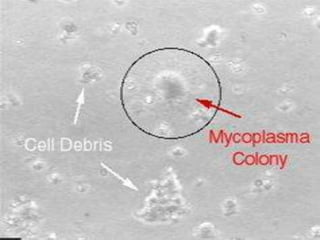
This document discusses several types of mycoplasma bacteria. It describes their morphology, cultural characteristics, and the diseases they cause. The most common pathogenic mycoplasma are M. pneumoniae, M. hominis, M. urealyticum, and M. genitalium. M. pneumoniae causes atypical pneumonia. M. hominis and M. urealyticum can cause infections in the urogenital tract and lead to infertility. M. genitalium is associated with urethritis and pelvic inflammatory disease. Laboratory diagnosis involves culture studies, biochemical studies, and serological tests like complement fixation and ELISA. Tetracycline and erythromycin are commonly used for treatment