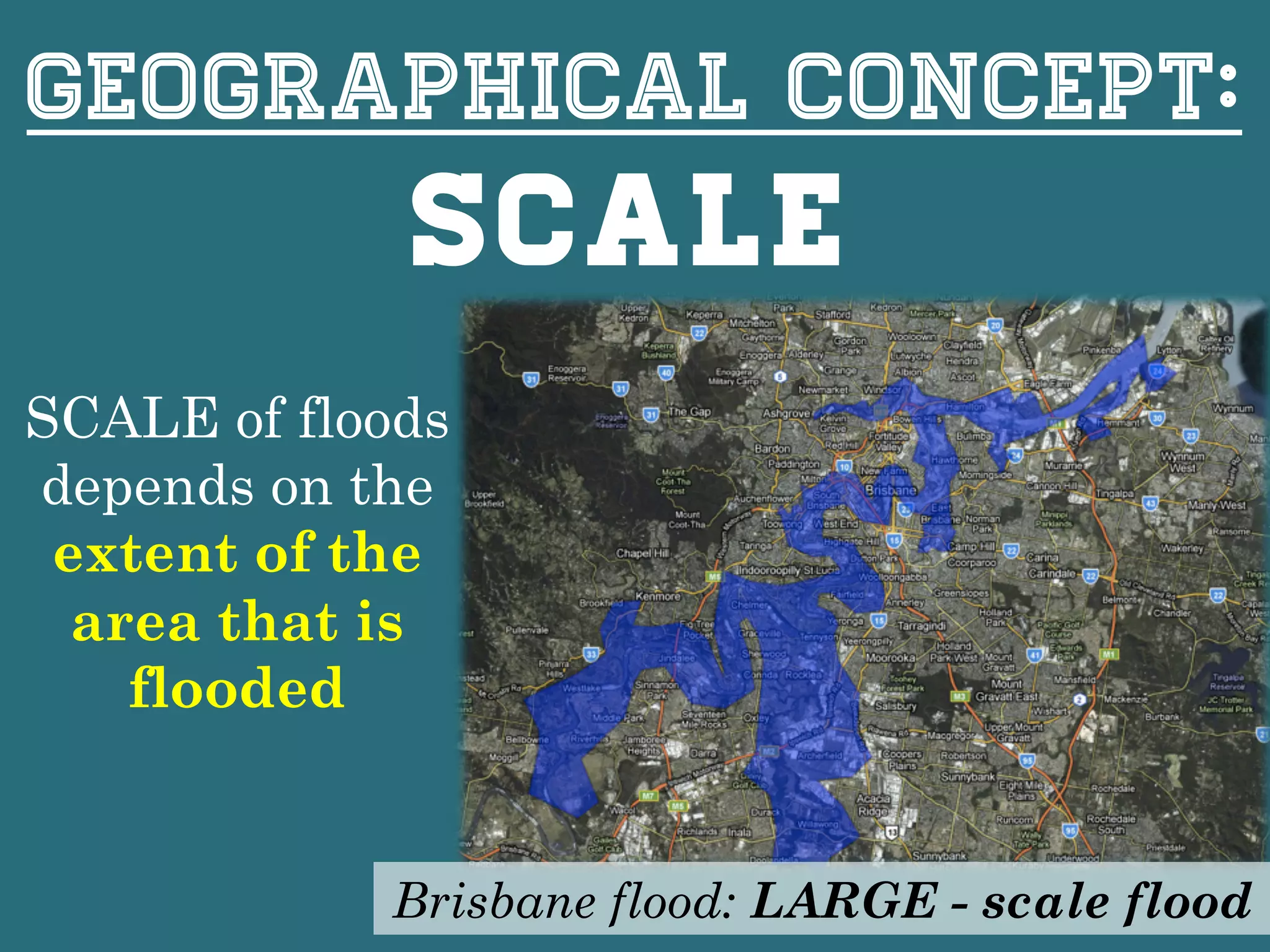
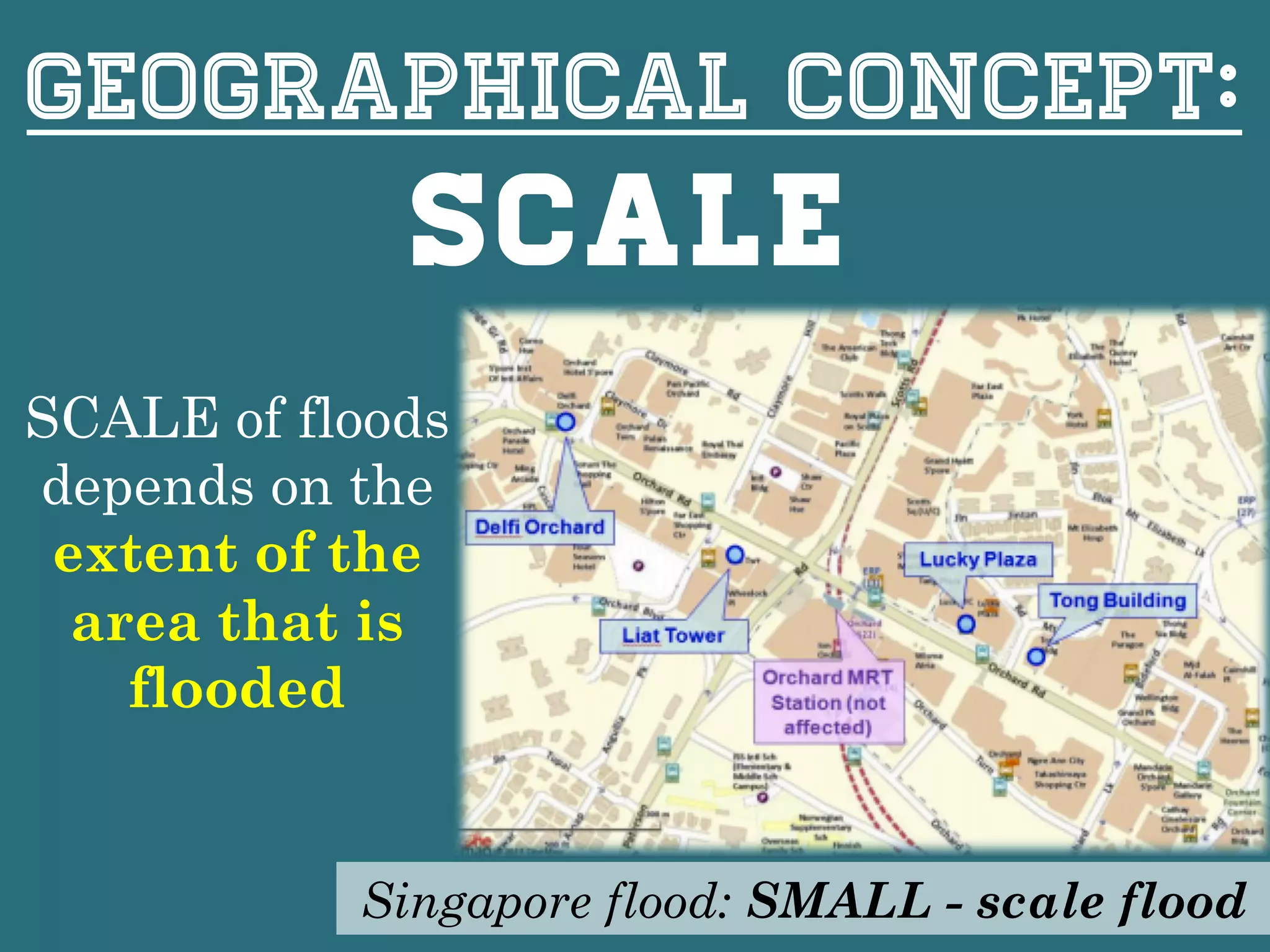
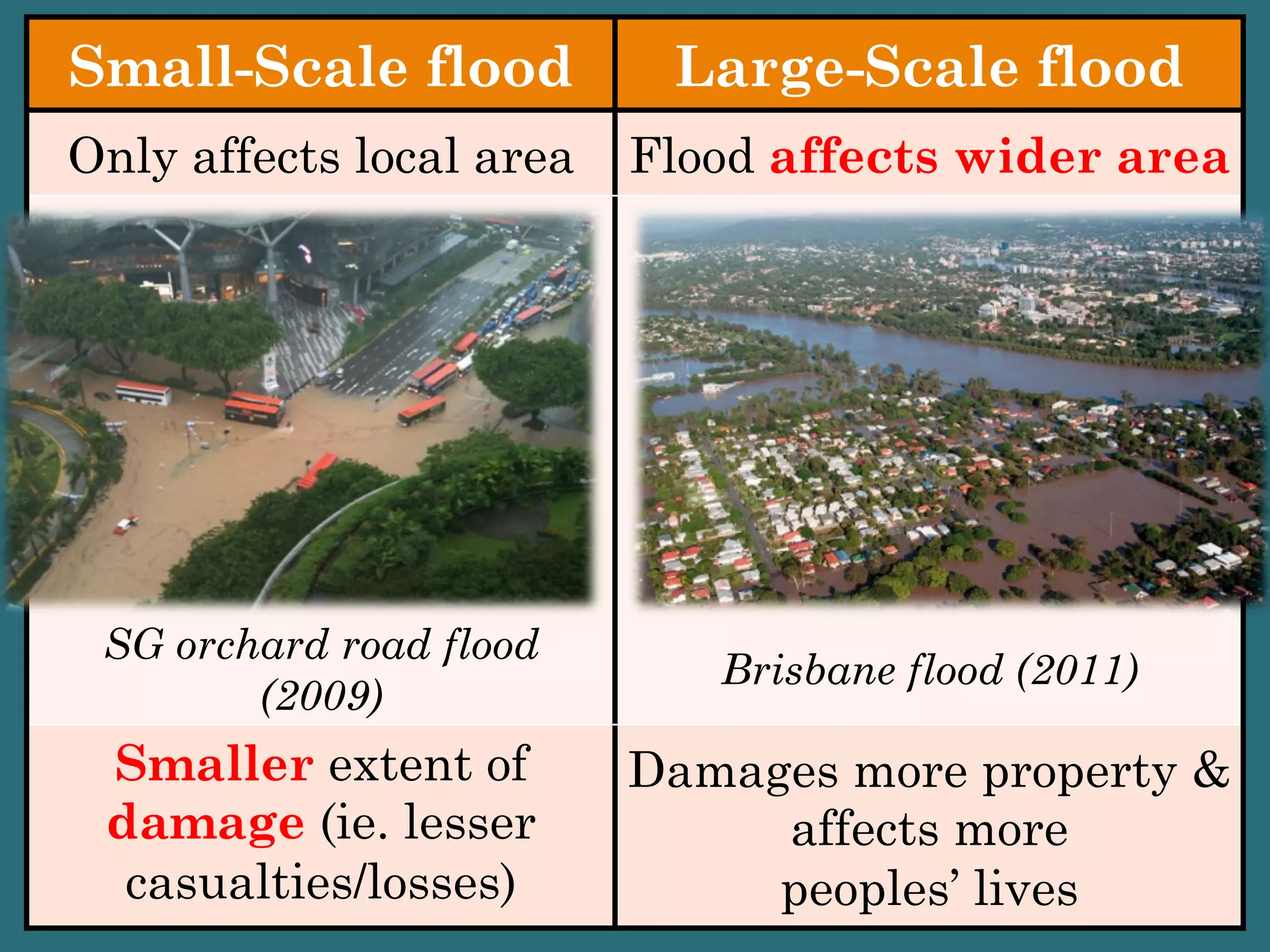
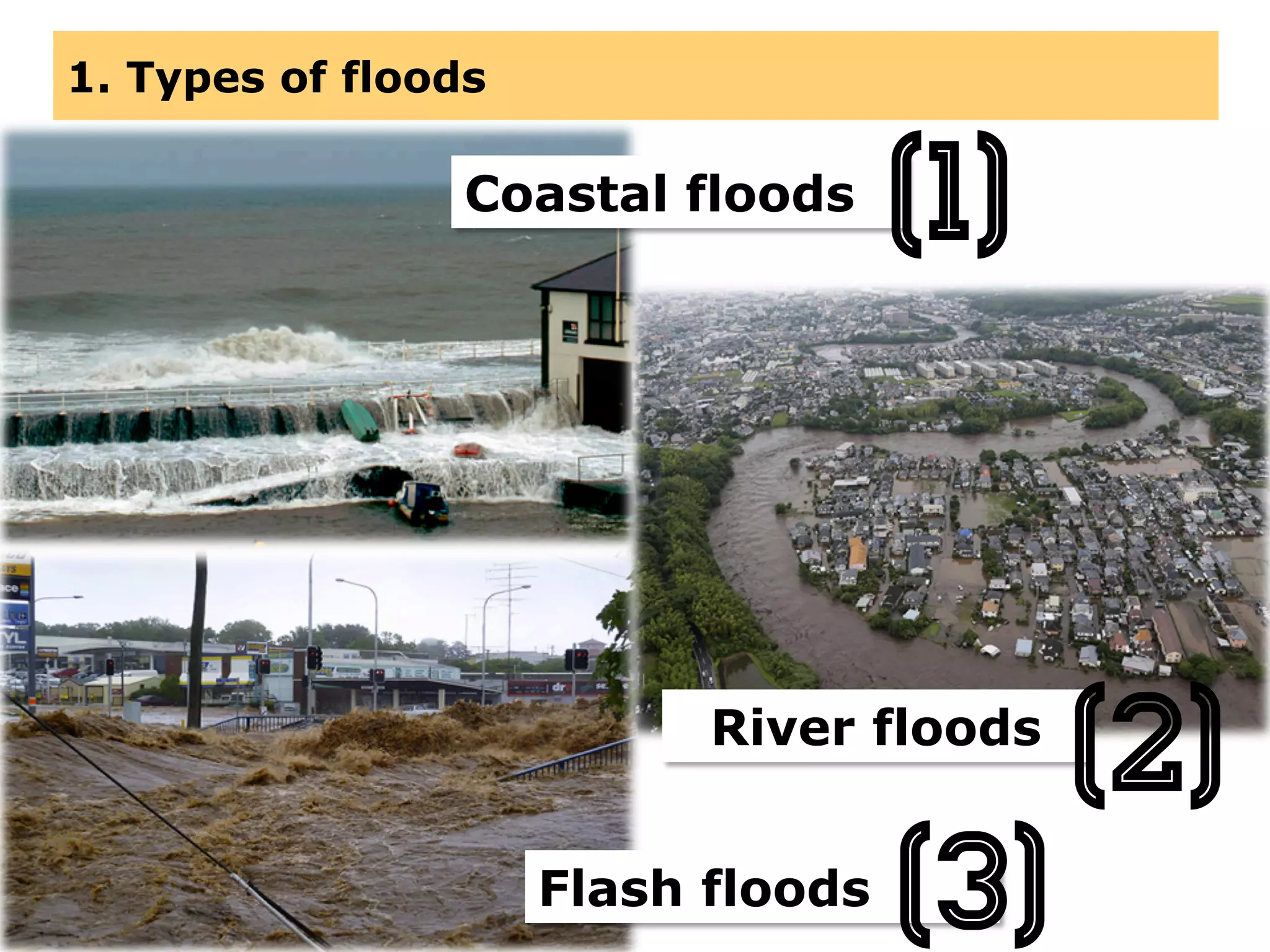
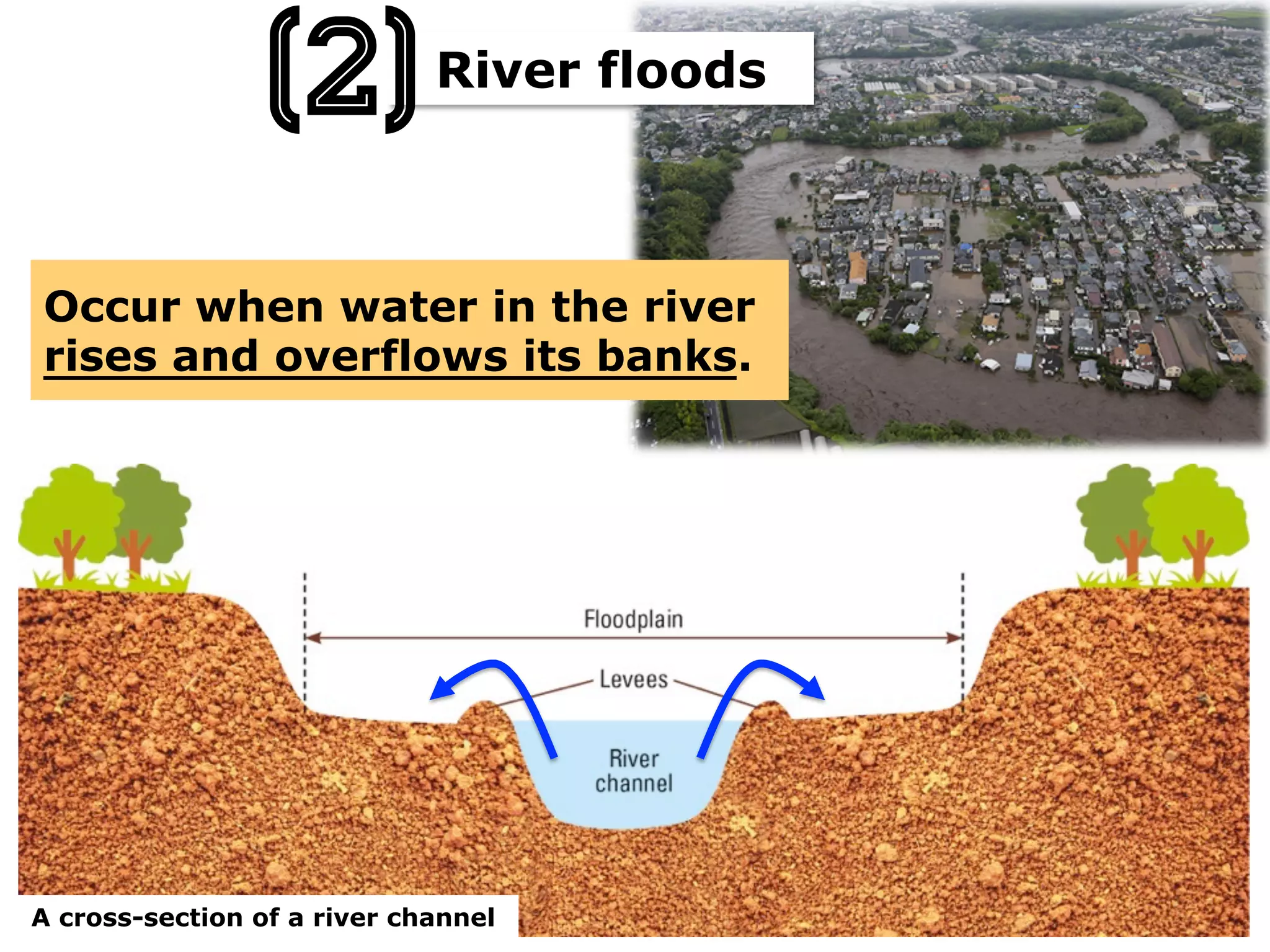
