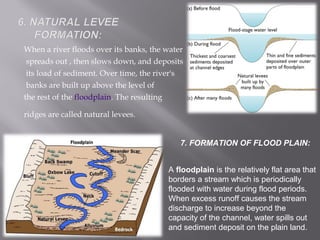
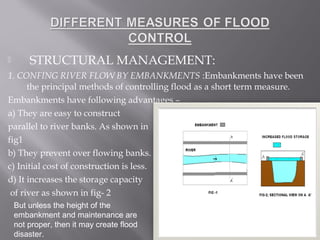
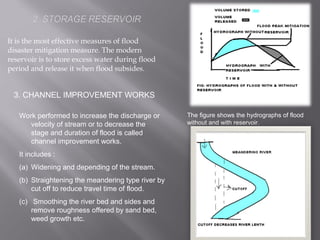
The document discusses floods, defining them as the overflow of water that submerges land not usually covered, and outlines various causes including heavy rainfall, snow melt, and human activities like deforestation and poor water management. It also categorizes different types of floods (river, coastal, flash, etc.) and highlights the devastating impacts of historical floods, such as those in China and India. Additionally, strategies for flood management and mitigation, including structural solutions and ecological measures, are addressed.