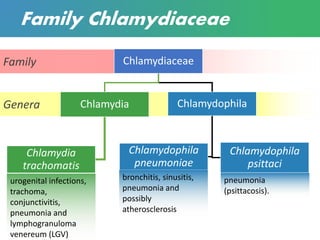
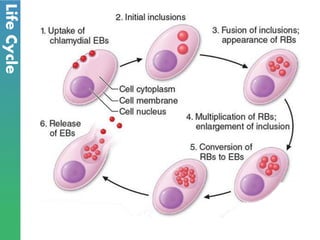
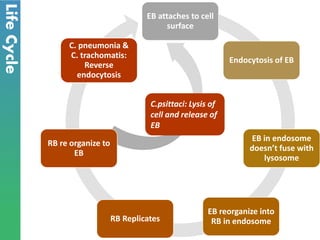
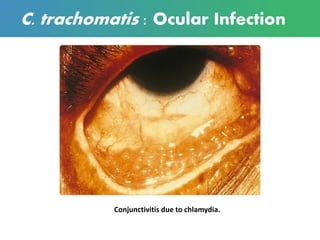
Chlamydia is a sexually transmitted bacterial infection caused by Chlamydia trachomatis. It infects epithelial cells in the genital tract, eyes, and respiratory system. C. trachomatis has two forms - infectious elementary bodies and metabolically active reticulate bodies. It undergoes a life cycle within host cells involving endocytosis, replication of reticulate bodies, and release of new elementary bodies. Genital infection is often asymptomatic but can cause pelvic inflammatory disease and infertility in women. Diagnosis is via nucleic acid amplification tests on genital specimens. Treatment is with antibiotics but prevention requires safe sex practices and partner treatment.