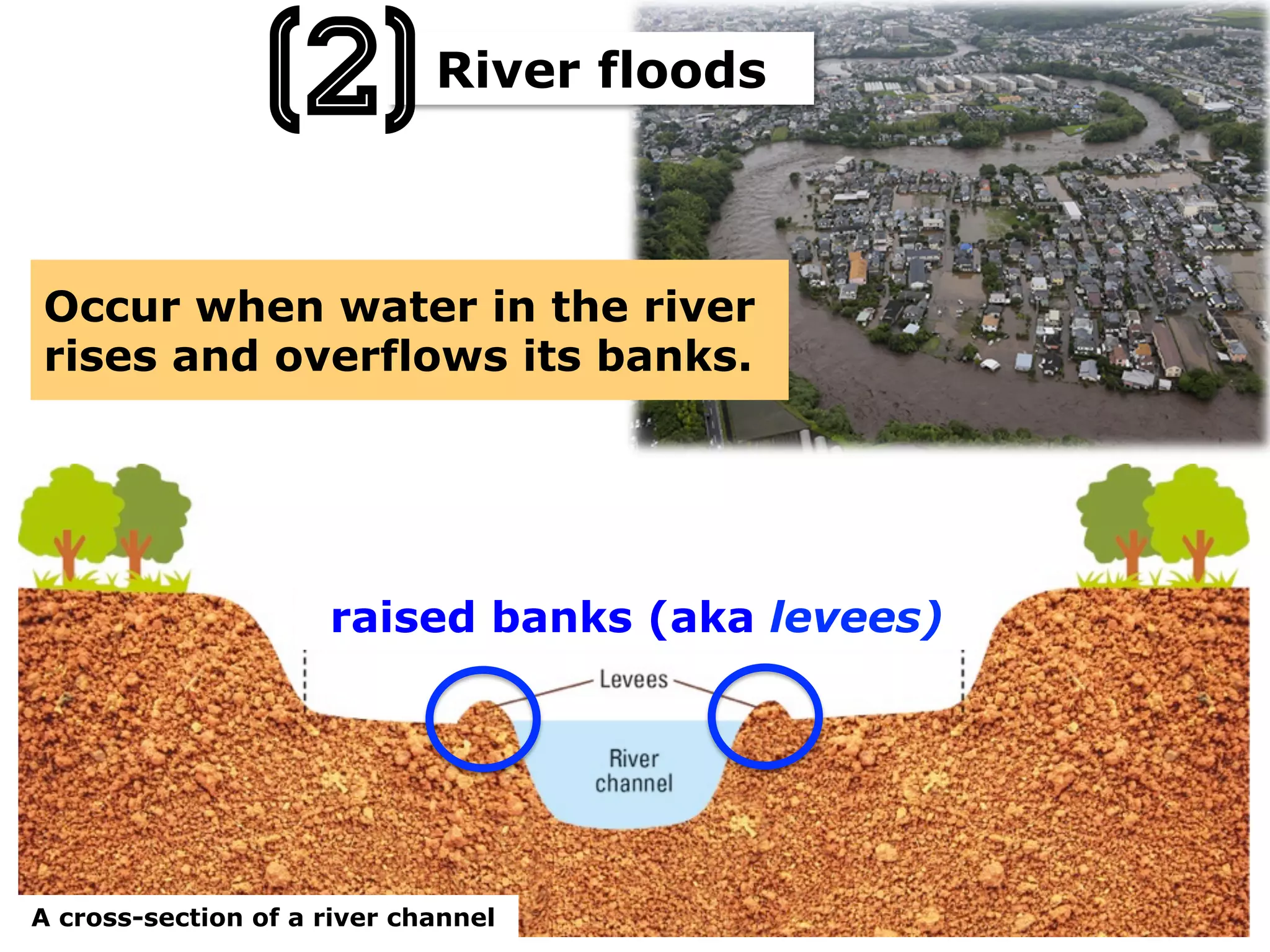
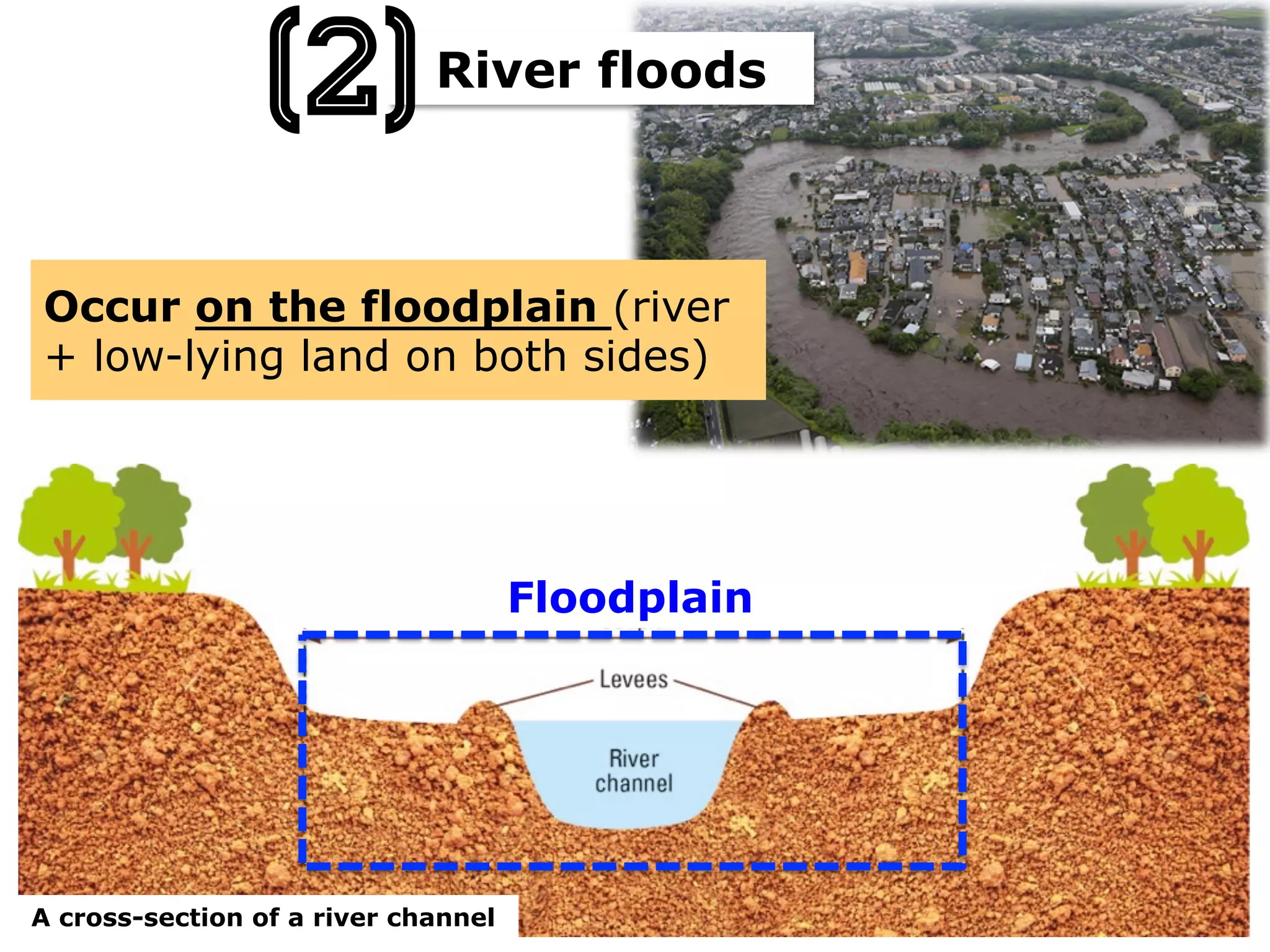
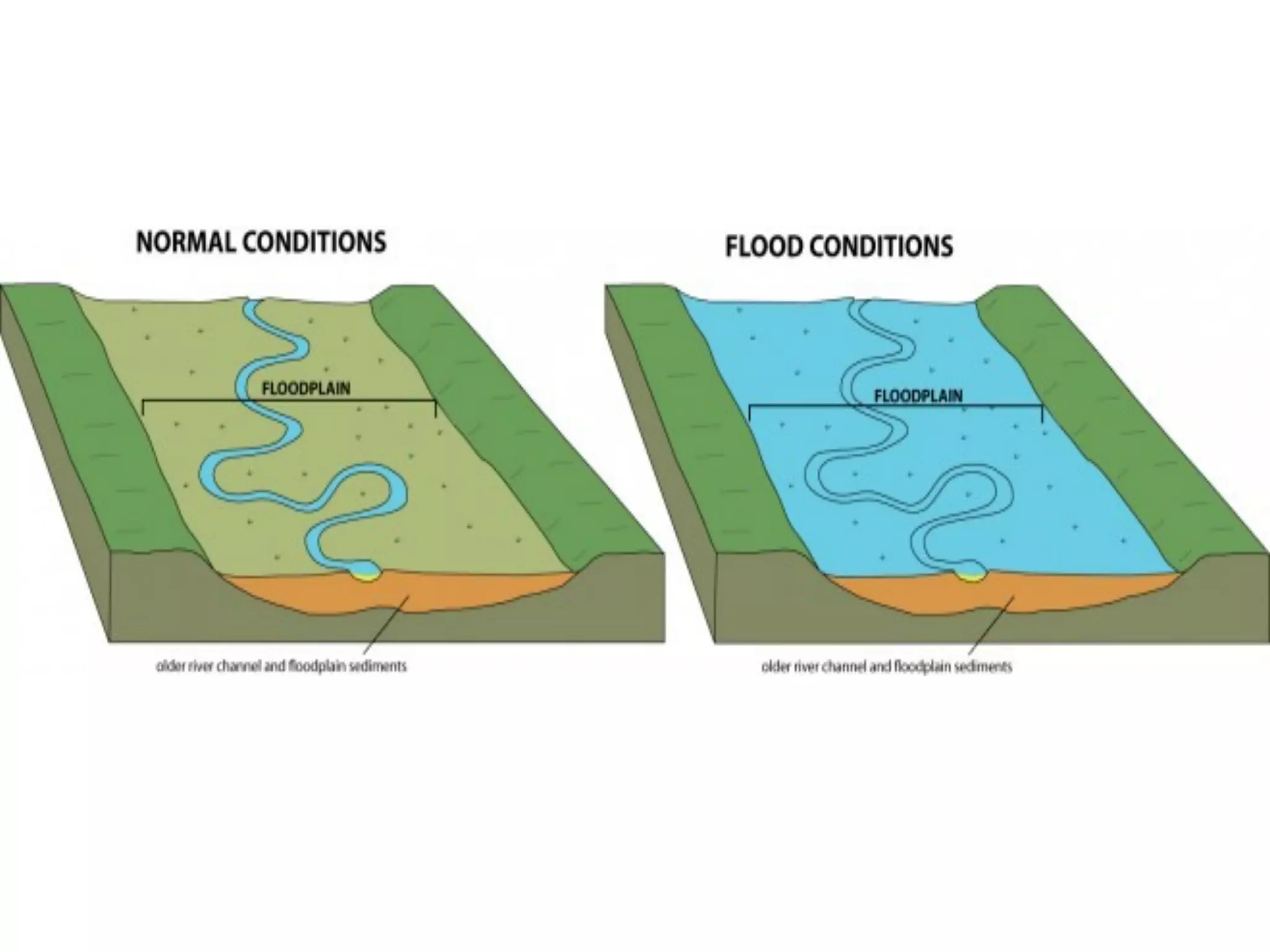
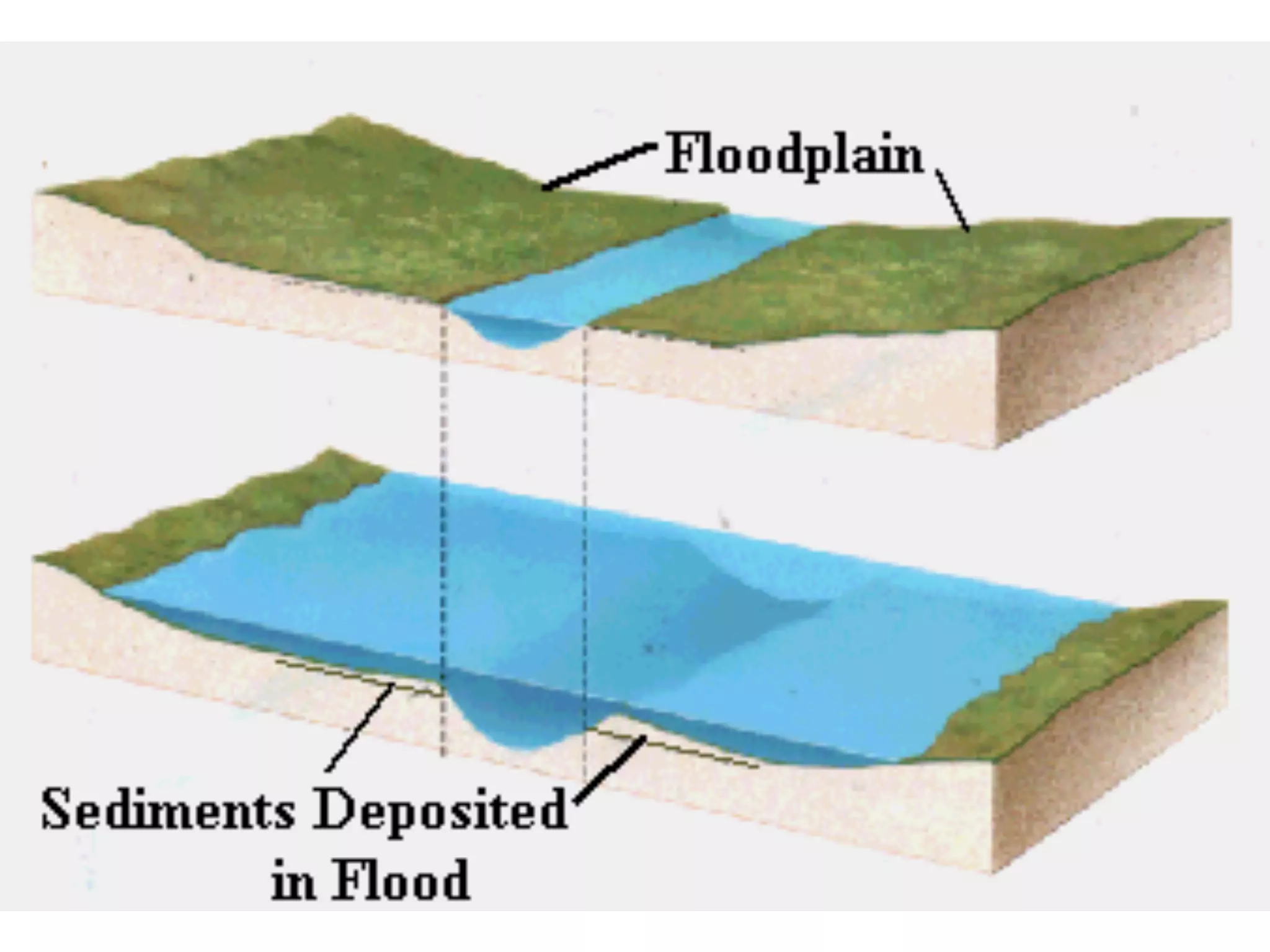
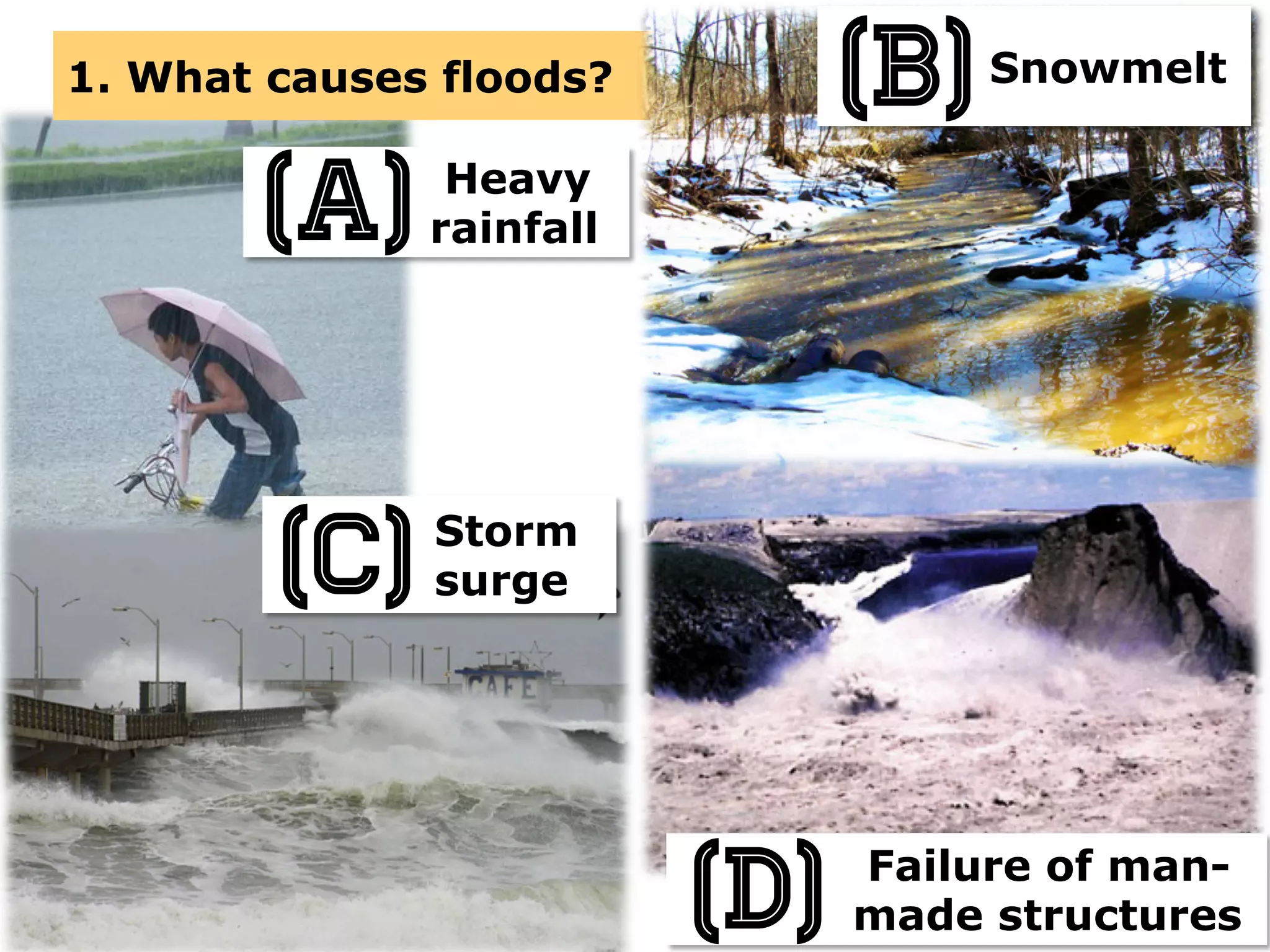
