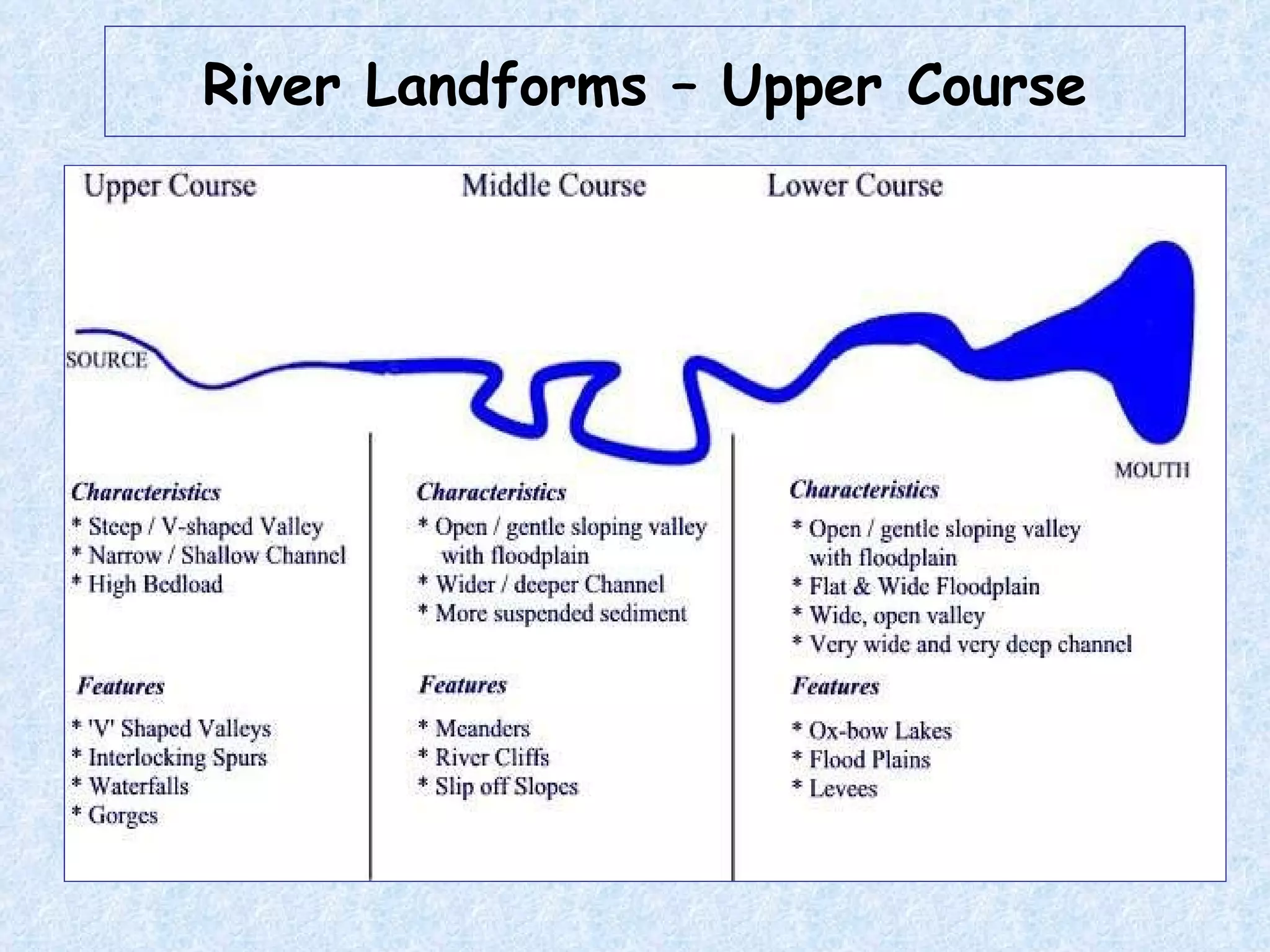
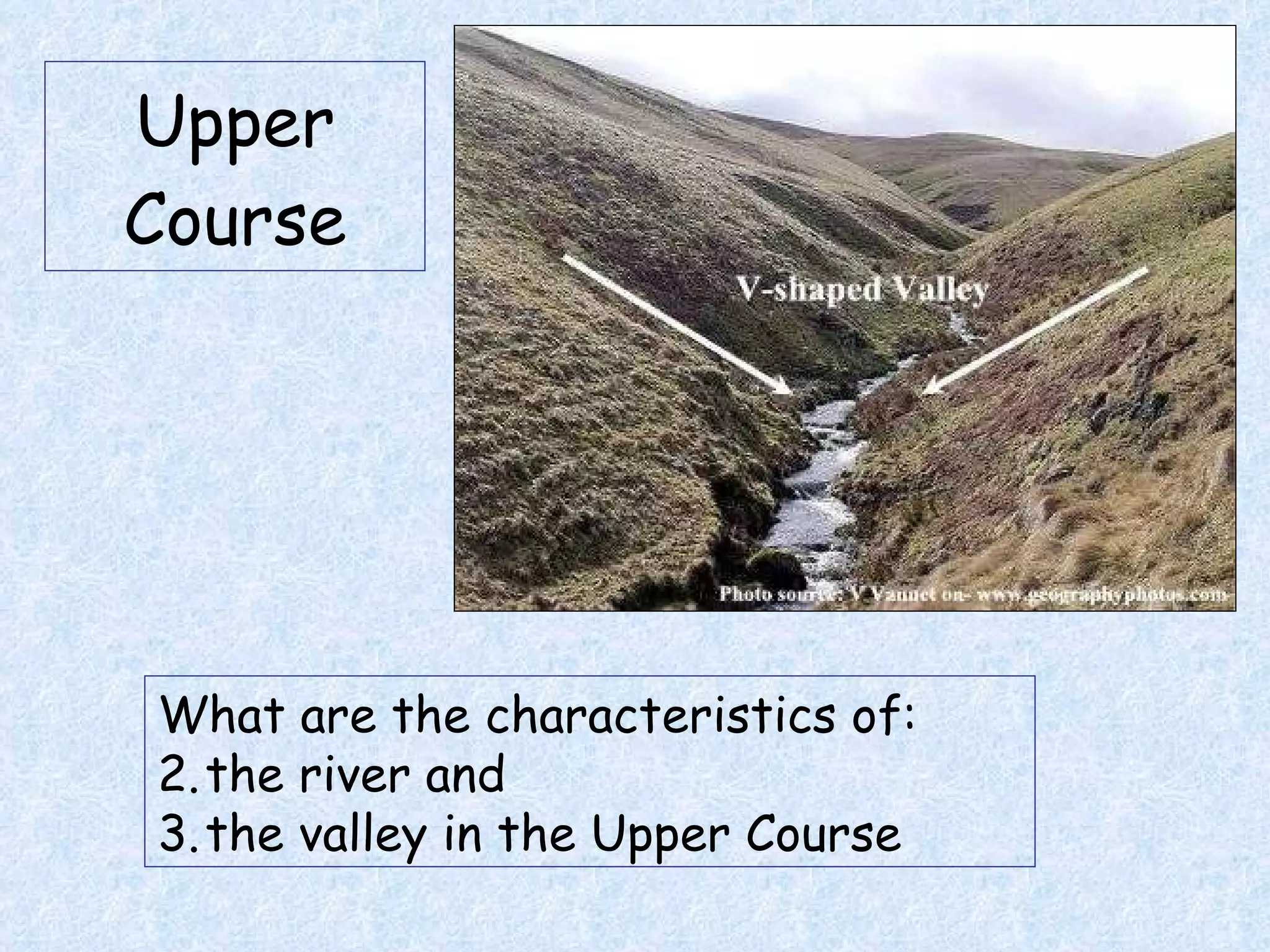
