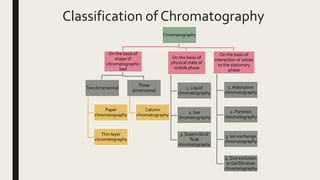
Chromatography is a method of separating components of a mixture through their interactions with two phases - a stationary phase and a mobile phase. The components are distributed between the phases based on properties like solubility and affinity. There are several types of chromatography classified by the shape of the stationary phase (e.g. thin layer), the state of the mobile phase (e.g. gas, liquid), or the interaction between solute and stationary phase (e.g. adsorption, partition). Chromatography techniques are used in various applications including pharmaceutical quality control, forensic analysis, and biological research like protein purification.