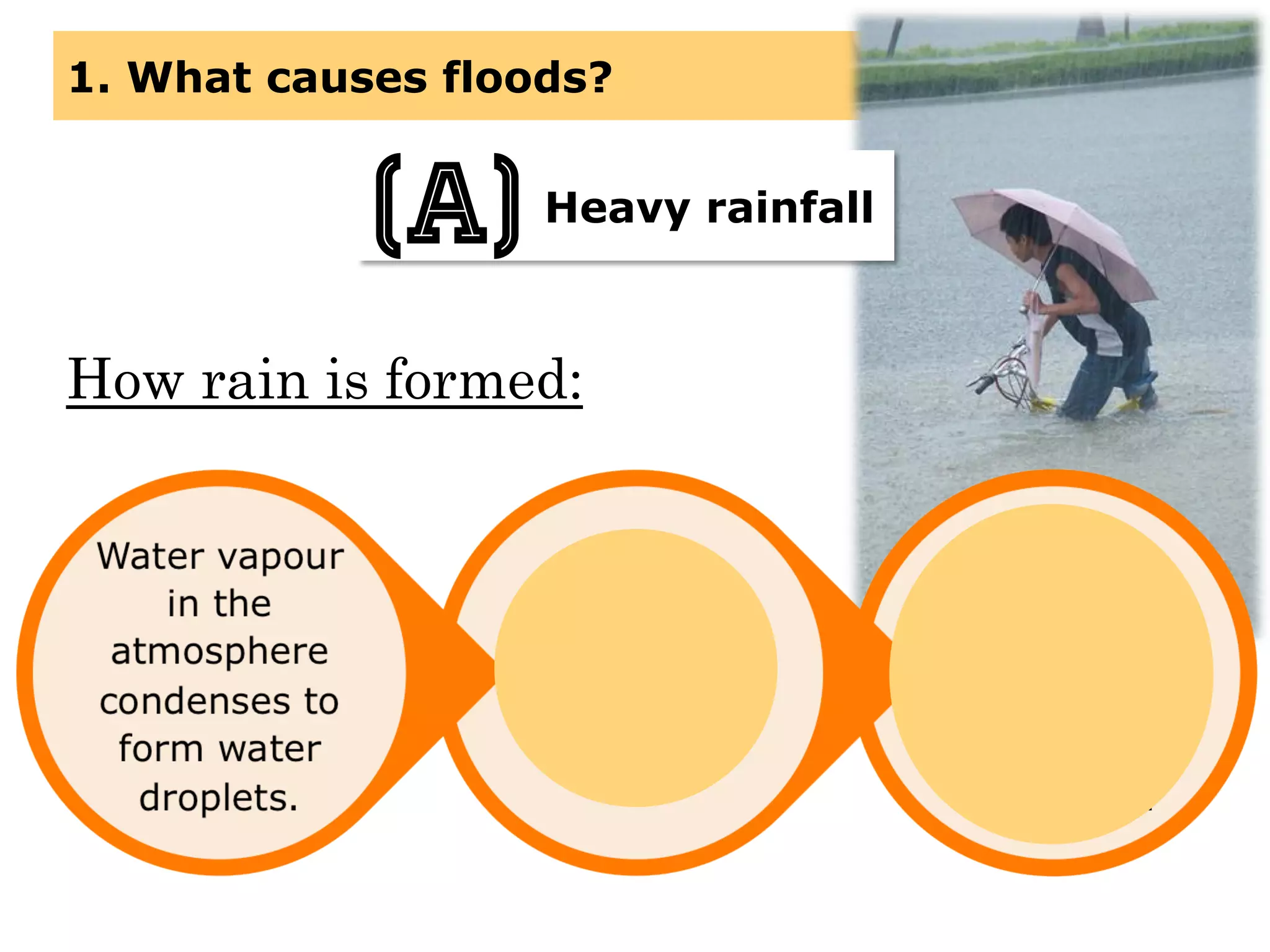
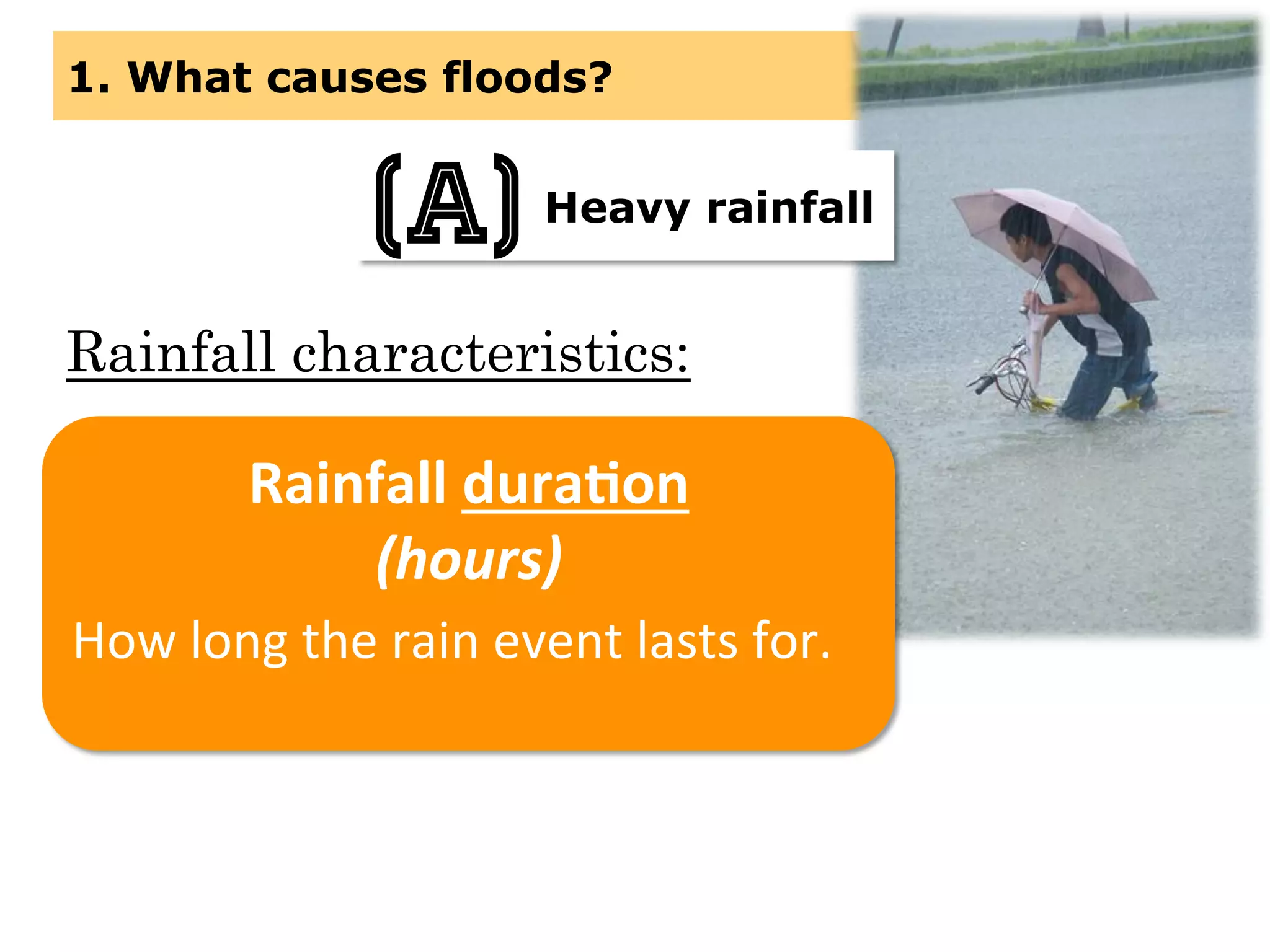
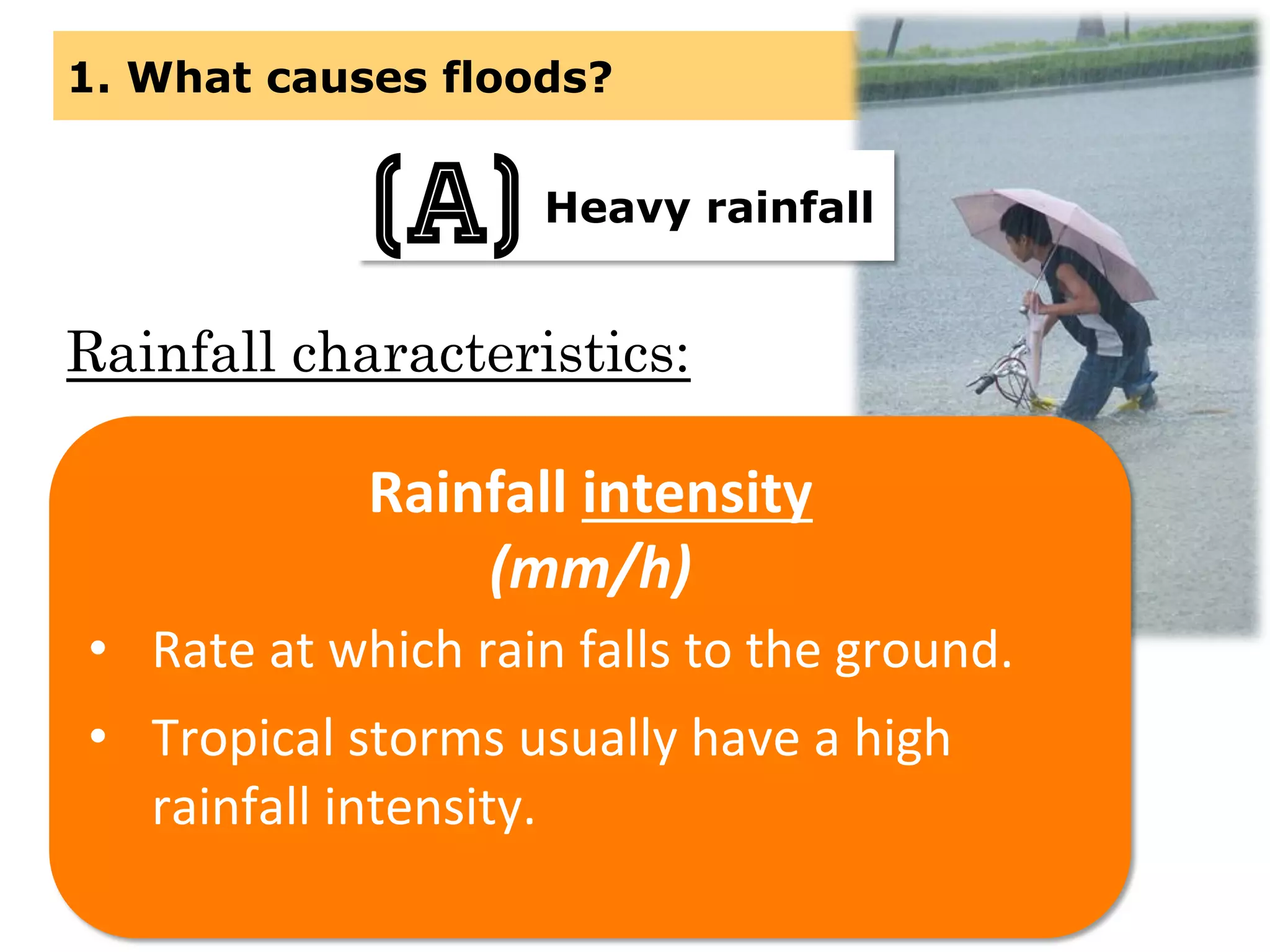
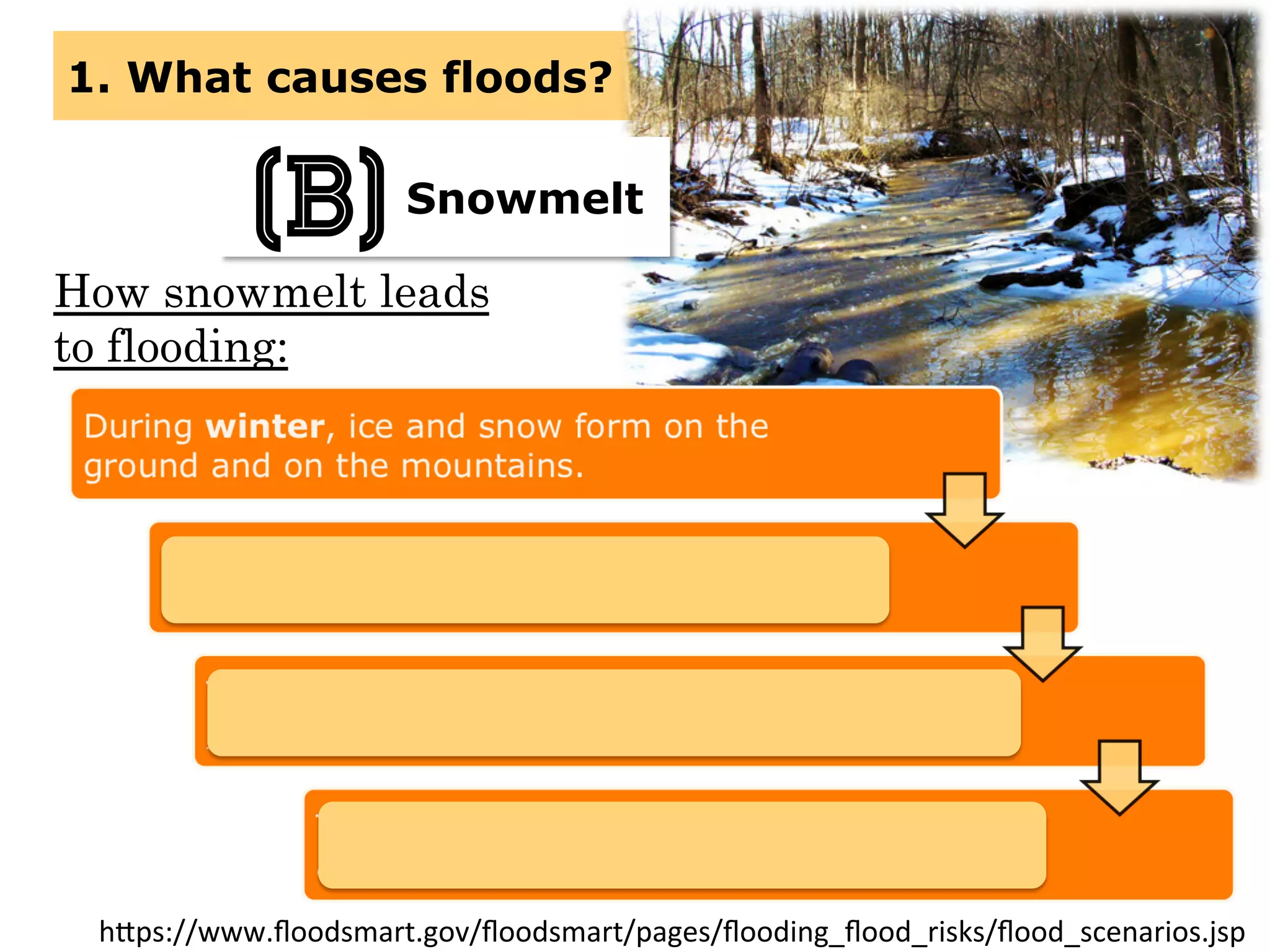
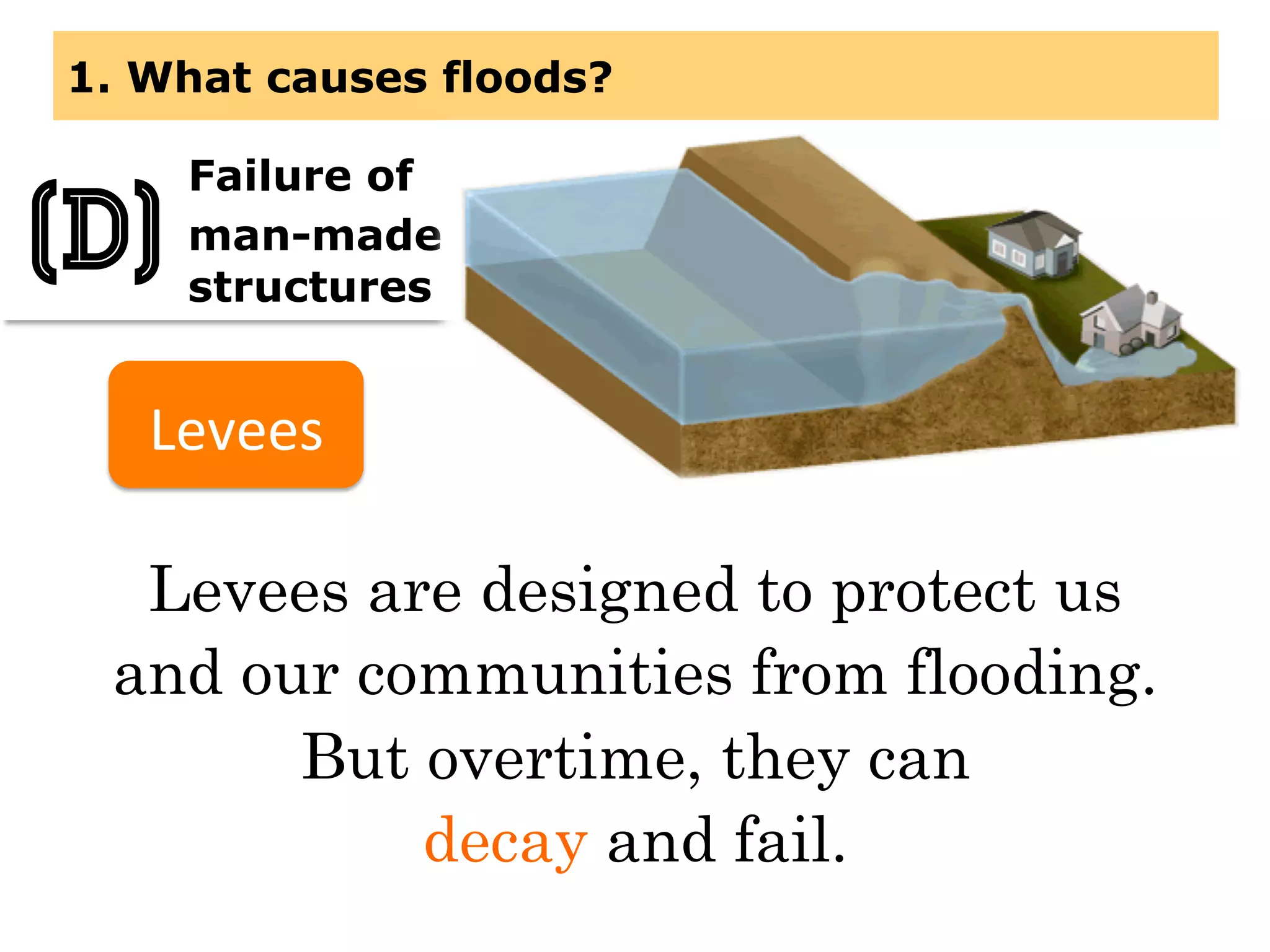