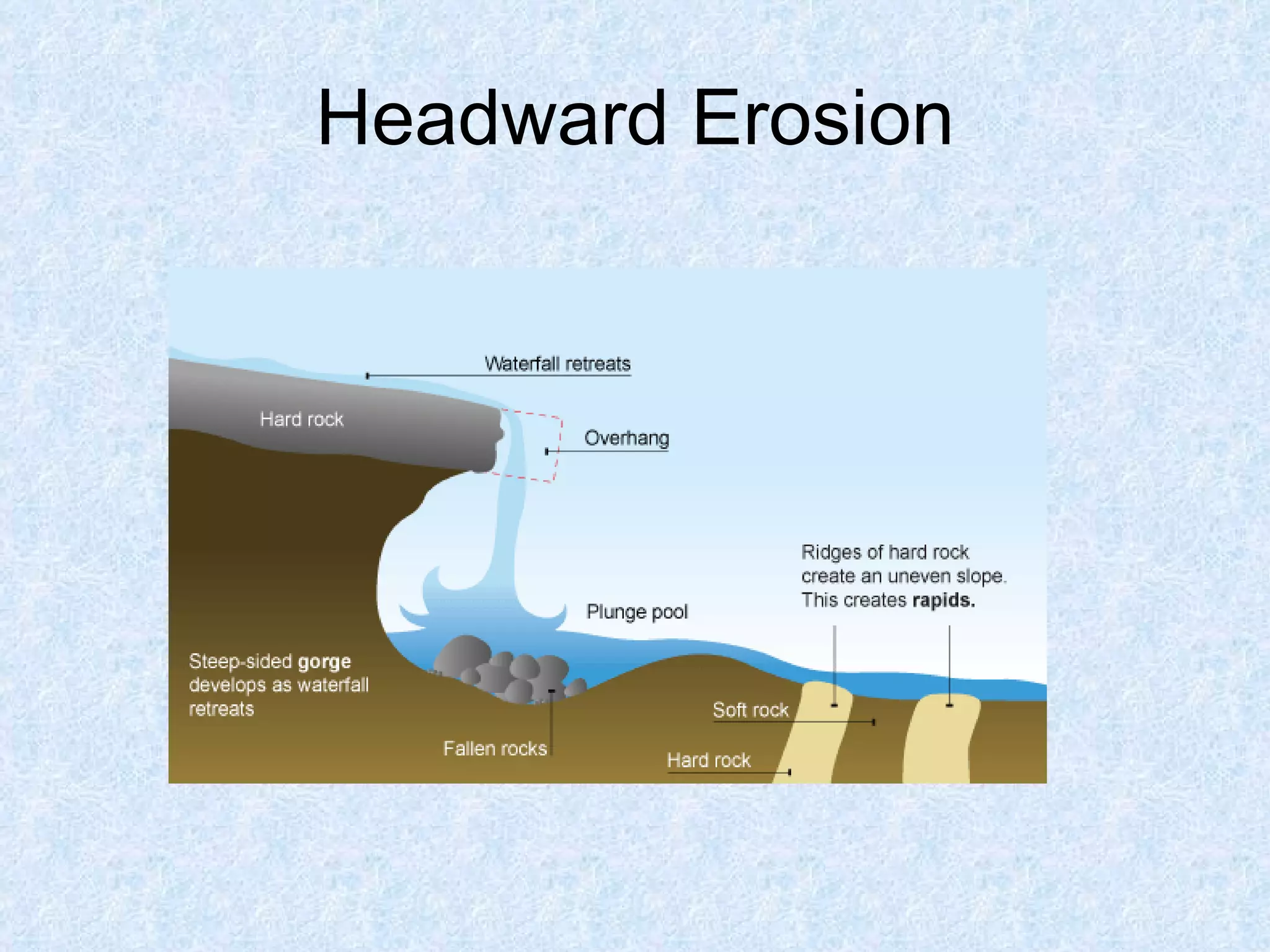
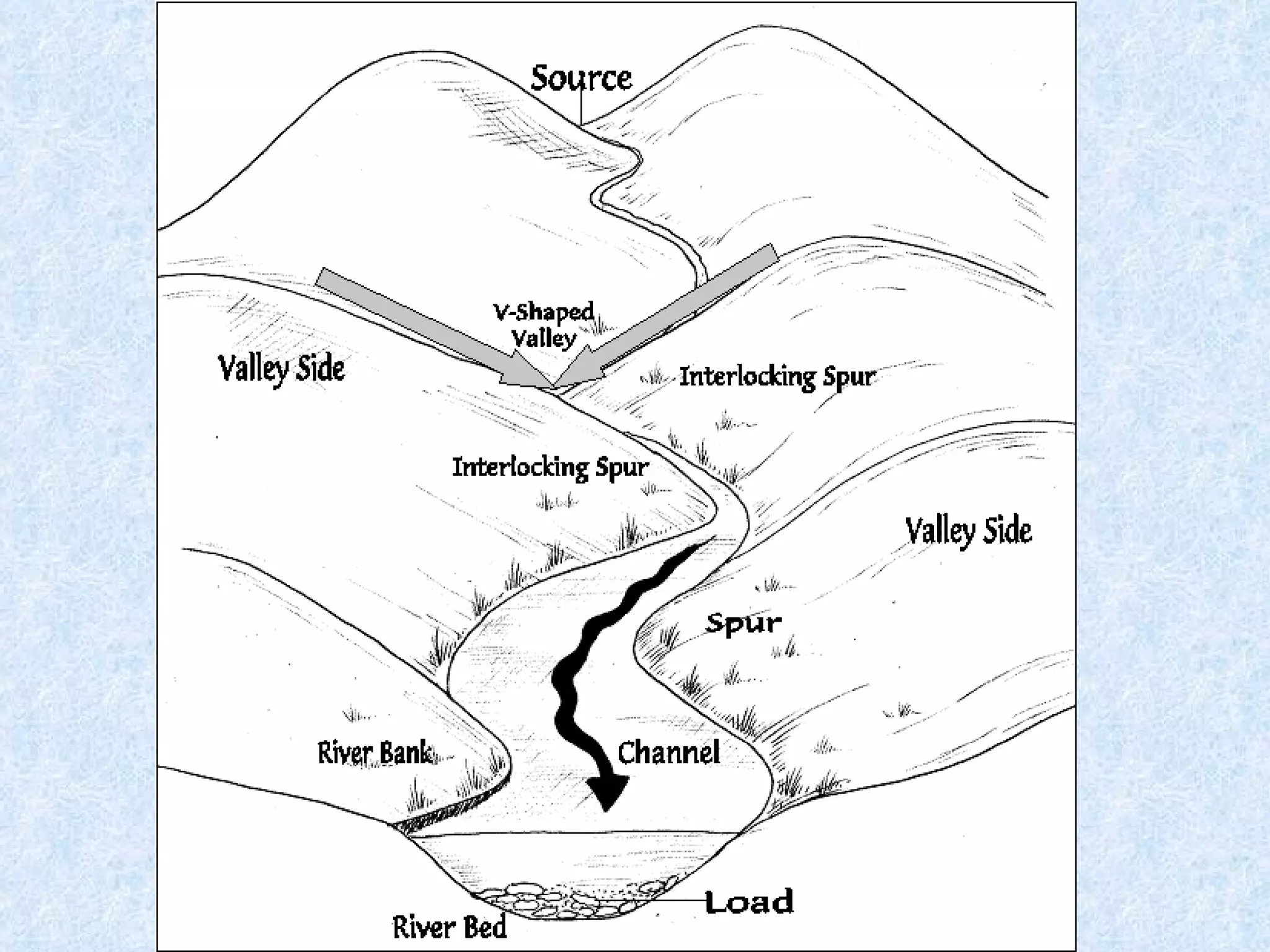
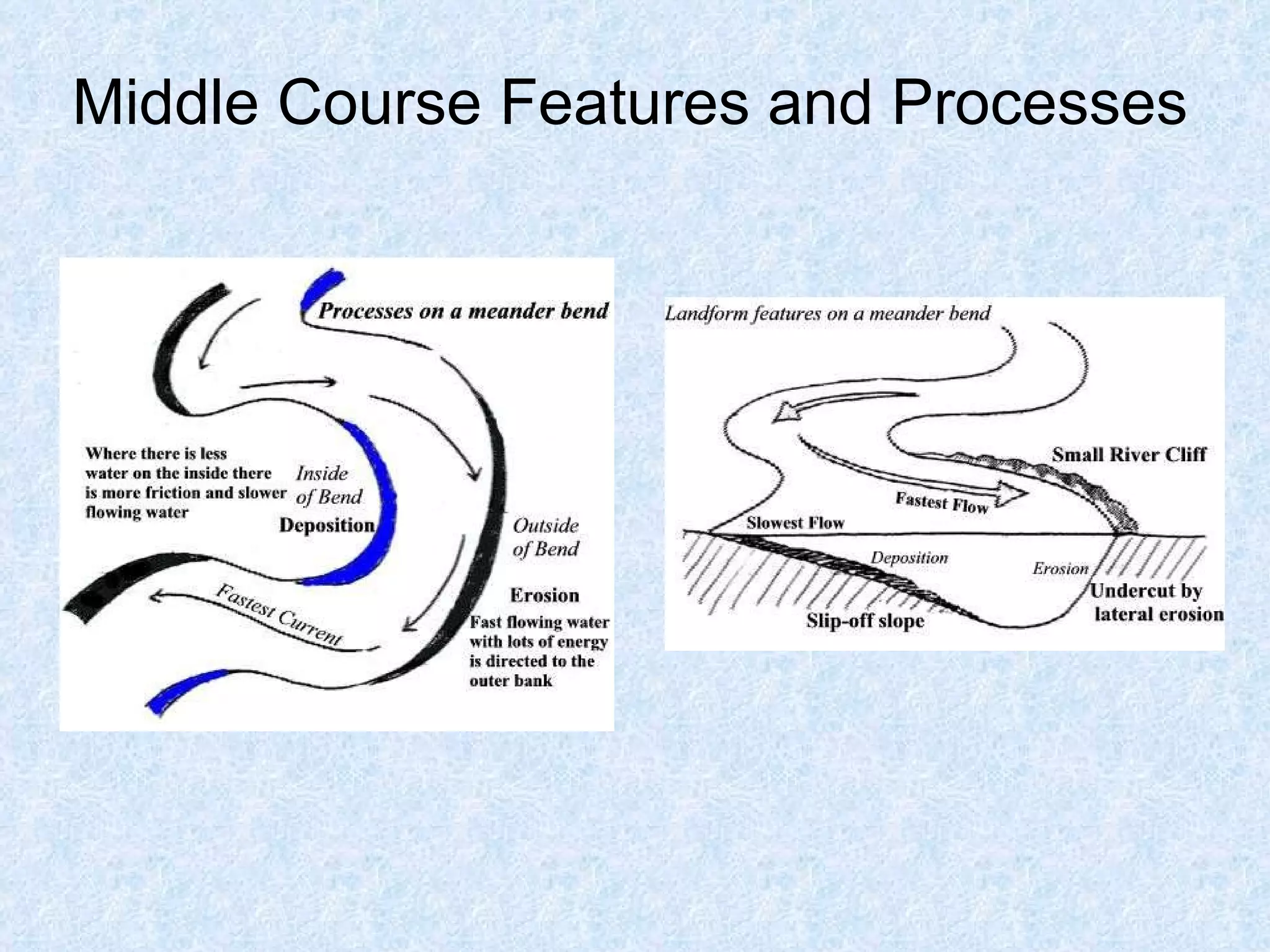
