Here are the key principles of the different chromatography techniques covered in the document:
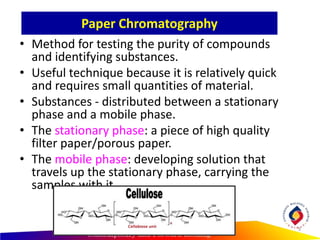
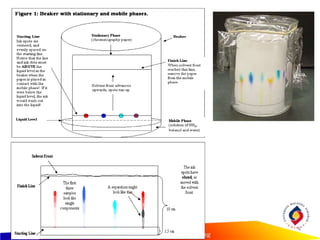
- Paper chromatography relies on the differential migration rates of compounds through a stationary phase (filter paper) based on their varying interactions with the mobile phase solvent. Components separate based on differences in solubility and affinity for the mobile vs. stationary phases.
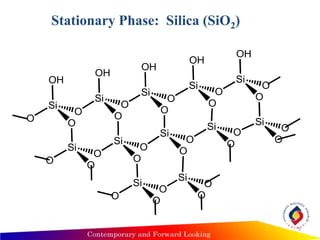
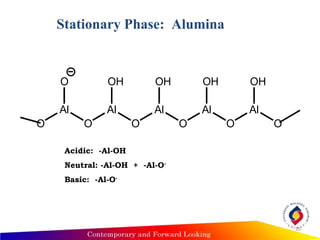
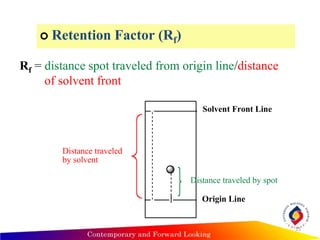
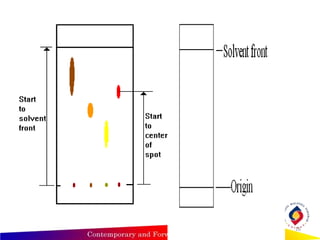
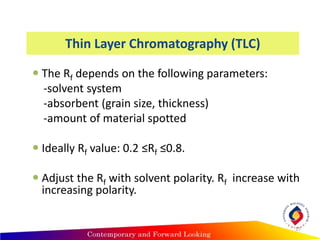
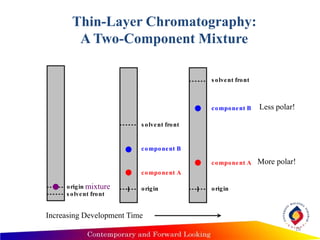
- Thin layer chromatography uses a thin stationary phase coating (e.g. silica gel) on a plate. Components separate based on differences in their partitioning behavior between the mobile liquid phase and stationary solid phase during capillary movement.
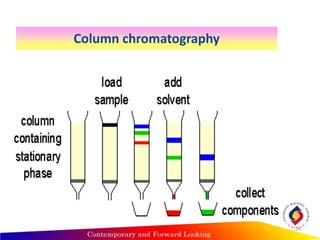
- Column chromatography uses a packed stationary phase within a column. Components separate based on differences in their distribution between the stationary phase adsorbent and percolating mobile phase