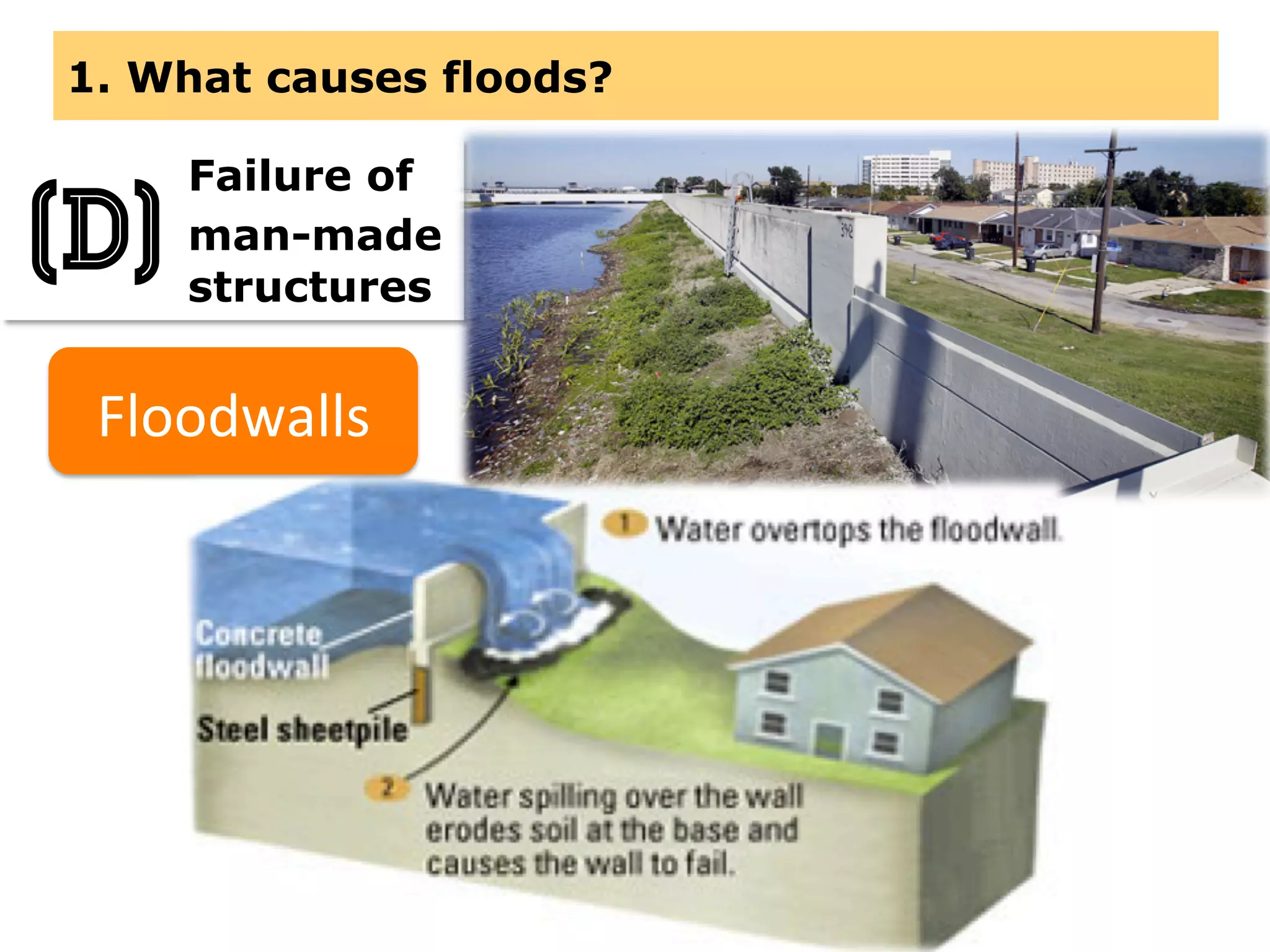
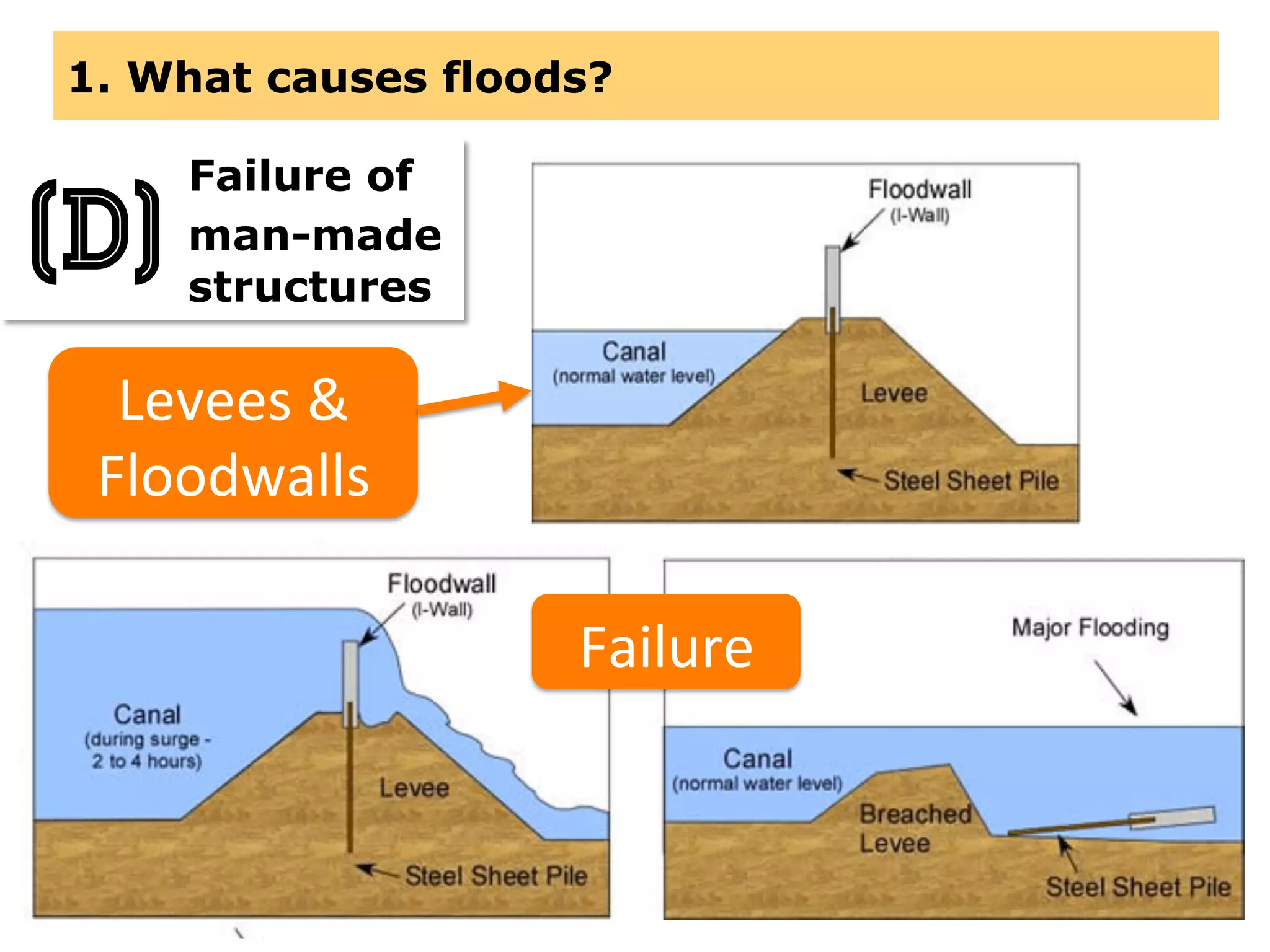
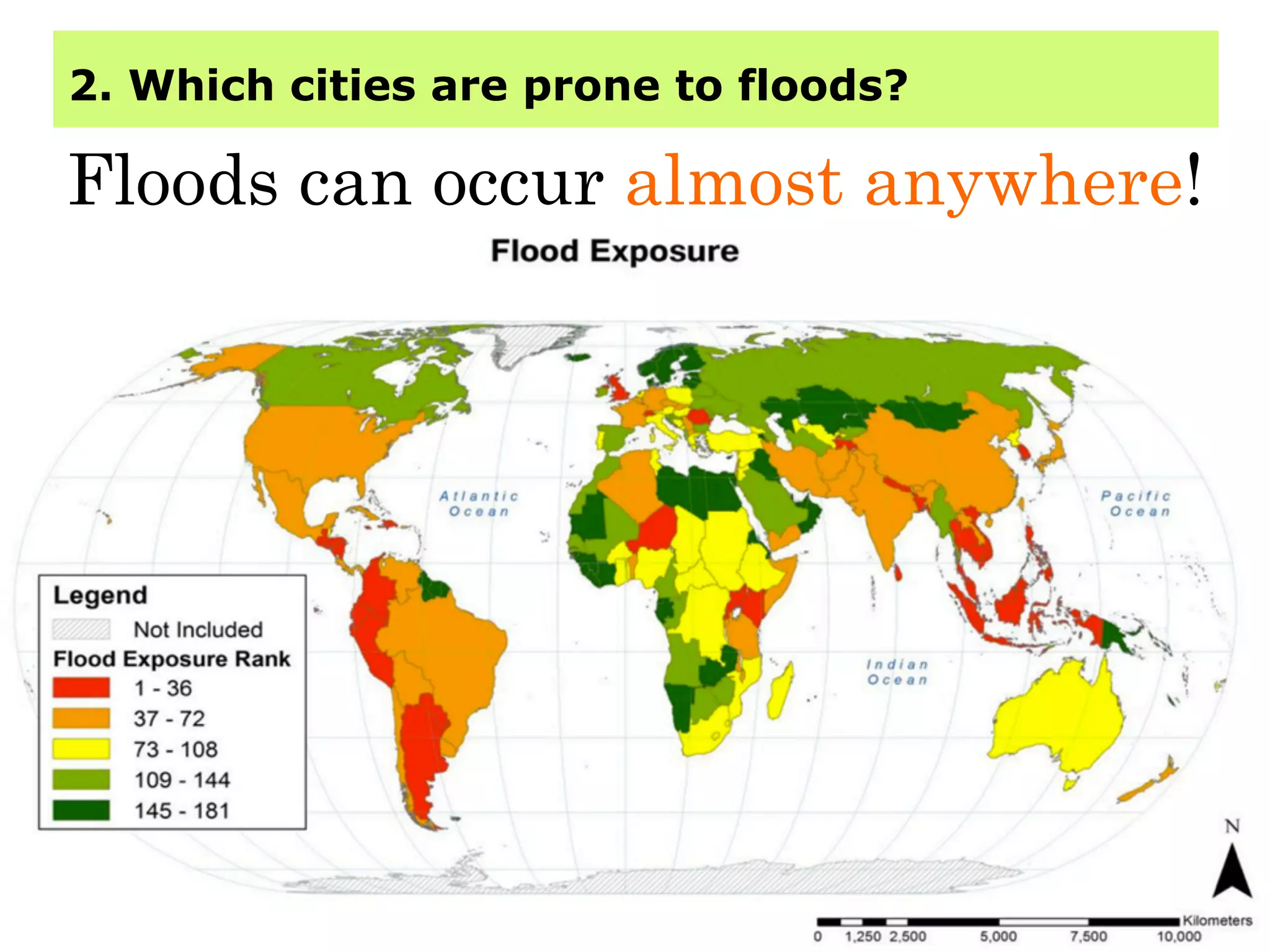
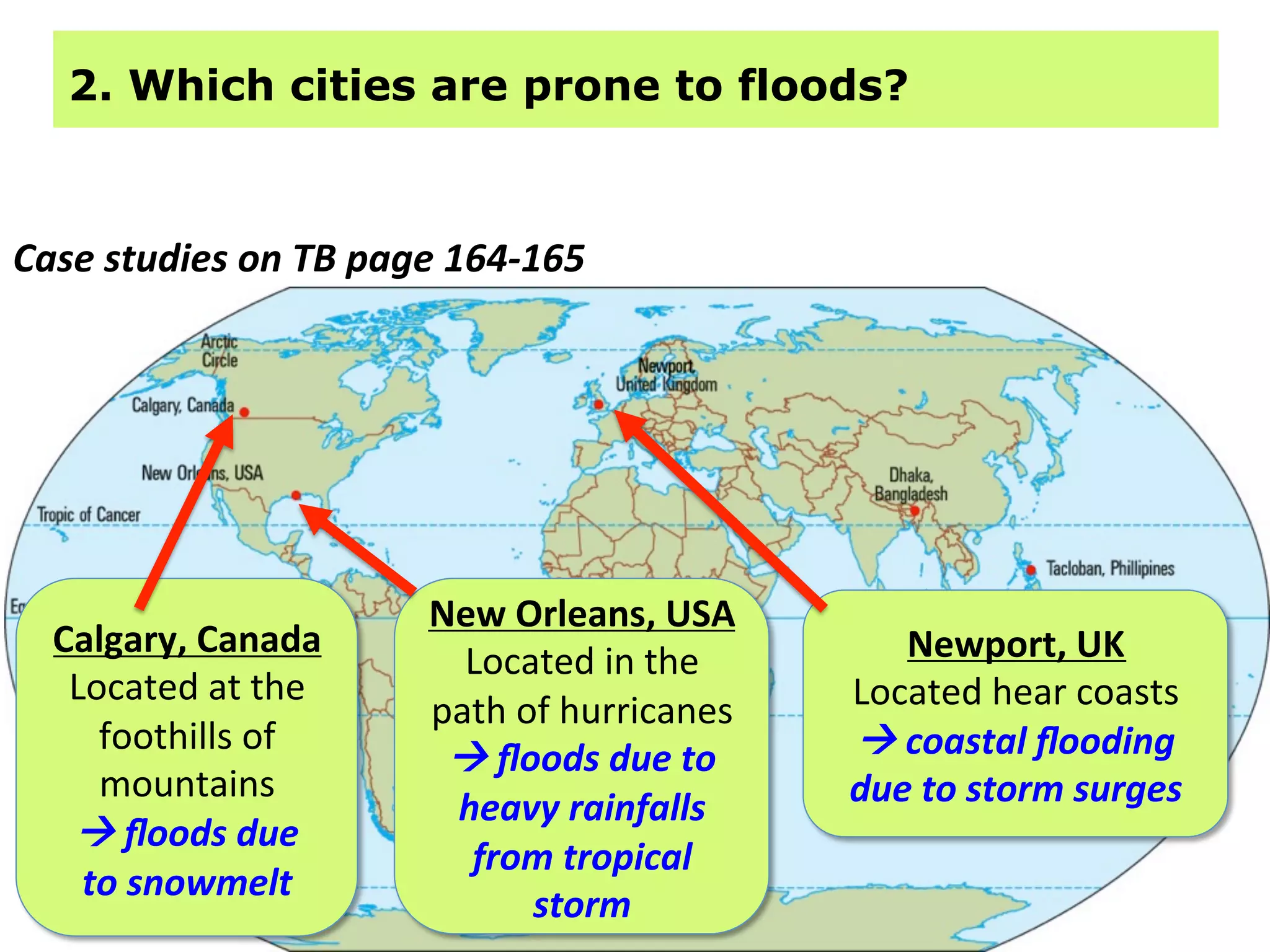
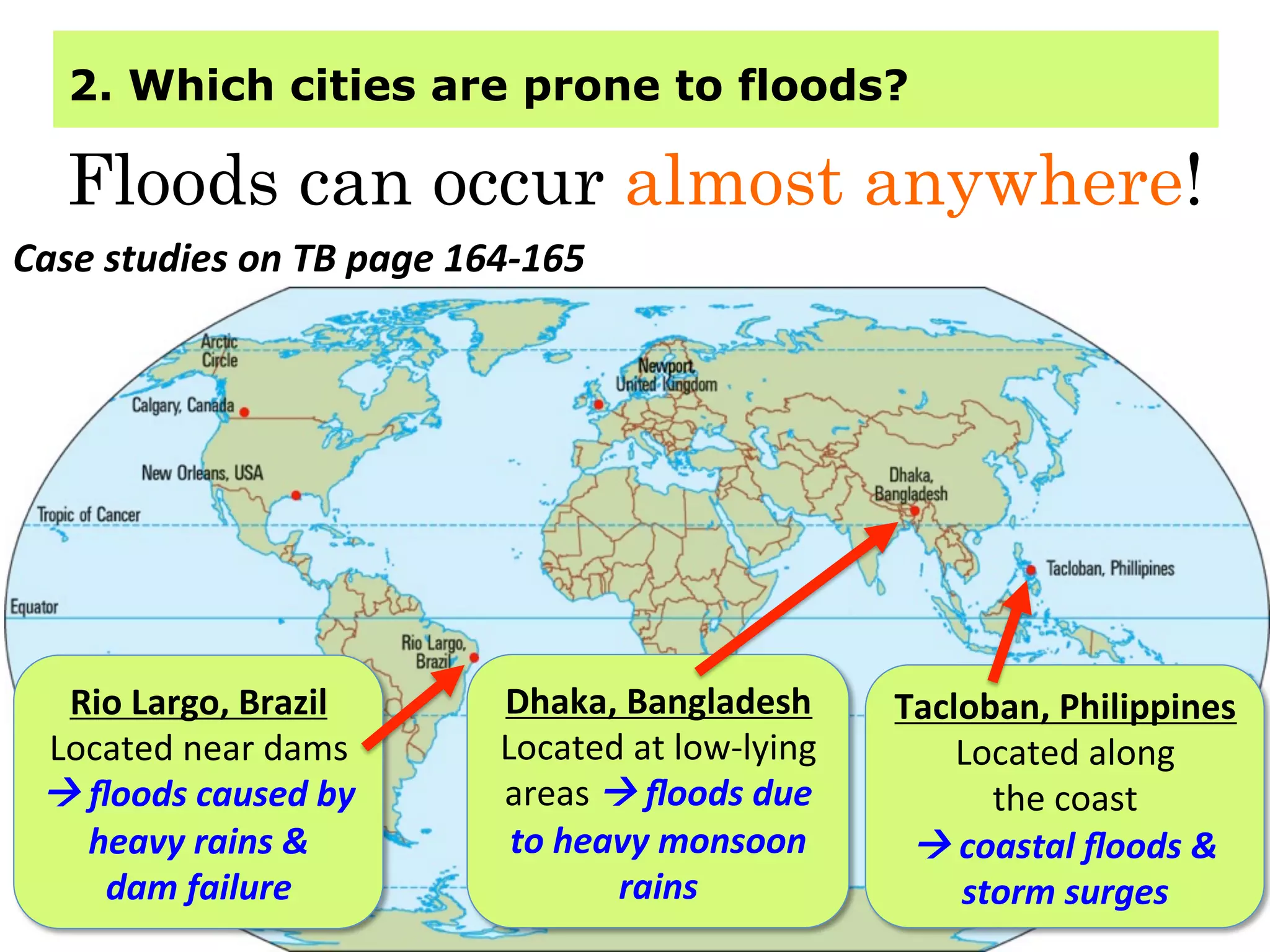
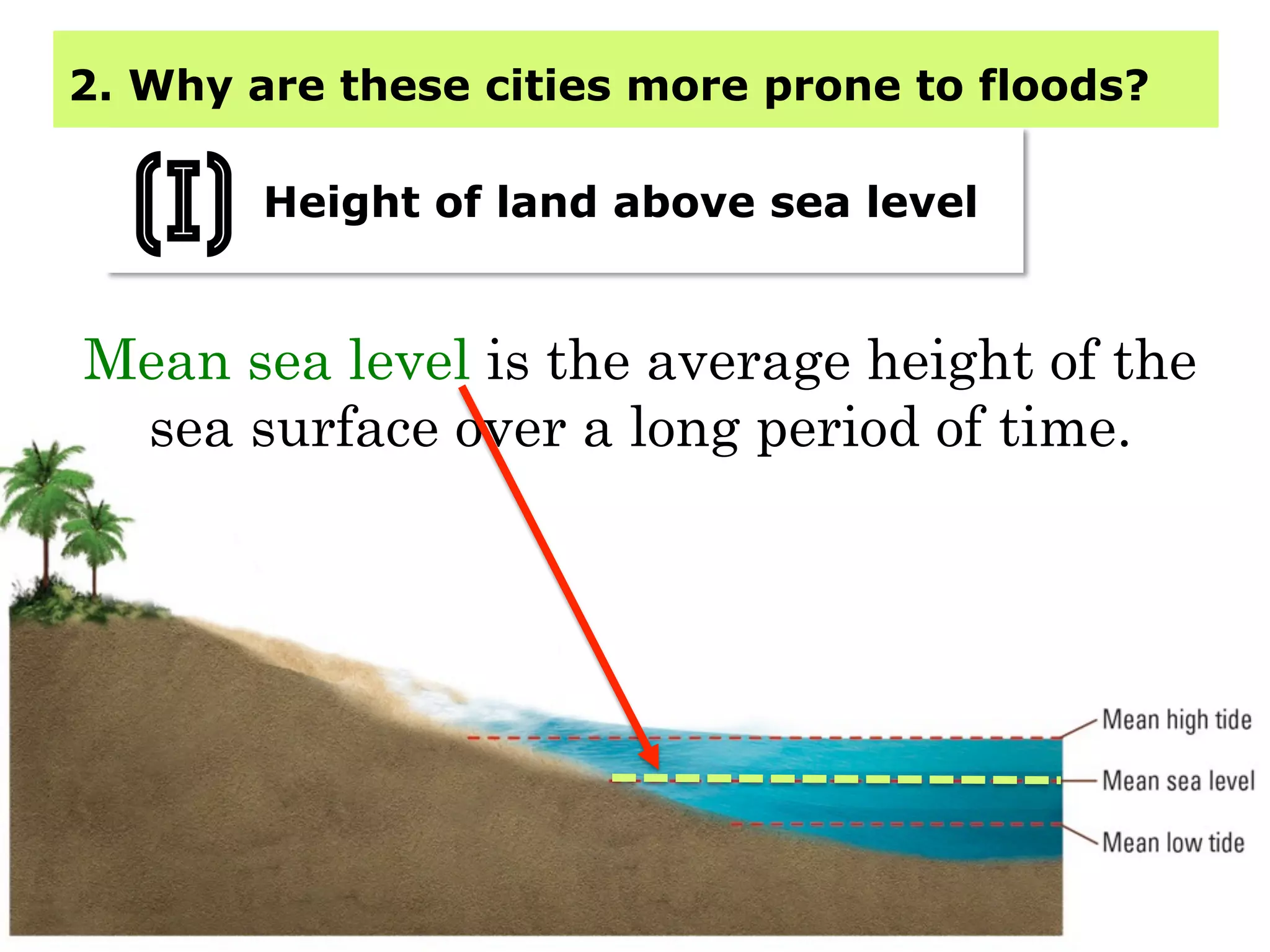
