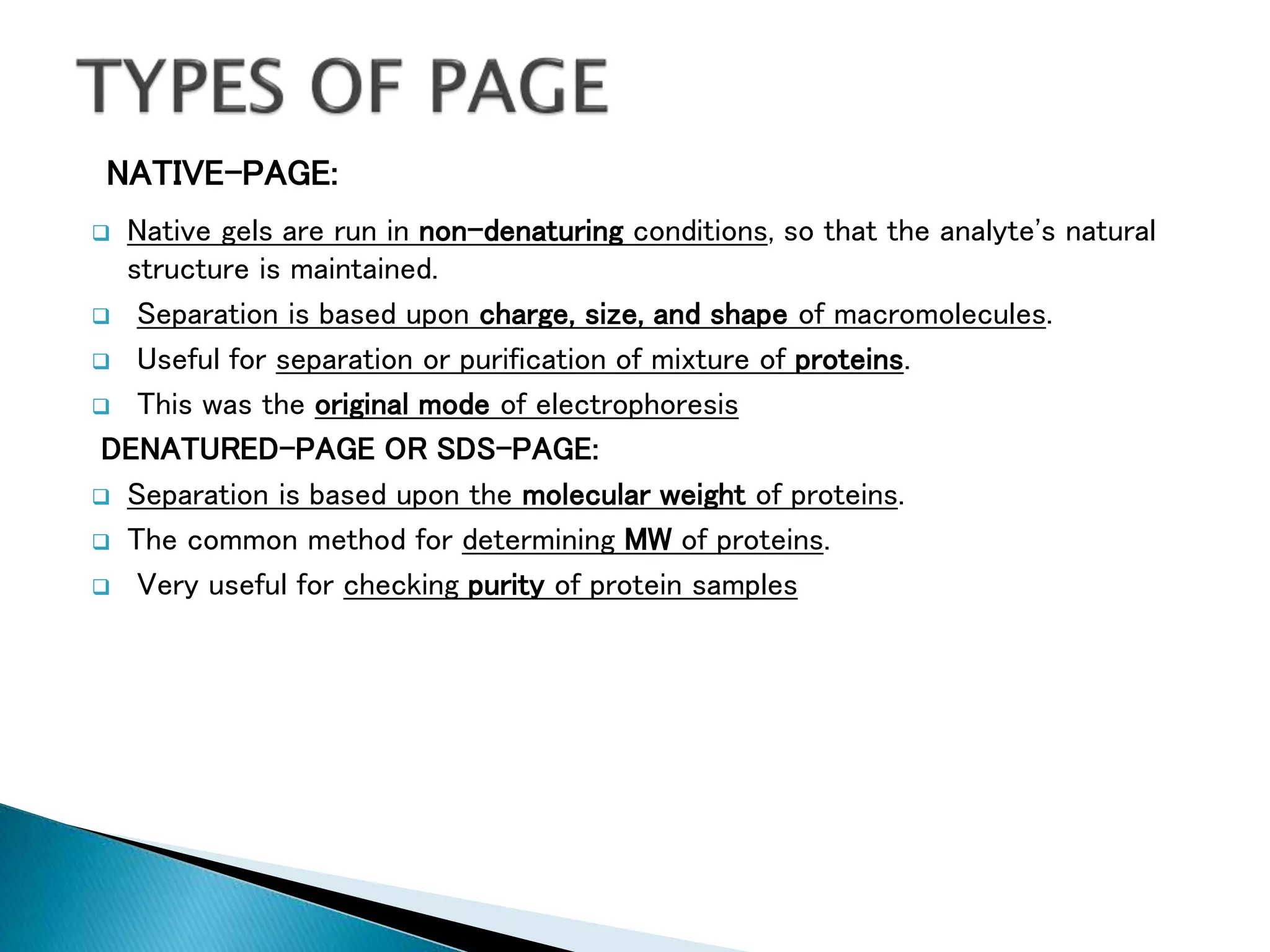
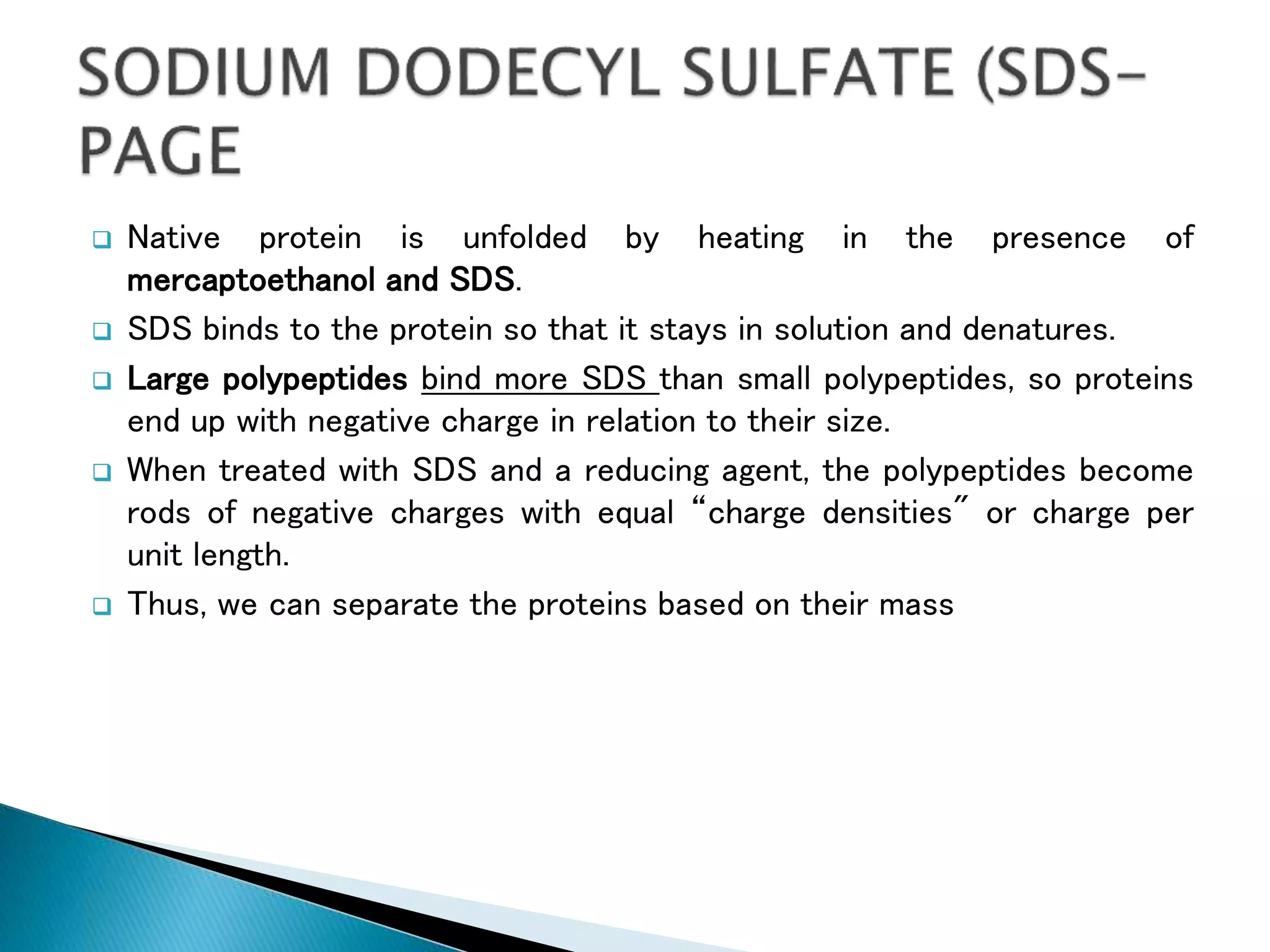
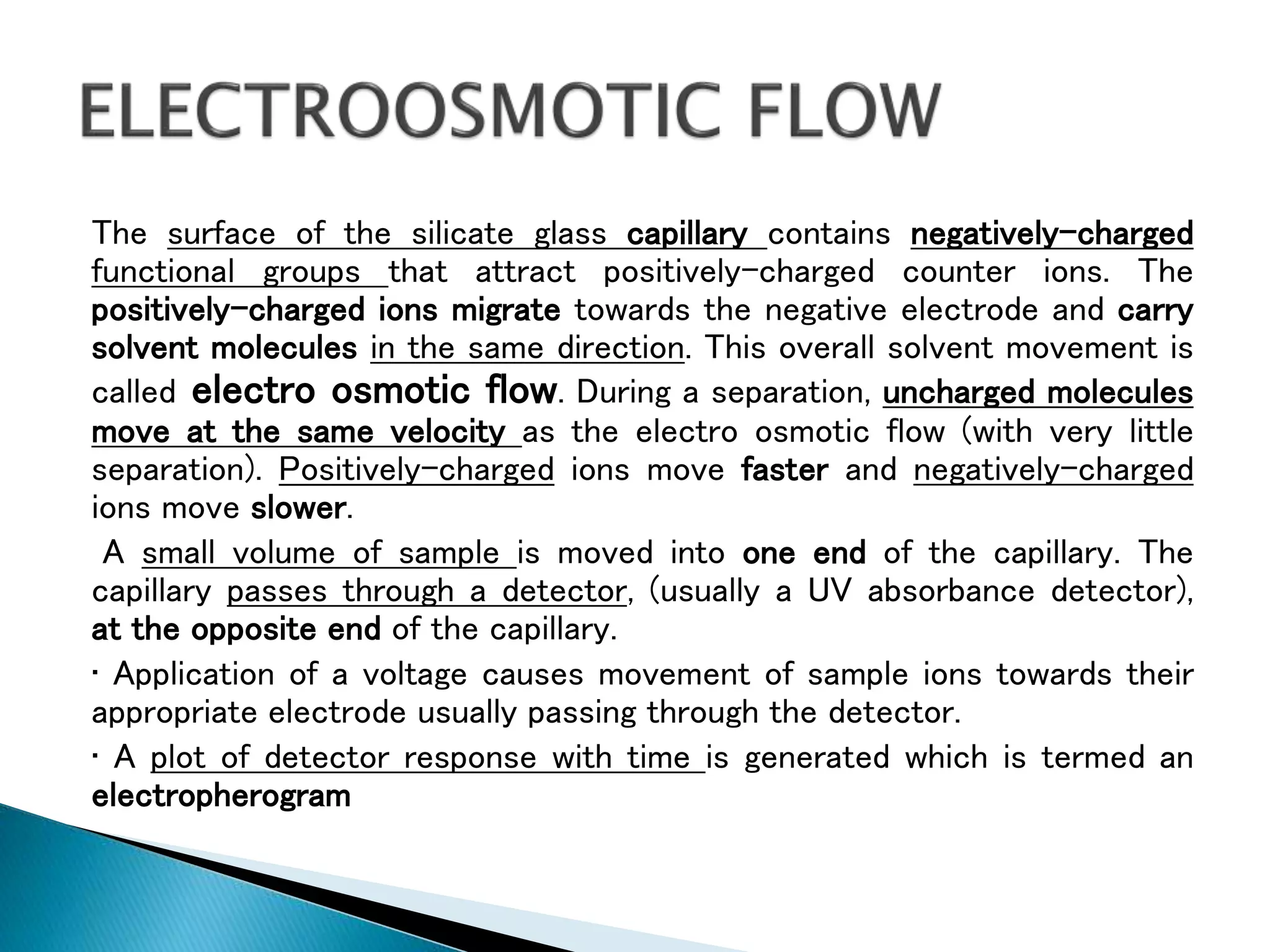
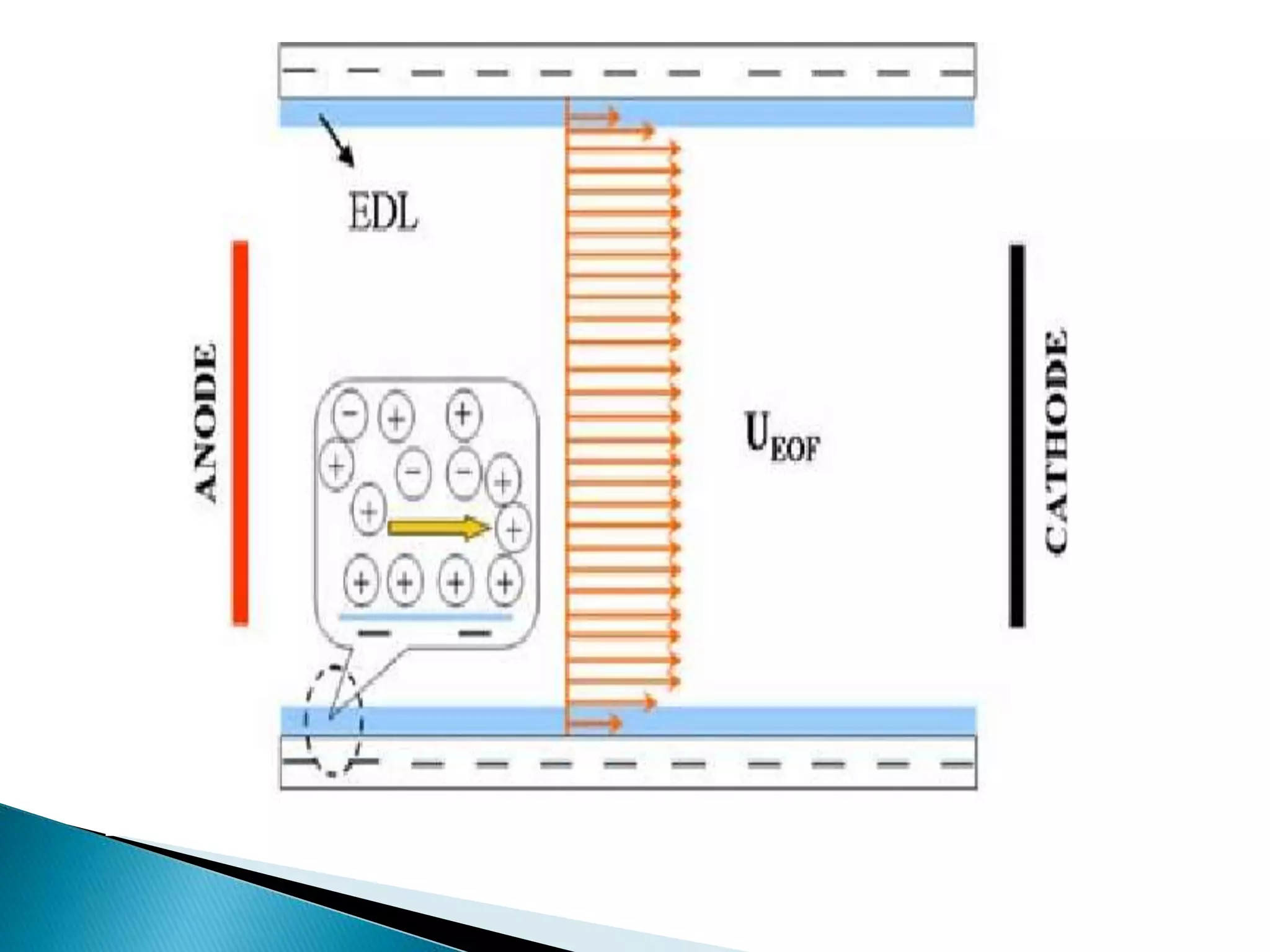
Electrophoresis is a technique used to separate charged particles such as proteins or nucleic acids. It involves applying an electric field to migrate these particles through a buffer or gel based on their size and charge. There are several types of electrophoresis including paper, gel, capillary, and moving boundary which utilize different supporting media and techniques to achieve high resolution separations. Electrophoresis is widely used in biochemistry and molecular biology for analytical purposes.