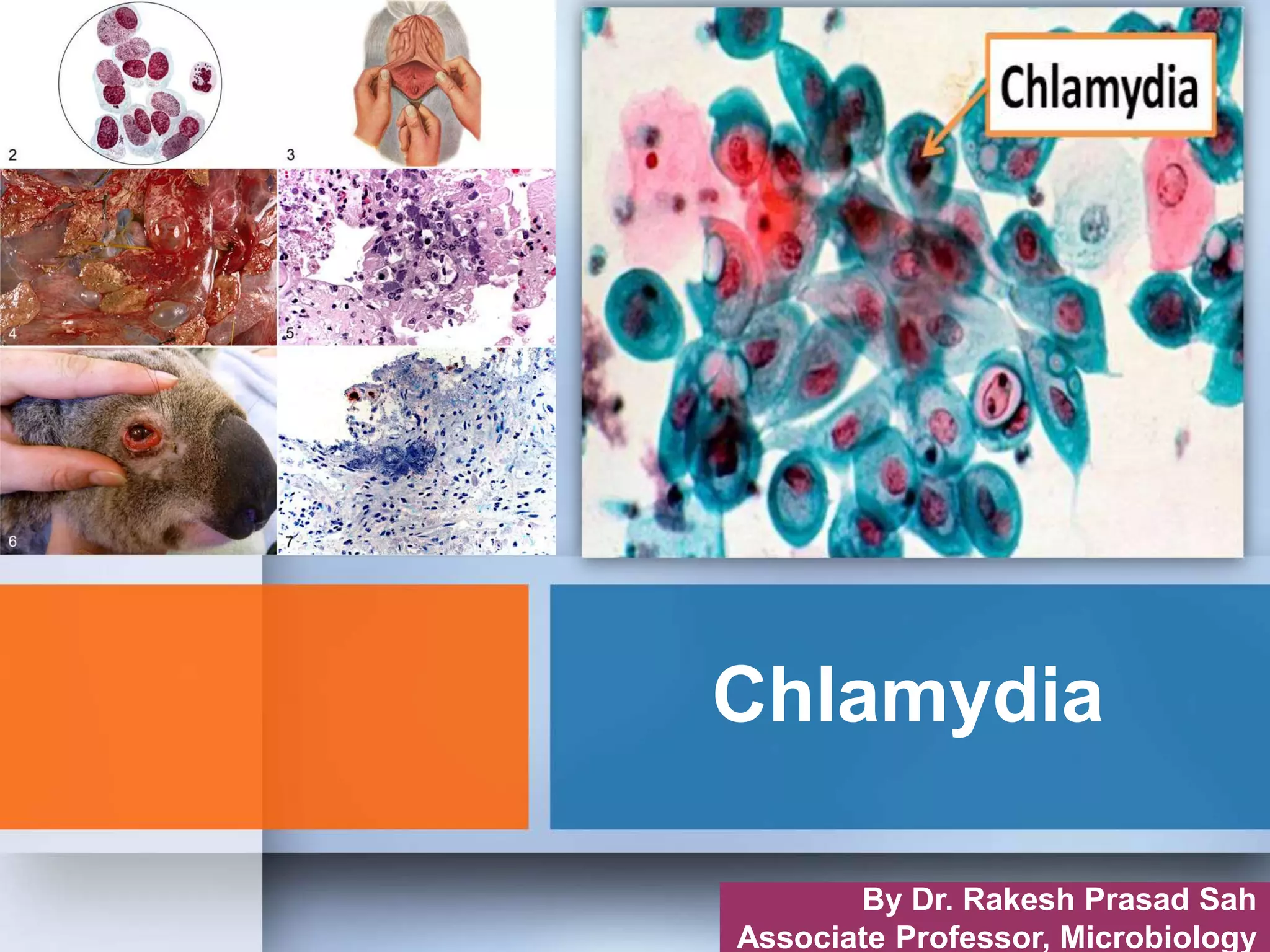
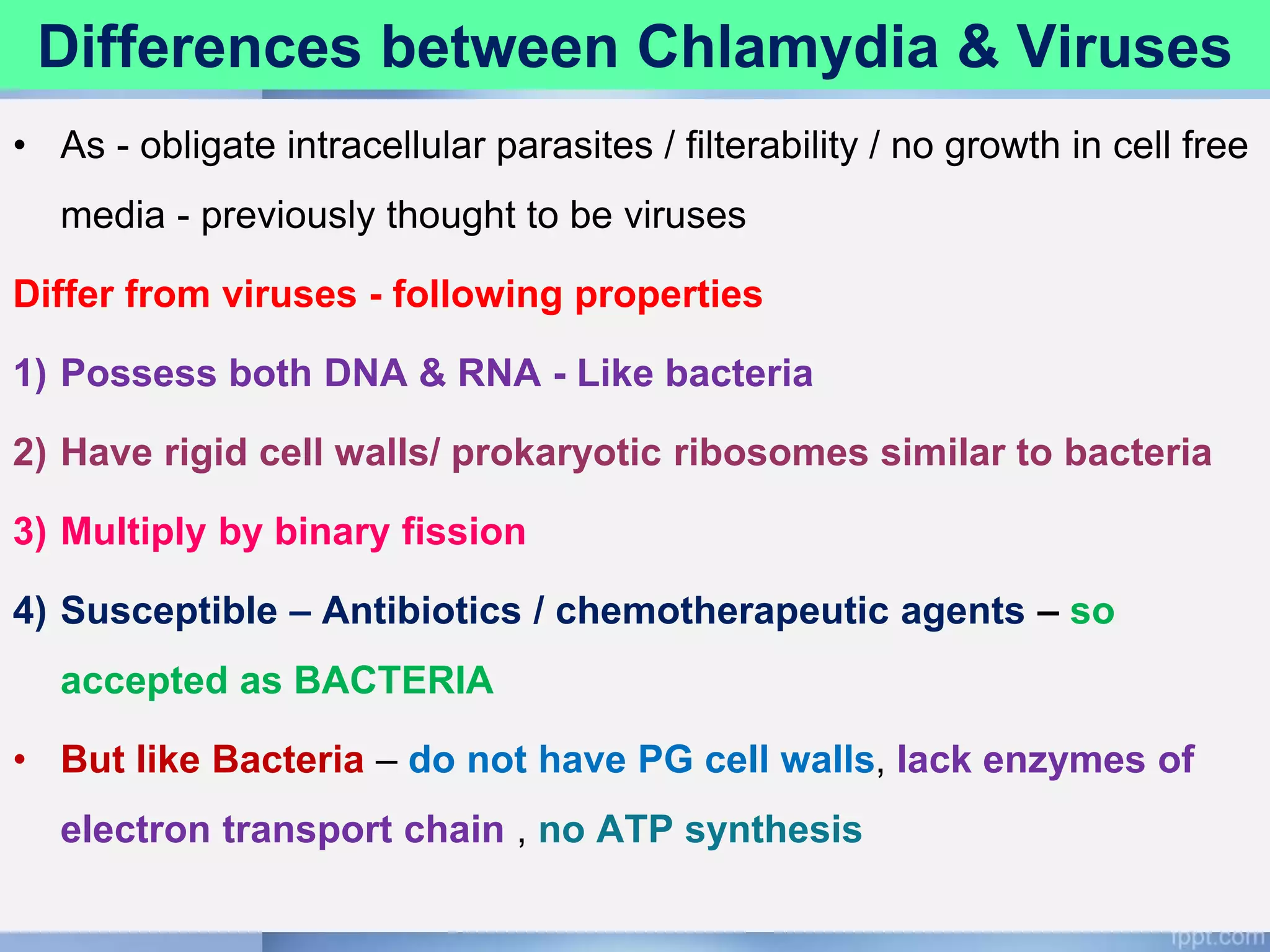
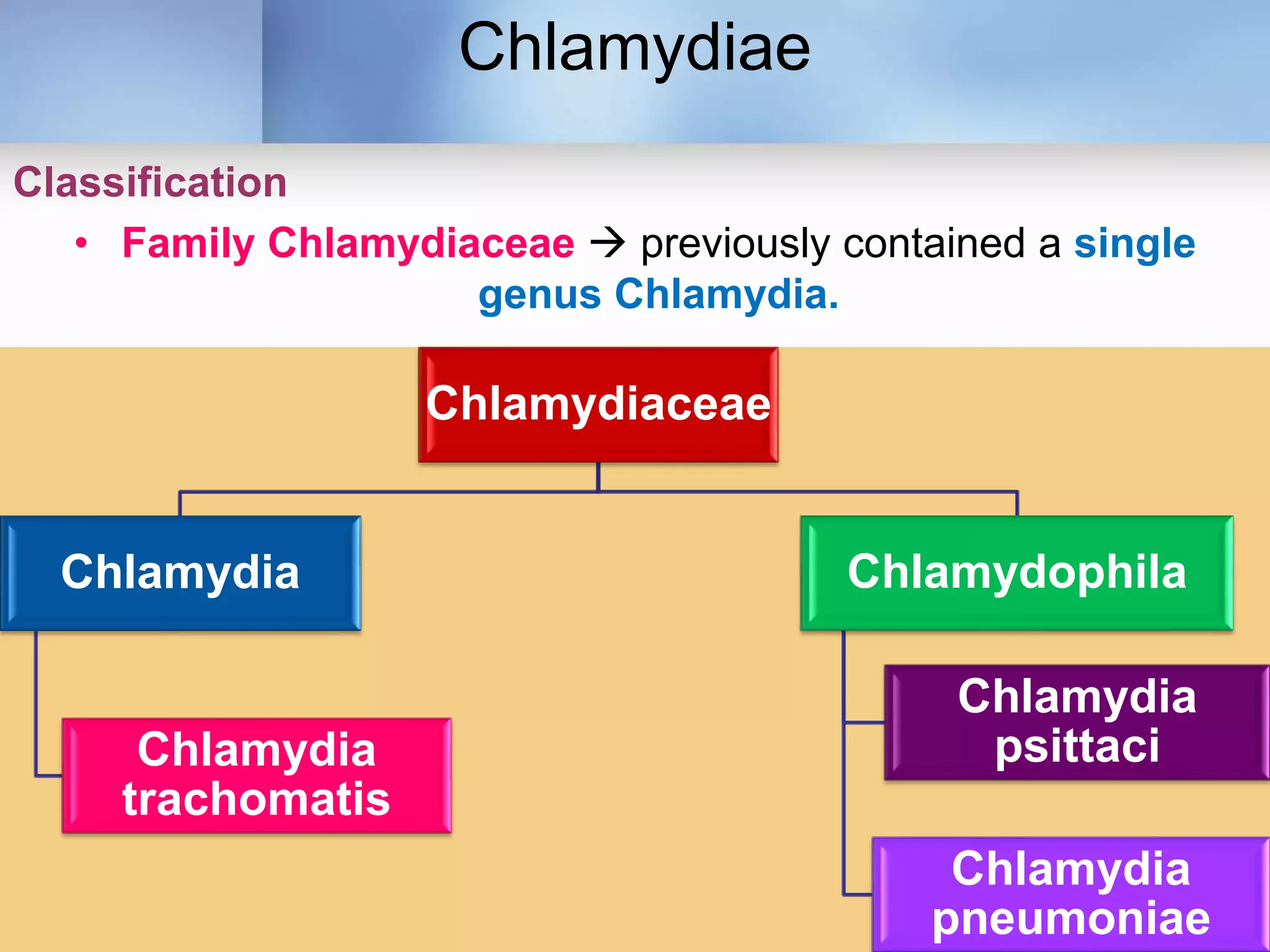
