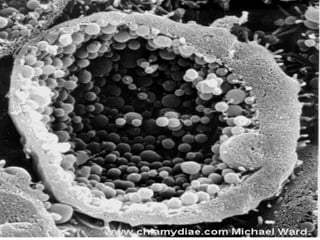
Chlamydiae are small, obligate intracellular parasites that lack the ability to produce their own ATP. There are three medically important species: C. pneumoniae, C. psittaci, and C. trachomatis. C. pneumoniae causes respiratory infections like pneumonia. C. psittaci infects birds and can be transmitted to humans, causing ornithosis or pneumonia. C. trachomatis causes ocular infections like trachoma and inclusion conjunctivitis as well as genital infections like lymphogranuloma venereum and non-gonococcal urethritis. Diagnosis involves microscopy, culture studies, serological tests, and skin tests. Treatment involves sulfon