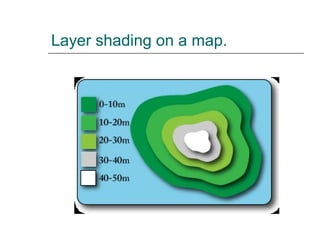
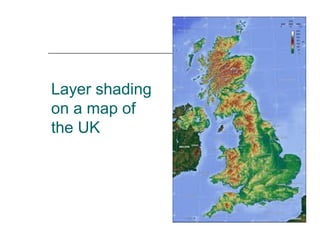
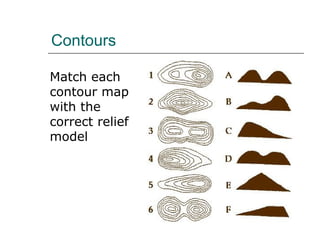
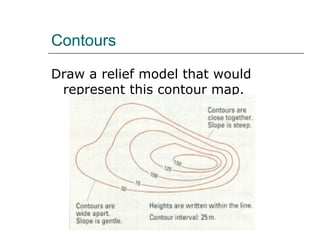
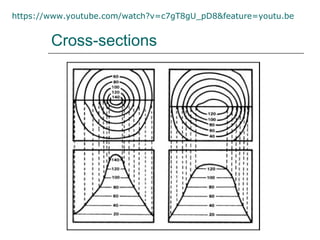
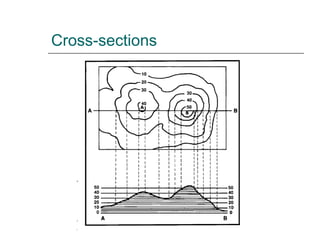
The document discusses different ways to show relief or land height on maps. It describes layer shading, where different colors represent height ranges; spot heights which specify exact heights of prominent features; and trig stations which provide very accurate heights. Contour lines join points of equal height, with closer lines indicating steeper slopes, and they can be used to represent the shape of the land or draw cross-sections showing the land profile.