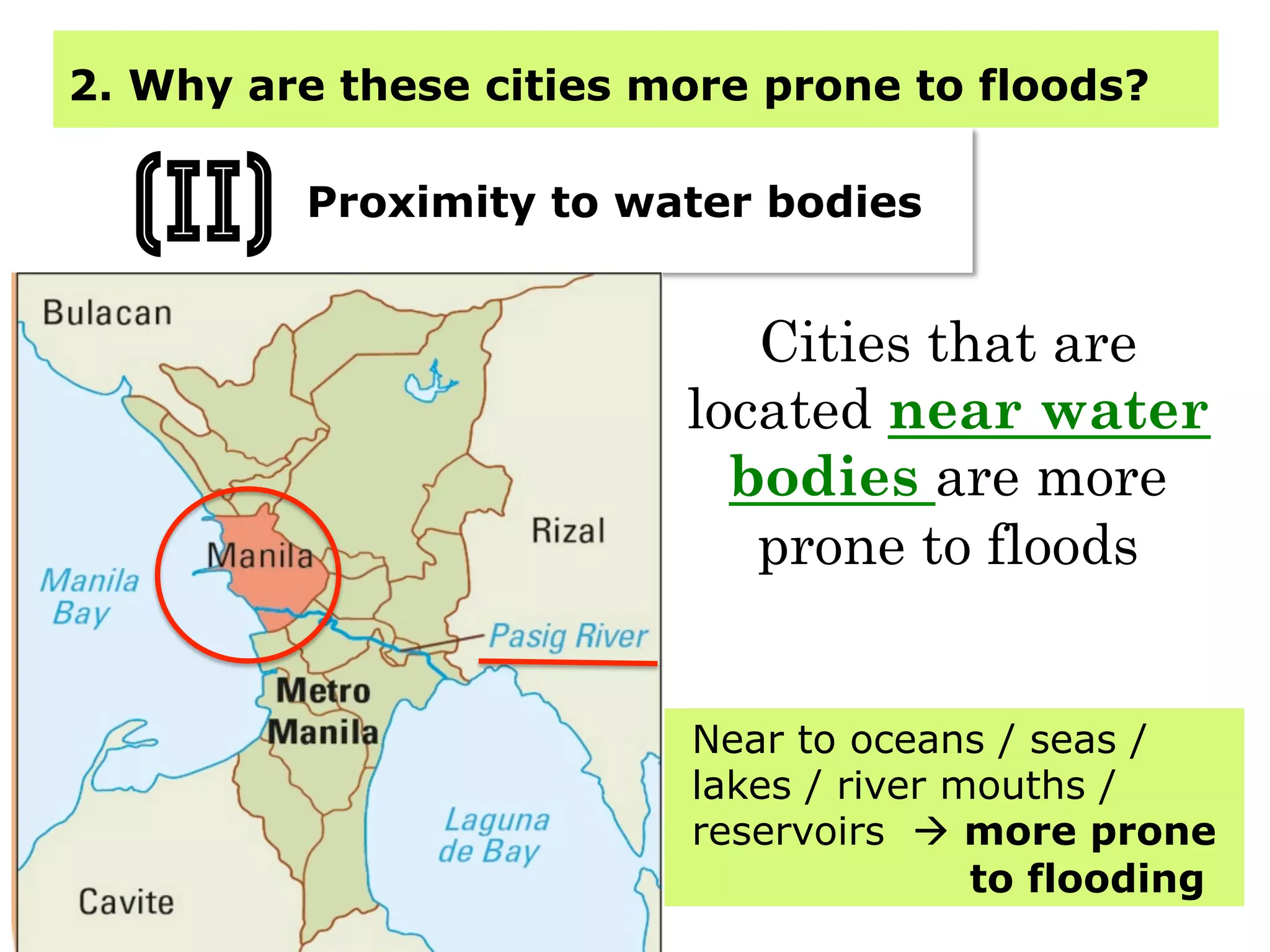
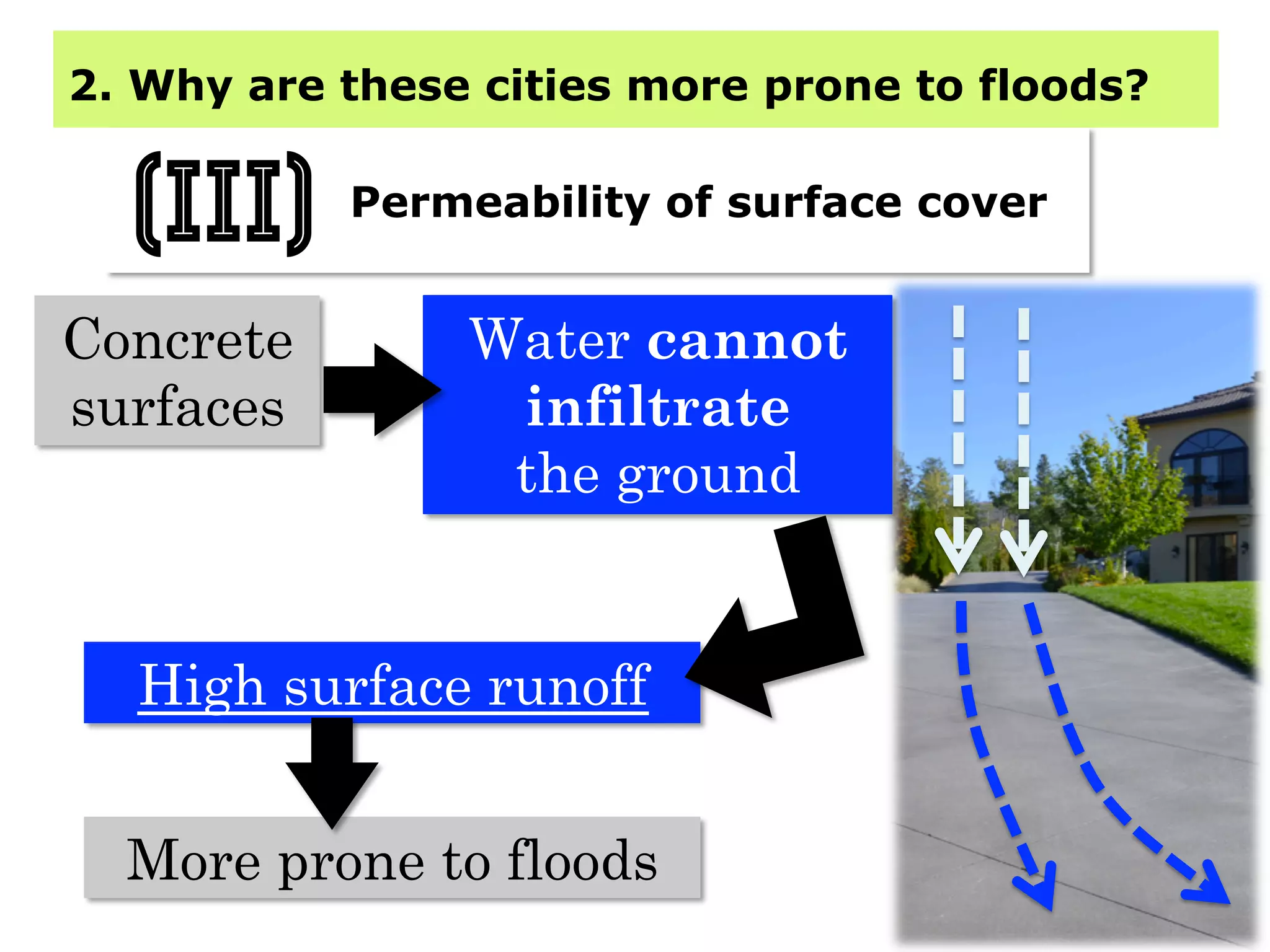
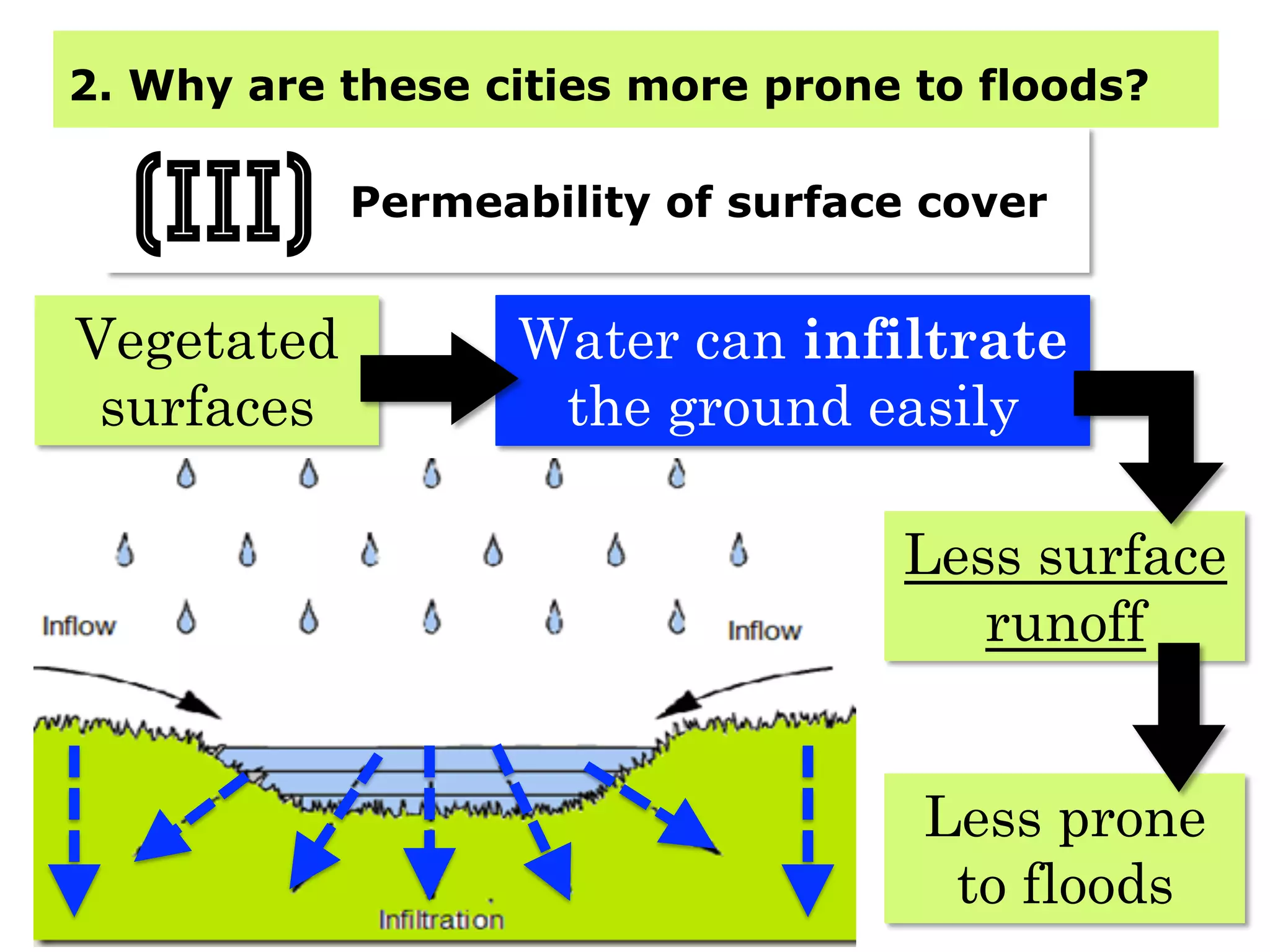
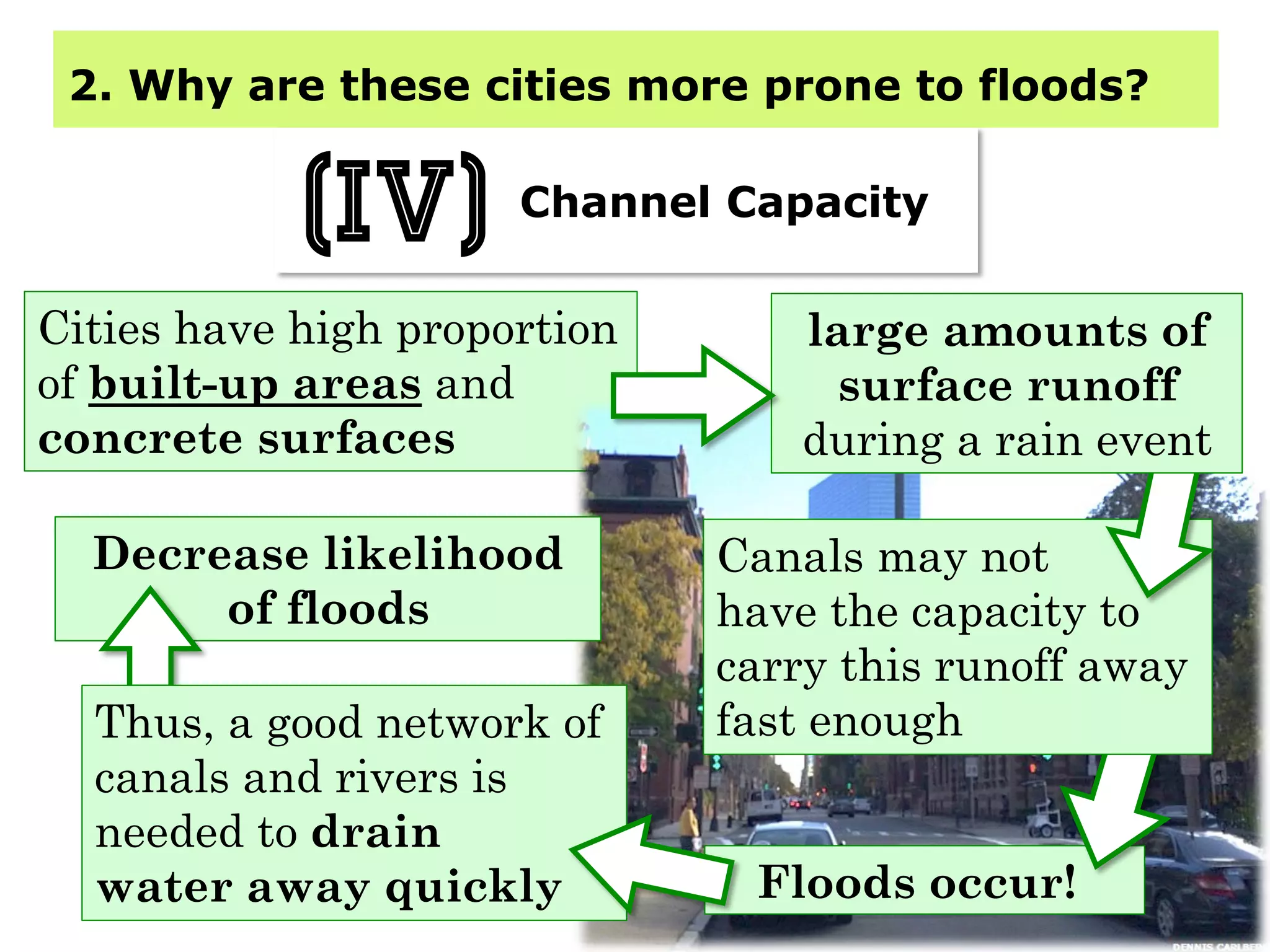
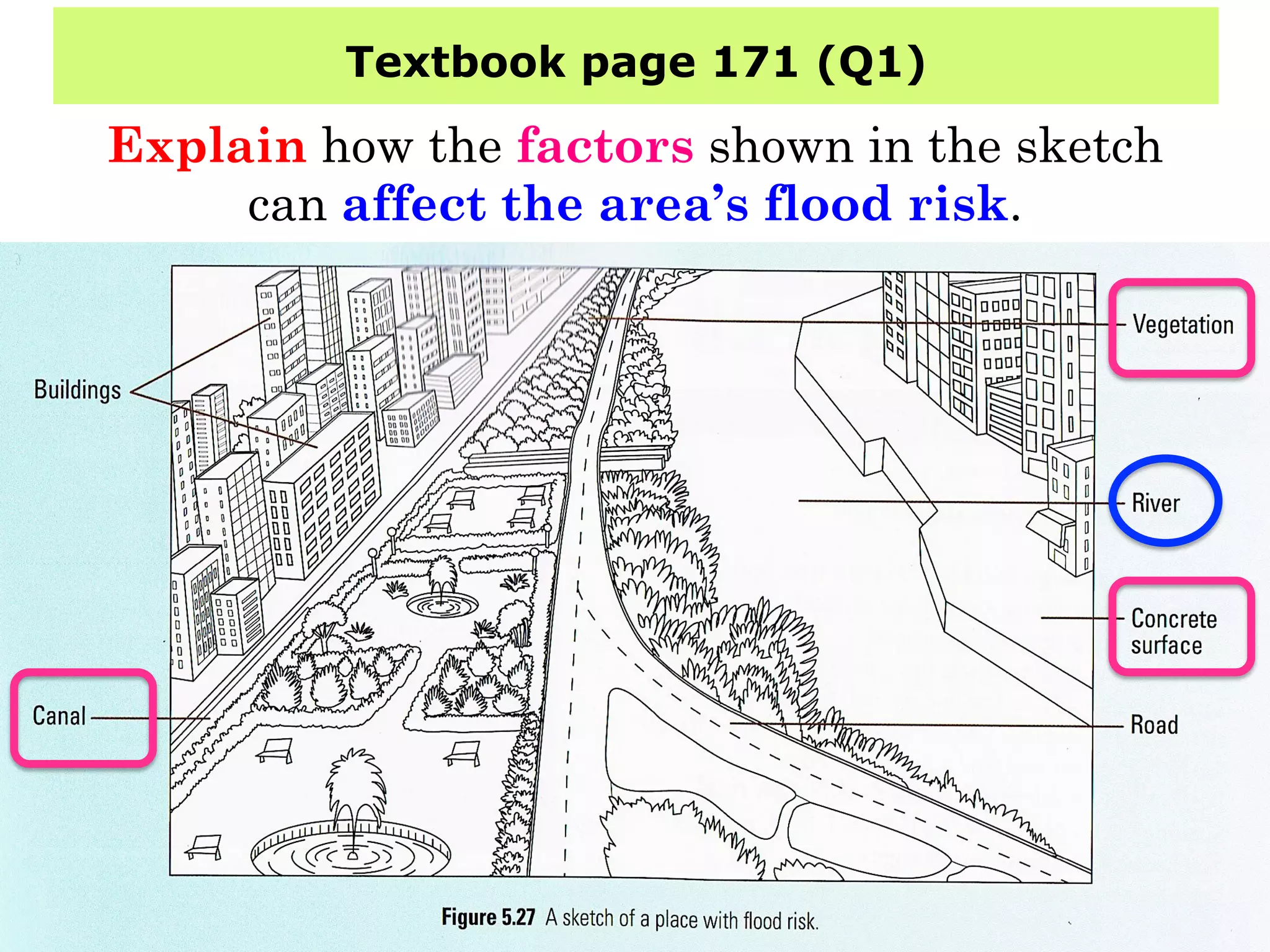