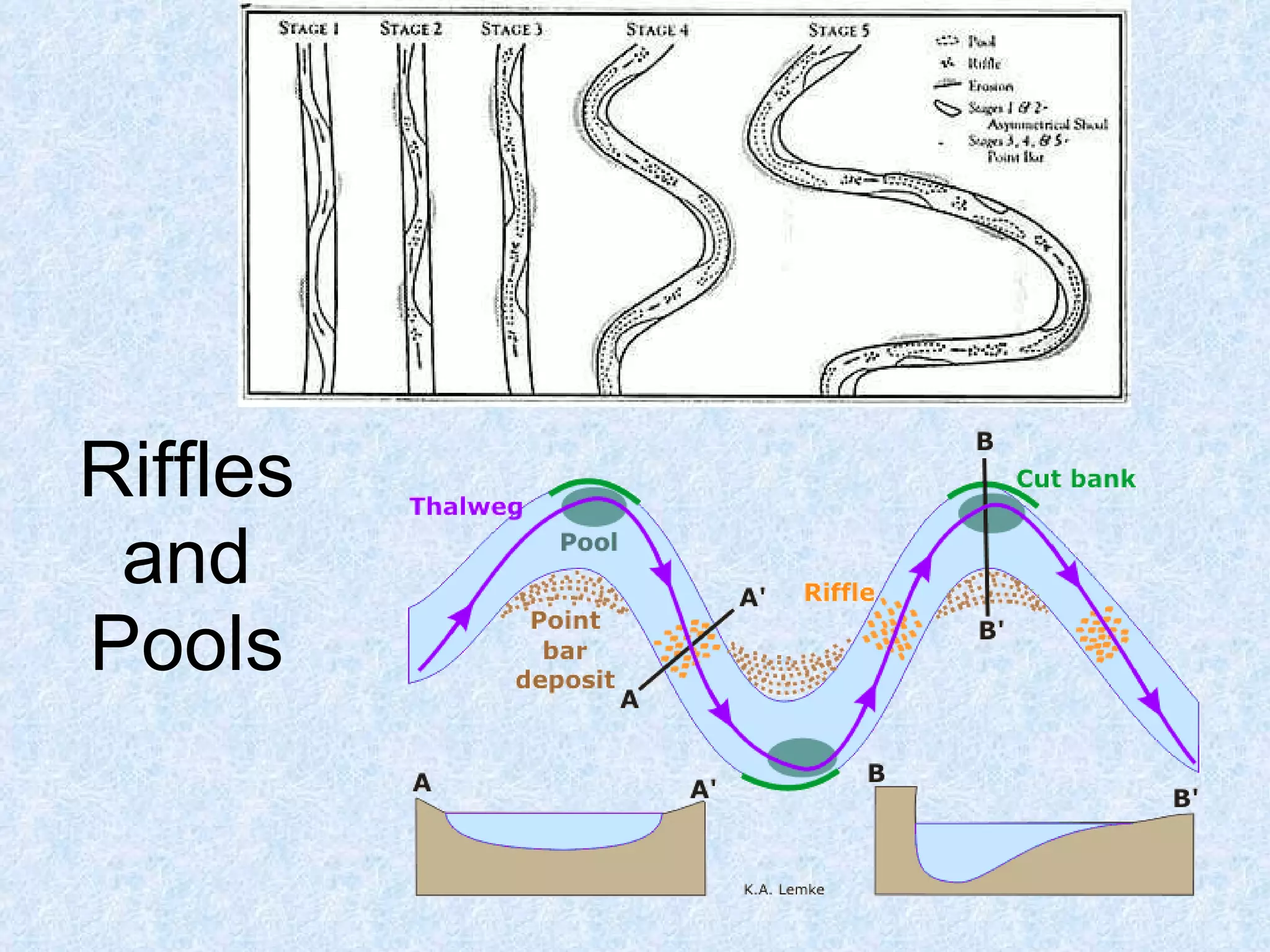
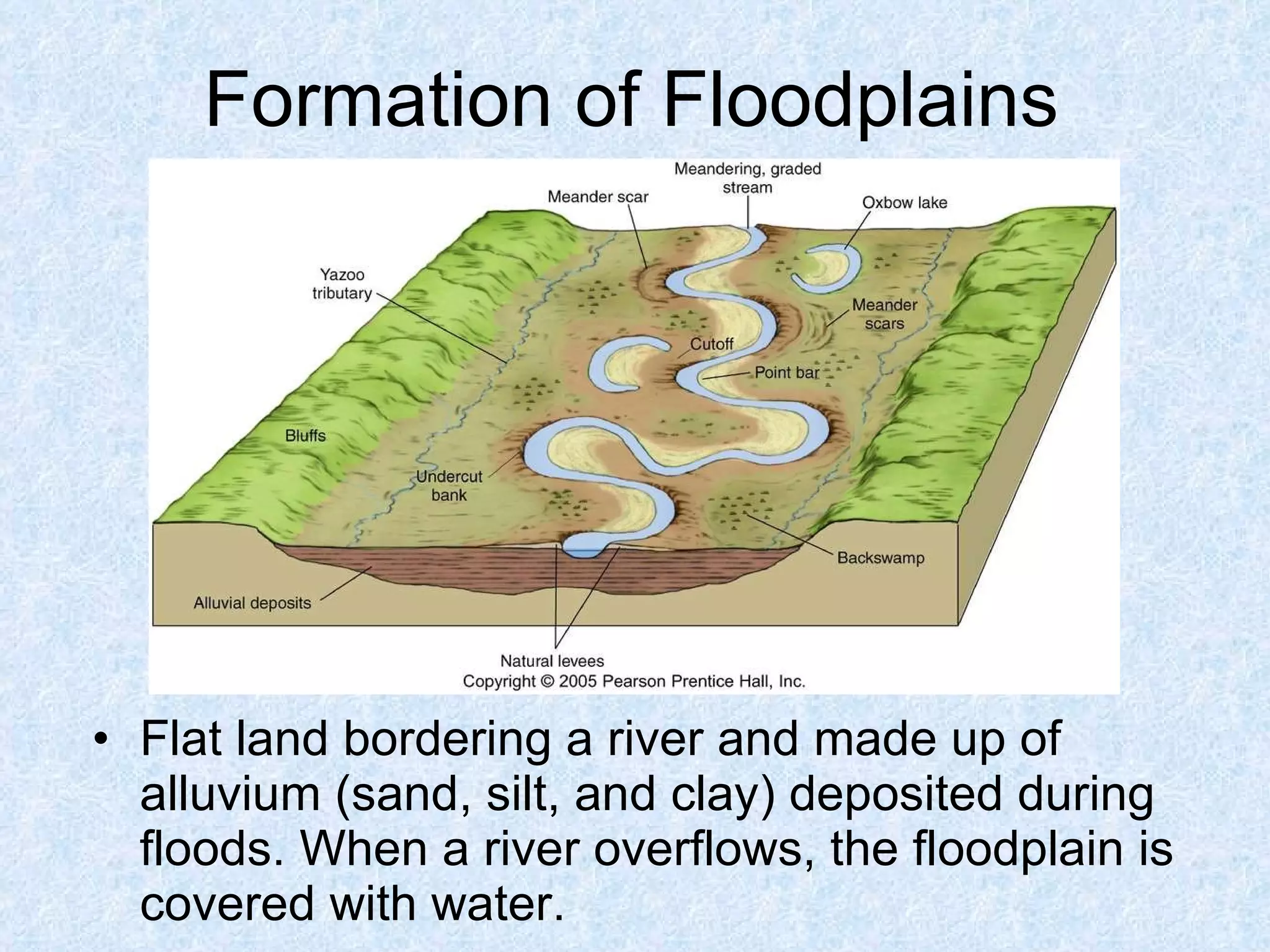
The upper course of a river has low water volume and flows through a narrow, steep-sided V-shaped valley. It erodes vertically, forming interlocking spurs as the river is forced to swing around resistant rock outcrops. A V-shaped valley forms through vertical erosion in the river channel and weathering of valley sides, causing material to move downslope and be transported away by the river over time.