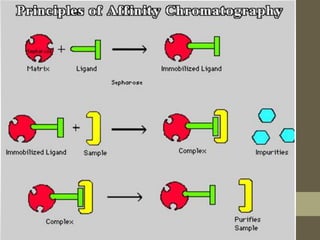
Affinity chromatography is a method used to purify biomolecules like proteins and nucleic acids based on specific interactions between the biomolecule and a ligand immobilized on a solid support. When a mixture is passed through the column, the target biomolecule will bind to the ligand while other molecules pass through. The bound biomolecule can then be separated by changing conditions like pH or introducing a competing molecule to displace it. Affinity chromatography offers highly specific purification of target molecules in a single step.