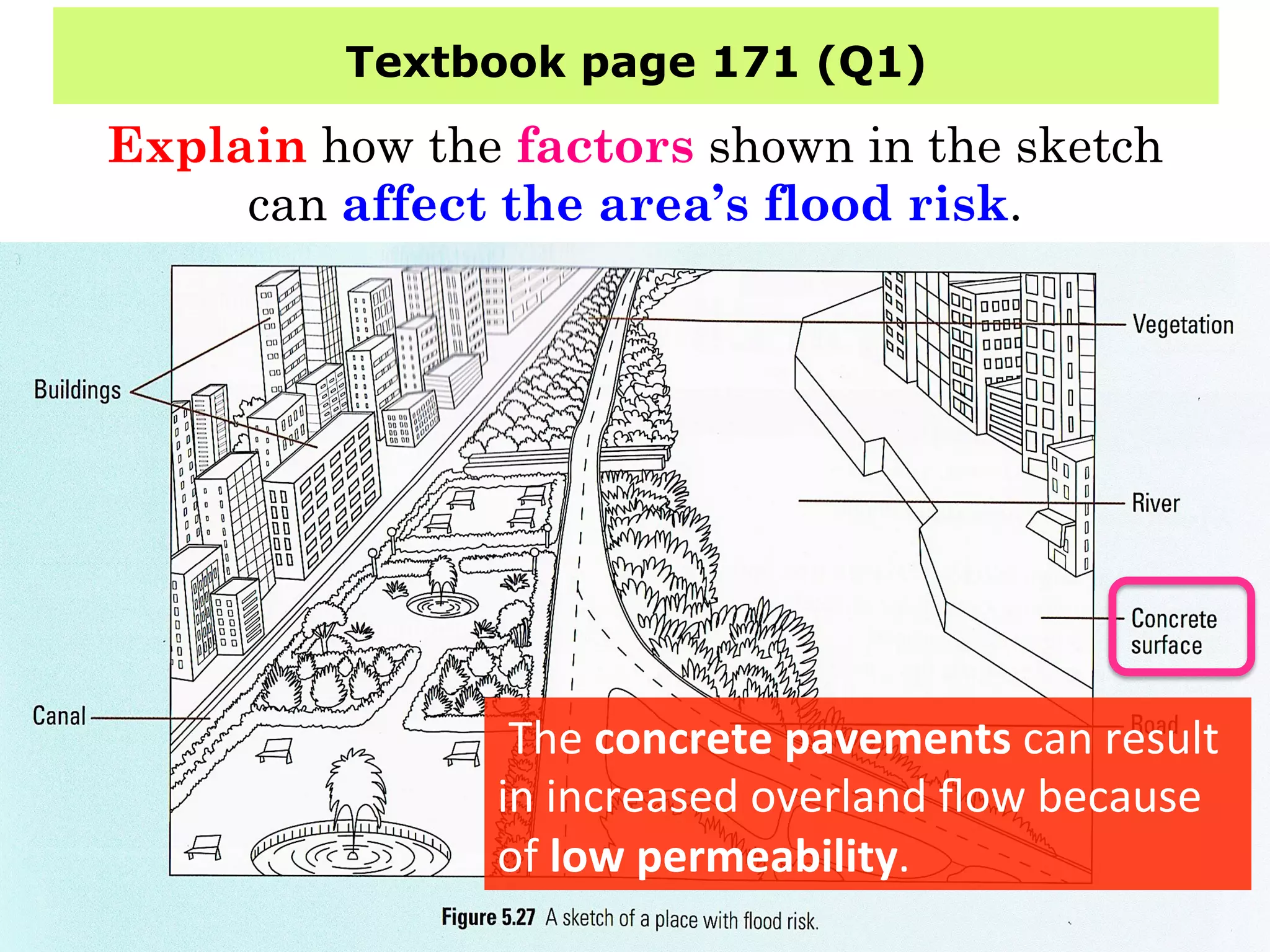
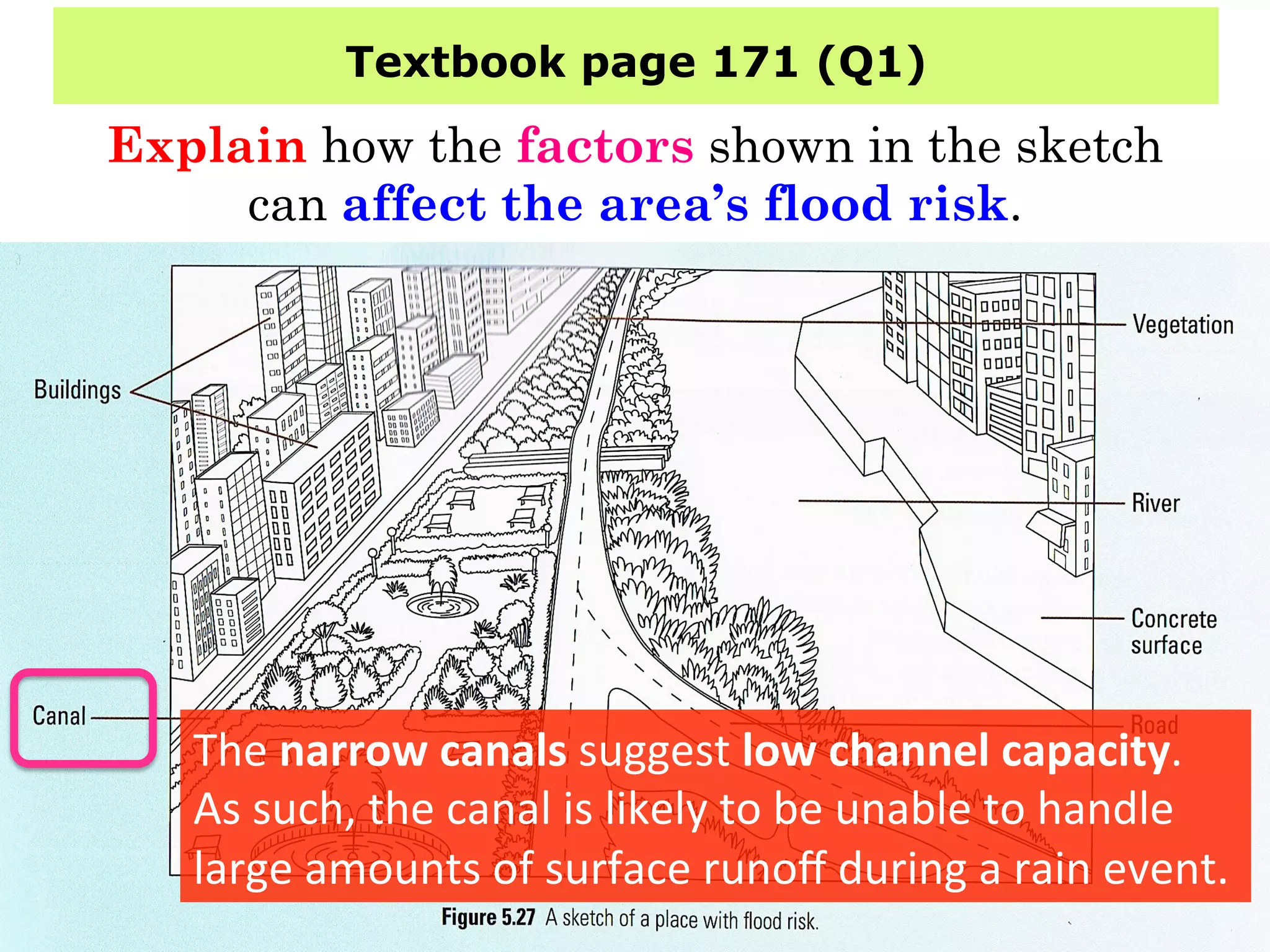
This document provides information about floods, including what causes floods, types of floods, and cities that are prone to flooding. It discusses that floods are large amounts of water overflowing onto dry land. They can be caused by heavy rainfall, snowmelt, storm surge, or the failure of man-made structures like dams and levees. Cities located in low-lying areas, near water bodies, or with low permeability surfaces are more at risk of flooding. The document also examines flash floods, river floods, and coastal floods in more detail.