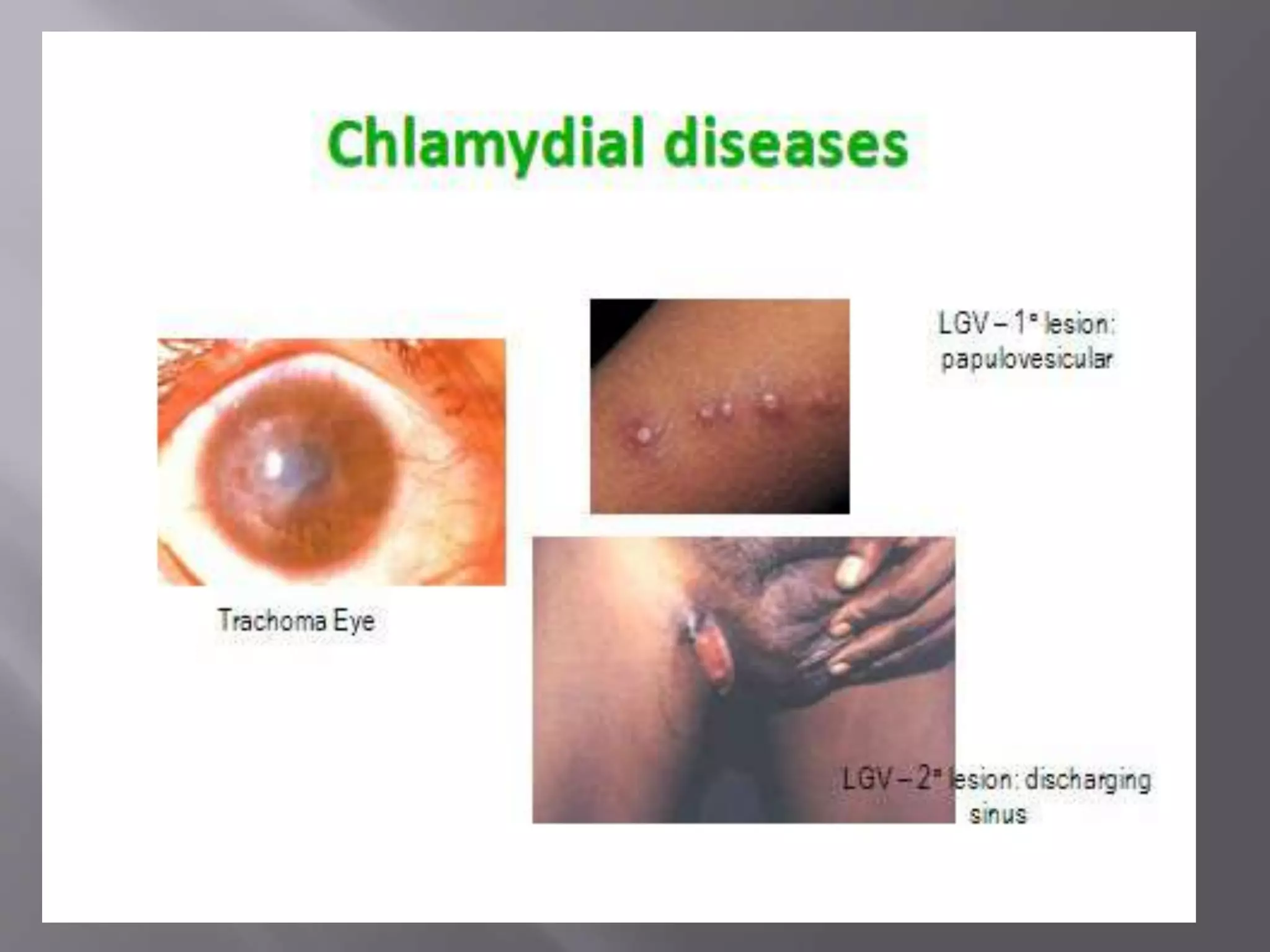
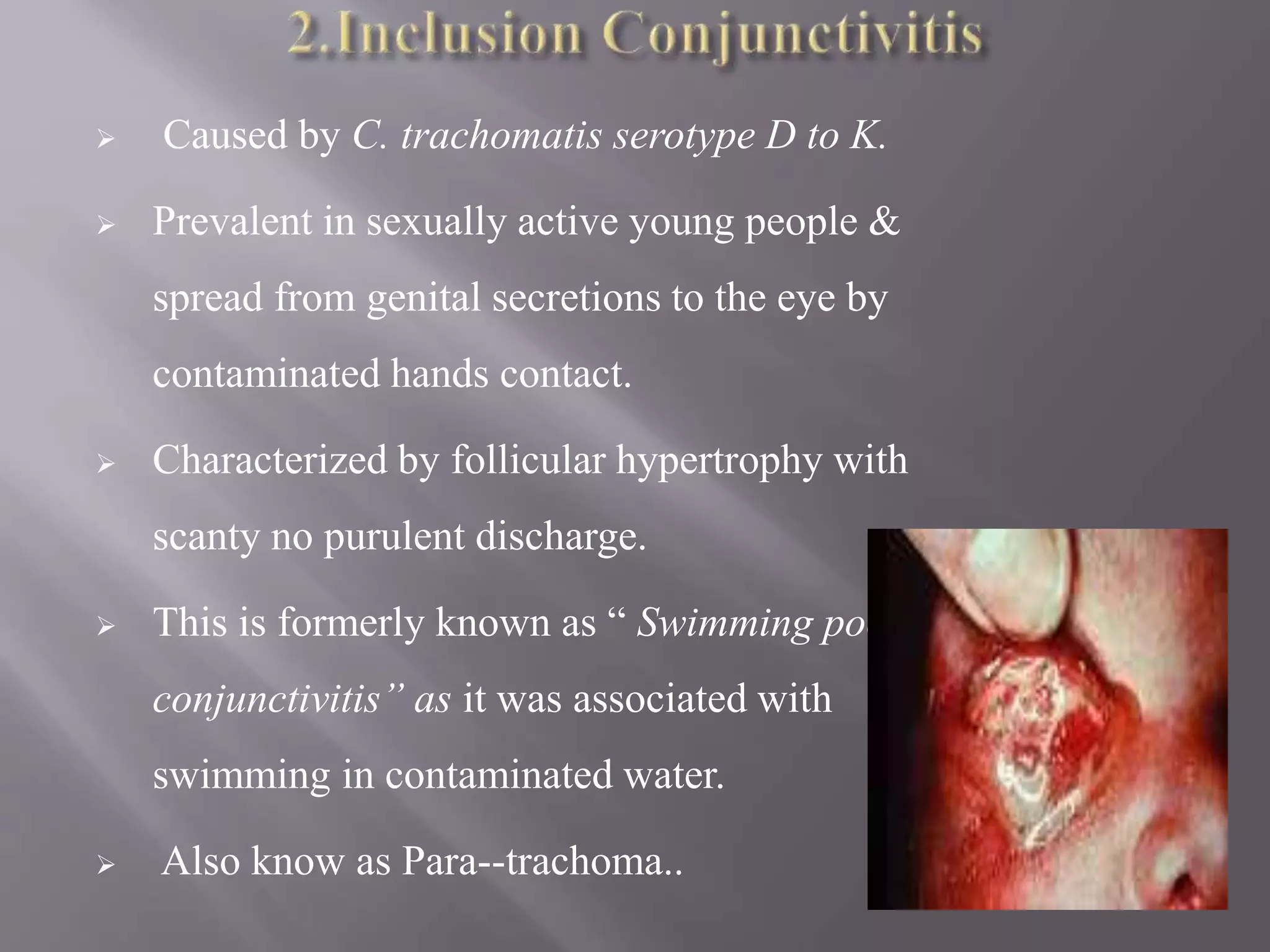
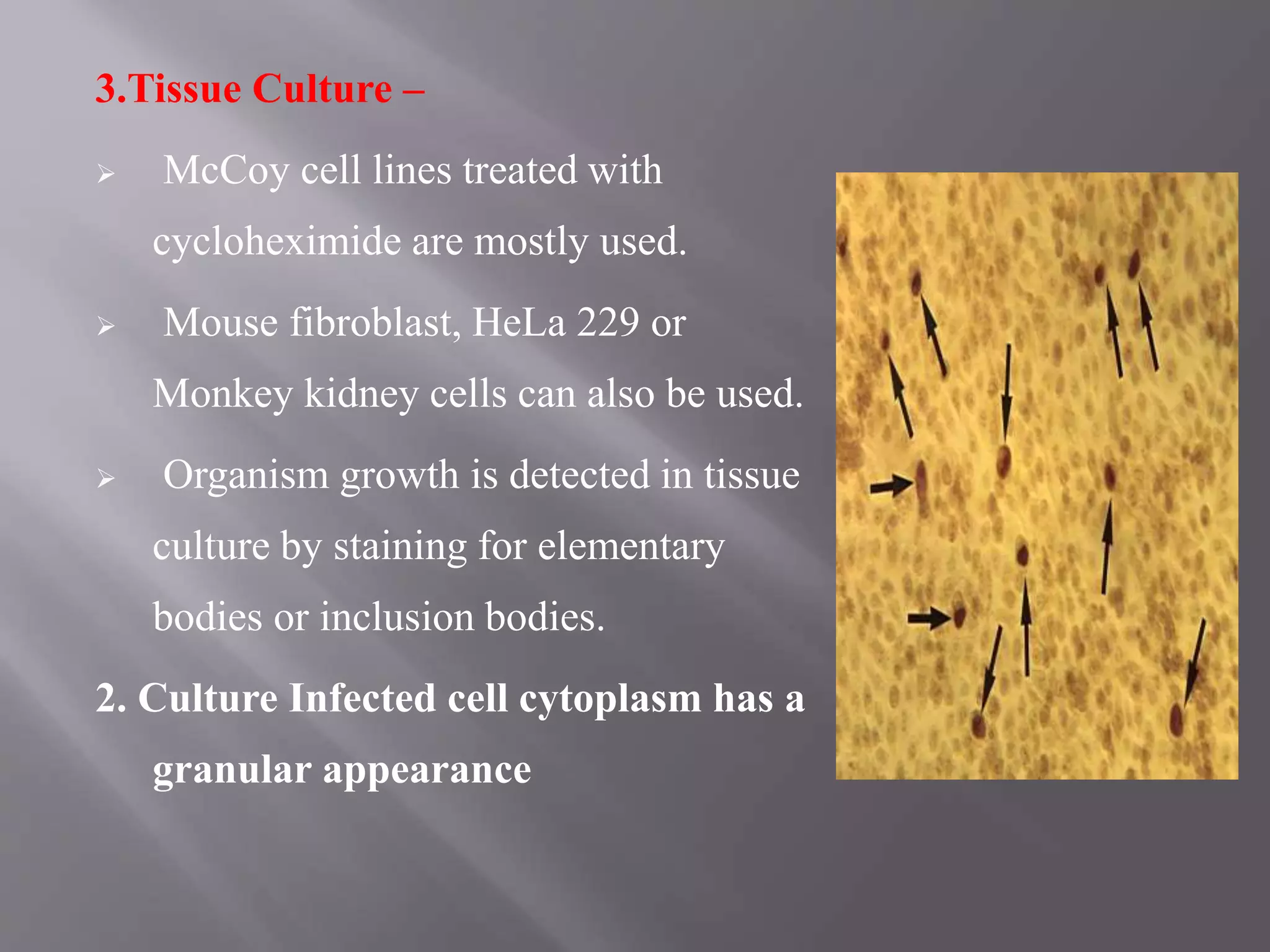
Chlamydia is an obligate intracellular parasite that can cause diseases like trachoma, lymphogranuloma venereum, and psittacosis in birds and mammals. It exists in two forms - the infectious elementary body and the replicative reticulate body. Chlamydia can cause diseases like trachoma, genital chlamydiasis, inclusion conjunctivitis, and pneumonia. Diagnosis involves microscopic examination of samples for inclusion bodies, culturing the organism from samples, or detecting chlamydial antigens or antibodies. Treatment involves antibiotics like tetracyclines, erythromycin, and sulfonamides.