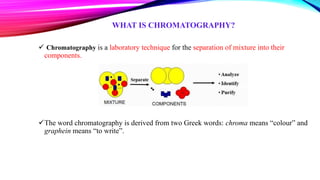
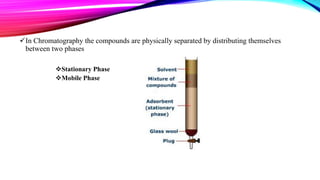
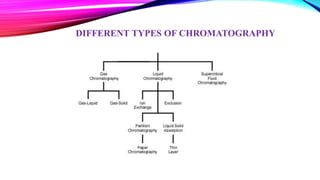
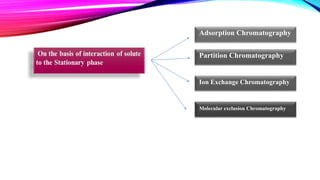
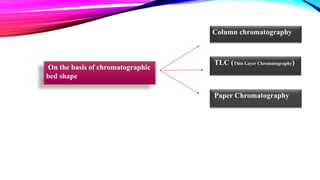
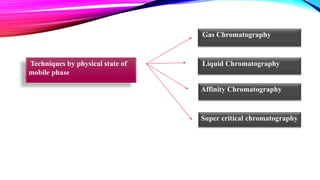
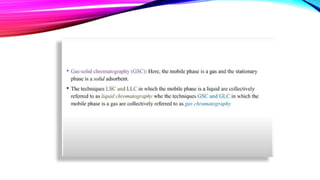
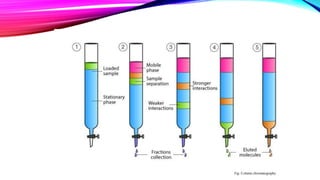
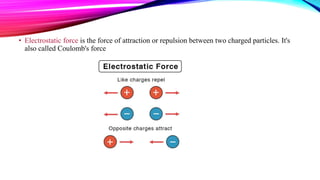
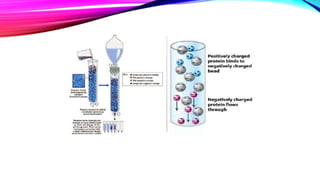
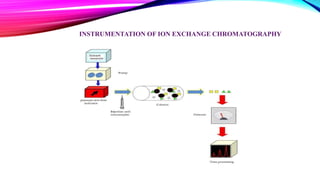
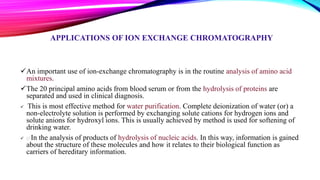
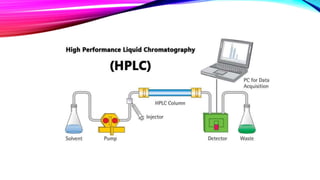
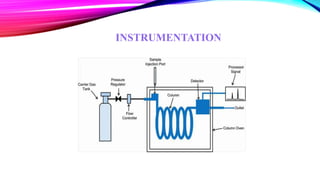
Chromatography is a laboratory technique used to separate mixtures into individual components. It works by distributing the components between two phases, usually a stationary phase and a mobile phase. There are several types of chromatography defined by the stationary and mobile phases used, including gas chromatography which uses an inert gas as the mobile phase, and high performance liquid chromatography which uses high pressure to force a liquid mobile phase through a column. Chromatography has many applications in fields like chemistry and biochemistry for analyzing and purifying compounds.