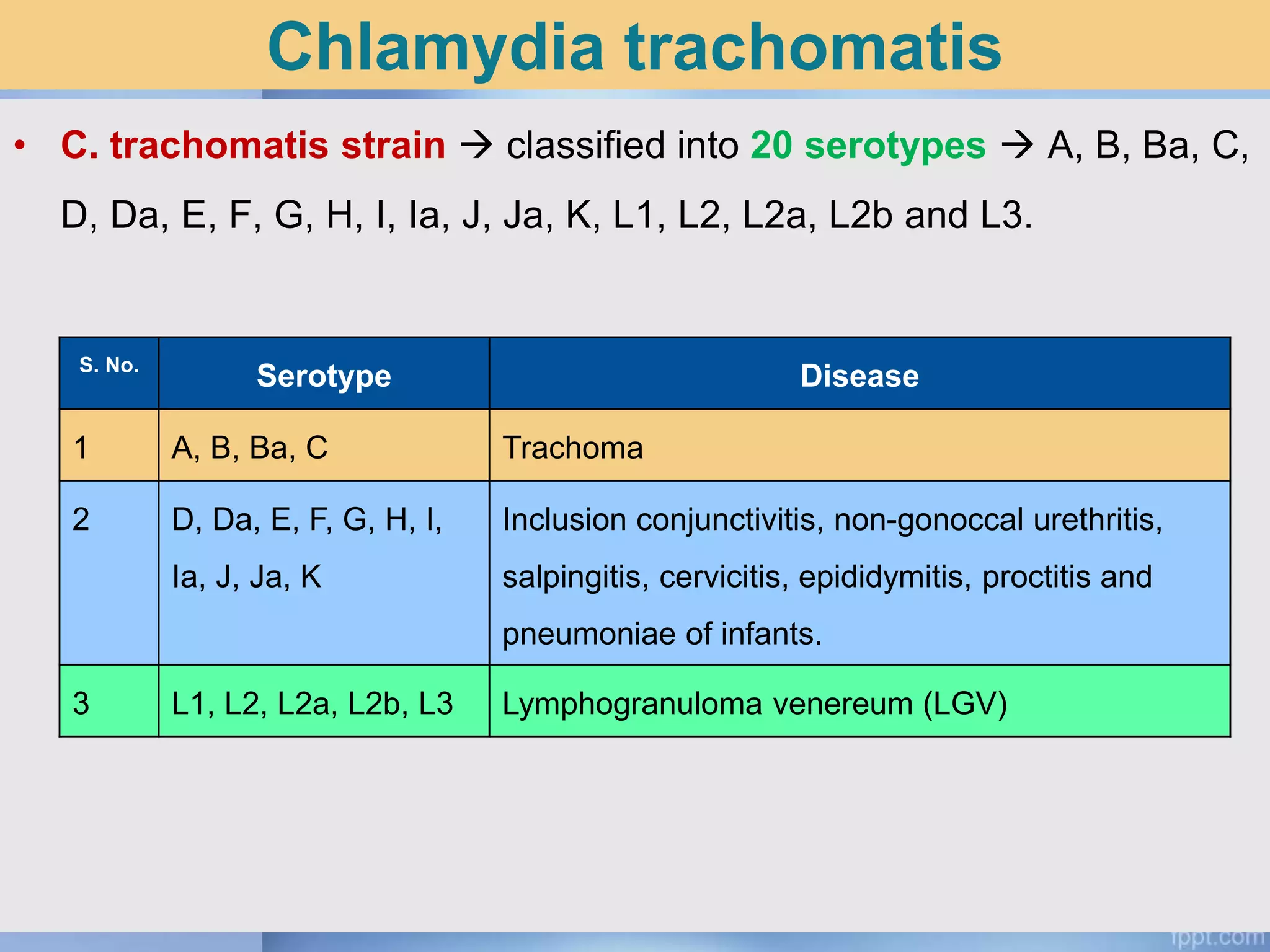
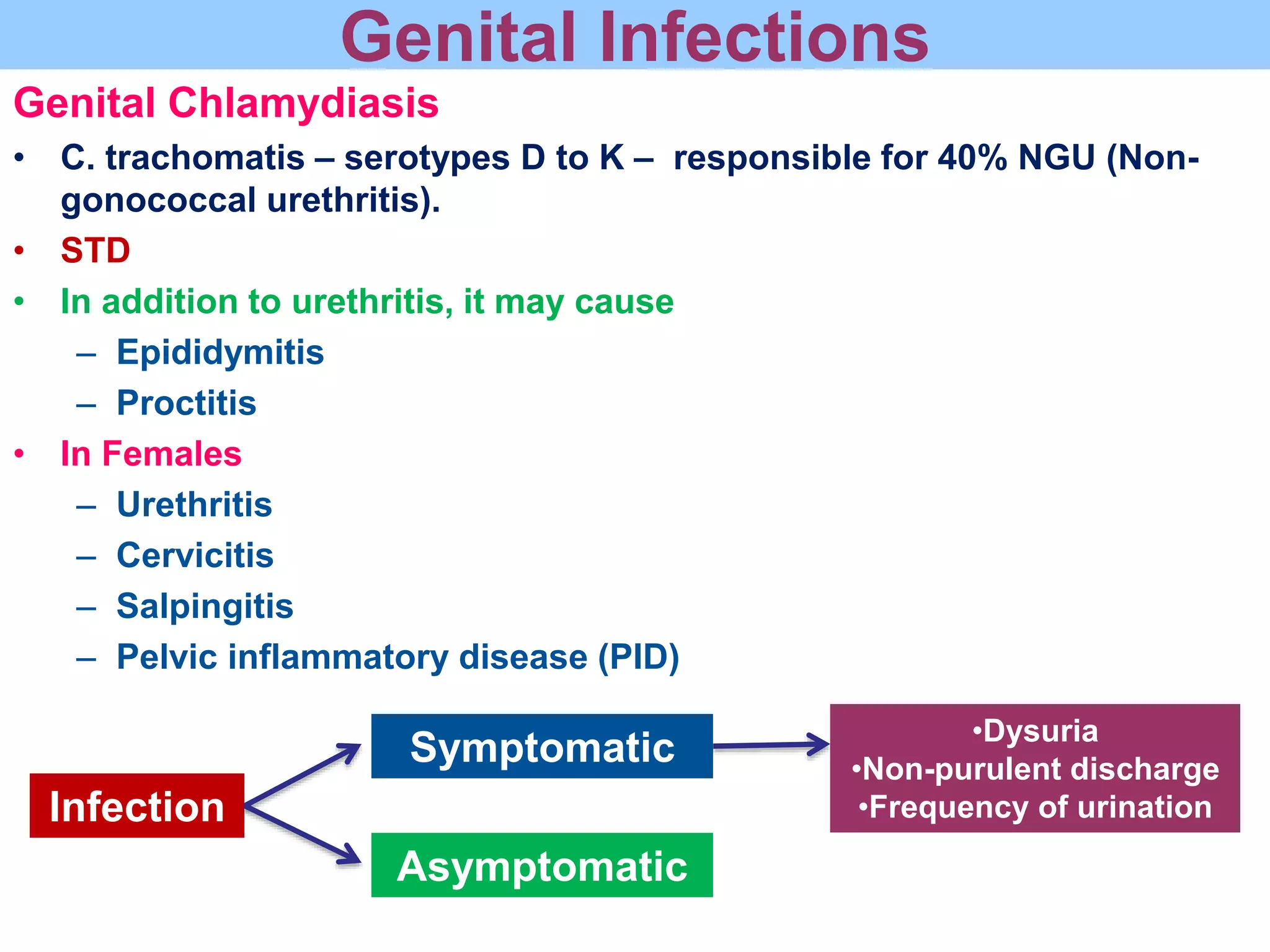
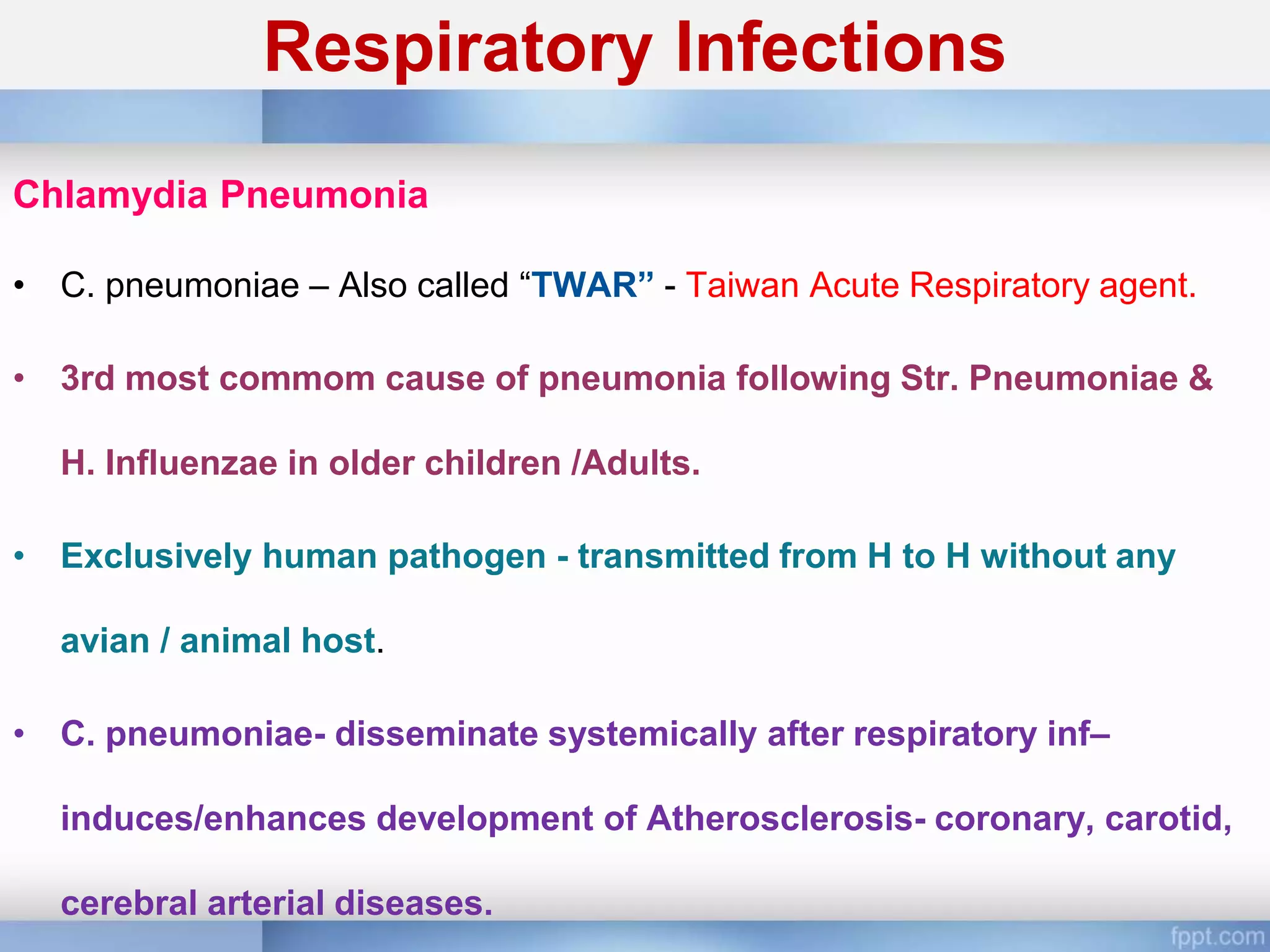
Chlamydia is an obligate intracellular parasite that can cause various diseases in humans. It exists in two forms - the elementary body, which is the infectious form, and the reticulate body, which is the replicative form inside host cells. Chlamydia trachomatis is the most common species and has multiple serotypes that can cause trachoma, genital infections, or lymphogranuloma venereum. Diagnosis involves direct detection of the organism by microscopy or antigen tests, isolation in cell culture, and serological detection of antibodies.